Quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry
... this principle to more than one gradient direction. In the case of QWLSI, four replicas are created by a specific 2D diffraction grating. In this case, two gradients along two perpendicular directions are measured and then integrated to determine the field intensity and phase [20]. The interferogram ...
... this principle to more than one gradient direction. In the case of QWLSI, four replicas are created by a specific 2D diffraction grating. In this case, two gradients along two perpendicular directions are measured and then integrated to determine the field intensity and phase [20]. The interferogram ...
L16
... There are two major classes of interferences which can be identified in atomic absorption spectroscopy. The first class is related to spectral properties of components other than atomized analyte and is referred to as spectral interferences. The other class of interferences is related to the chemica ...
... There are two major classes of interferences which can be identified in atomic absorption spectroscopy. The first class is related to spectral properties of components other than atomized analyte and is referred to as spectral interferences. The other class of interferences is related to the chemica ...
LCI
... autocorrelation function for each field of the interferometer is unchanged. It is only their cross-correlation that is sensitive to unbalanced dispersion. Perhaps a more accurate description is to say that, in the presence of dispersion, the cross-correlation time is larger than the autocorrelation ...
... autocorrelation function for each field of the interferometer is unchanged. It is only their cross-correlation that is sensitive to unbalanced dispersion. Perhaps a more accurate description is to say that, in the presence of dispersion, the cross-correlation time is larger than the autocorrelation ...
Principles of TEM image formation Principles of TEM image
... phase variations over the plane surface. T(x,y) = A0exp[iφ(x,y)], for simplicity : A0 = 1 Assuming that the object is thin and phase shift φ is small The approximation of the emerged wave might be described as ...
... phase variations over the plane surface. T(x,y) = A0exp[iφ(x,y)], for simplicity : A0 = 1 Assuming that the object is thin and phase shift φ is small The approximation of the emerged wave might be described as ...
Visible Light, Wide-Angle Graded Metasurface for Back Reflection
... with only two discretization steps yields a retroreflection efficiency larger than 75%. The reason behind this robustness is again associated with the nature of our design. First, the diffraction phenomenon is nonresonant and therefore inherently robust to perturbations. Second, the period Λ determines ...
... with only two discretization steps yields a retroreflection efficiency larger than 75%. The reason behind this robustness is again associated with the nature of our design. First, the diffraction phenomenon is nonresonant and therefore inherently robust to perturbations. Second, the period Λ determines ...
Phase contrast and DIC - Nikon Imaging Center at UCSF
... of phase are all-important. Why then had phases never been considered before … in the microscope?” • Phases difficult to see – Must convert phase differences to intensity differences Frits Zernike ...
... of phase are all-important. Why then had phases never been considered before … in the microscope?” • Phases difficult to see – Must convert phase differences to intensity differences Frits Zernike ...
Chapter 4: Two-Beam Interference
... We have learned about the magnitudes of interference effects, and their extreme sensitivity to weak beams, but we will generally be more interested in the geometry of these fringe effects. In particular, we will want to know where these moiré-like fringes are formed, and what their spacings and orie ...
... We have learned about the magnitudes of interference effects, and their extreme sensitivity to weak beams, but we will generally be more interested in the geometry of these fringe effects. In particular, we will want to know where these moiré-like fringes are formed, and what their spacings and orie ...
Lecture Notes
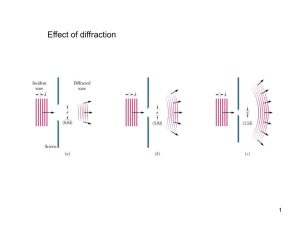
... engineering fields. In this chapter we explain diffraction using the wave nature of light and discuss several applications of diffraction in science and technology. ...
... engineering fields. In this chapter we explain diffraction using the wave nature of light and discuss several applications of diffraction in science and technology. ...
Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for Chemical
... the interference pattern are on a local scale with respect to the ADF detector and are integrated by it. Only the changes in the total intensity falling on the detector affect the image. The thickness dependence of the Z-contrast image is therefore much simpler than that of a BF image. For instance, ...
... the interference pattern are on a local scale with respect to the ADF detector and are integrated by it. Only the changes in the total intensity falling on the detector affect the image. The thickness dependence of the Z-contrast image is therefore much simpler than that of a BF image. For instance, ...
Example
... • For Fraunhofer diffraction, the intensity of the center of the central maximum decreases if the slit size is reduced. This is clear from the figure. If the slit is narrower, fewer rays (representing the paths of Huygen’s wavelets) reach P0. • The first minimum occurs for a sin = , so when a is ...
... • For Fraunhofer diffraction, the intensity of the center of the central maximum decreases if the slit size is reduced. This is clear from the figure. If the slit is narrower, fewer rays (representing the paths of Huygen’s wavelets) reach P0. • The first minimum occurs for a sin = , so when a is ...
Integrated Optics
... INTRODUCTION Integrated optical devices or alternatively called the photonic integrated circuits, are the important dives in high speed coherent optical communication. They can various functions like, phase, amplitude, and polarization modulation, and also wavelength filters. The main material which ...
... INTRODUCTION Integrated optical devices or alternatively called the photonic integrated circuits, are the important dives in high speed coherent optical communication. They can various functions like, phase, amplitude, and polarization modulation, and also wavelength filters. The main material which ...
Slide 1
... In order to overcome the limitations of imaging depth and relatively long response time of the former AO imaging system working at an optical wavelength of 532 nm, a new setup operating in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range using a GaAs photorefractive crystal has been developed. We demonstrat ...
... In order to overcome the limitations of imaging depth and relatively long response time of the former AO imaging system working at an optical wavelength of 532 nm, a new setup operating in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range using a GaAs photorefractive crystal has been developed. We demonstrat ...
Download PDF
... In summary, the scattering-phase theorem connects the phase image of a thin tissue slice to the scattering properties of the tissue. Note that the tissue can be mapped in terms of ls and g values that are averaged over patches of area S. While this remarkable result may seem counterintuitive, its ph ...
... In summary, the scattering-phase theorem connects the phase image of a thin tissue slice to the scattering properties of the tissue. Note that the tissue can be mapped in terms of ls and g values that are averaged over patches of area S. While this remarkable result may seem counterintuitive, its ph ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy -TEM
... capable of magnifying objects 400 times. The first practical electron microscope was built by in 1938 and had 10 nm resolution. Although modern electron microscopes can magnify an object 2 million times, they are still based upon Ruska's prototype and his correlation between wavelength and magnifica ...
... capable of magnifying objects 400 times. The first practical electron microscope was built by in 1938 and had 10 nm resolution. Although modern electron microscopes can magnify an object 2 million times, they are still based upon Ruska's prototype and his correlation between wavelength and magnifica ...
Measurement of Surface Quality 1. Lyot Test 2. FECO 3. Nomarski
... The path difference between the two beams can be adjusted by laterally translating the Wollaston prism. When the axes of the polarizer and analyzer are parallel and the prism is centered, the path lengths are equal and white light is seen for a perfect test surface with no tilt. When the polarizer a ...
... The path difference between the two beams can be adjusted by laterally translating the Wollaston prism. When the axes of the polarizer and analyzer are parallel and the prism is centered, the path lengths are equal and white light is seen for a perfect test surface with no tilt. When the polarizer a ...
Experimental demonstration of a narrowband, angular tolerant
... To identify the parameters of the structure governing the angular and spectral linewidths, some approximate theories have been developed for gratings periodic along one direction (1D). It has been proved [1,6] that when only one eigenmode is excited (e.g., in oblique incidence), both the angular and ...
... To identify the parameters of the structure governing the angular and spectral linewidths, some approximate theories have been developed for gratings periodic along one direction (1D). It has been proved [1,6] that when only one eigenmode is excited (e.g., in oblique incidence), both the angular and ...
Vol. 26. Is. 5 - Society for Experimental Mechanics
... However, since we usually normalize the speed relative to vacuum, the path length has units of distance. Optical path length ⫽ [physical distance traveled] times [index of refraction] Editor’s Note: Optical Methods: Back to Basics, is organized by ET Technical Editor, Kristin Zimmerman, General Moto ...
... However, since we usually normalize the speed relative to vacuum, the path length has units of distance. Optical path length ⫽ [physical distance traveled] times [index of refraction] Editor’s Note: Optical Methods: Back to Basics, is organized by ET Technical Editor, Kristin Zimmerman, General Moto ...
Optical pulse generation using a low-voltage electro-optic
... Recently, the interest in all-optical processing of microwave and millimeter-wave signals is growing because of the advantages with respect to electronic processing. Indeed, the larger time-bandwidth products, insensitivity to electromagnetic interference, low loss, light weight and high data-transf ...
... Recently, the interest in all-optical processing of microwave and millimeter-wave signals is growing because of the advantages with respect to electronic processing. Indeed, the larger time-bandwidth products, insensitivity to electromagnetic interference, low loss, light weight and high data-transf ...
TAP 322- 3: Grating calculations
... The longest visible wavelength is that of red light with = 750 nm. The shortest visible wavelength is violet where = 400nm. Use this information to calculate the width of the angle into which the first-order spectrum is spread out when white light is shone onto the grating. ...
... The longest visible wavelength is that of red light with = 750 nm. The shortest visible wavelength is violet where = 400nm. Use this information to calculate the width of the angle into which the first-order spectrum is spread out when white light is shone onto the grating. ...
Week 9 Wed. (Lesson 15) Coherence and Optical Tomography
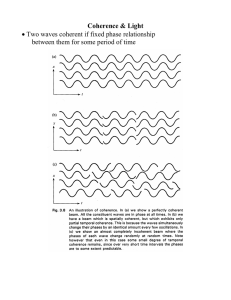
... • Required for interference and diffraction • Before lasers need to place slits far from source or pass light through slit so only part of source seen Temporal Coherence • Correlation of phase at the same point but at different times • Regular sources rapidly change phase relationships • Single atom ...
... • Required for interference and diffraction • Before lasers need to place slits far from source or pass light through slit so only part of source seen Temporal Coherence • Correlation of phase at the same point but at different times • Regular sources rapidly change phase relationships • Single atom ...
Three-dimensional imaging by sub-Nyquist
... to extract a fringe-contrast envelope from Fig. 2(b) as required for the more familiar methods of SWLI. The principal disadvantage with use of undersampled data is of course a reduced signal-to-noise ratio not only because fewer data are acquired but also because of aliasing of noise at higher frequ ...
... to extract a fringe-contrast envelope from Fig. 2(b) as required for the more familiar methods of SWLI. The principal disadvantage with use of undersampled data is of course a reduced signal-to-noise ratio not only because fewer data are acquired but also because of aliasing of noise at higher frequ ...
SignalsInstr
... You would hope that the signal characteristics (amplitude, phase, polarization, etc.) are telling you something about the physics of the sample. However, it could also be telling you about the physics of the instrumentation. For example, the light source might not have the same intensity at all wave ...
... You would hope that the signal characteristics (amplitude, phase, polarization, etc.) are telling you something about the physics of the sample. However, it could also be telling you about the physics of the instrumentation. For example, the light source might not have the same intensity at all wave ...
PHASE-CONTROL DEVICE
... Computing Block It calculates the square root of the sum of square of A and B from PCB every time we change the code A and B are changed. ...
... Computing Block It calculates the square root of the sum of square of A and B from PCB every time we change the code A and B are changed. ...
The Michelson Interferometer and Its Applications
... the hypothetical aether was indeed constant, then the Earth’s orbital velocity relative to this aether should exhibit observable relativistic effects. He devised and constructed an optical interferometer with which ...
... the hypothetical aether was indeed constant, then the Earth’s orbital velocity relative to this aether should exhibit observable relativistic effects. He devised and constructed an optical interferometer with which ...
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging

Phase-contrast X-ray imaging (PCI) or phase-sensitive X-ray imaging is a general term for different technical methods that use information concerning changes in the phase of an X-ray beam that passes through an object in order to create its images. Standard X-ray imaging techniques like radiography or computed tomography (CT) rely on a decrease of the X-ray beam's intensity (attenuation) when traversing the sample, which can be measured directly with the assistance of an X-ray detector. In PCI however, the beam's phase shift caused by the sample is not measured directly, but is transformed into variations in intensity, which then can be recorded by the detector.In addition to producing projection images, PCI, like conventional transmission, can be combined with tomographic techniques to obtain the 3D distribution of the real part of the refractive index of the sample. When applied to samples that consist of atoms with low atomic number Z, PCI is more sensitive to density variations in the sample than conventional transmission-based X-ray imaging. This leads to images with improved soft tissue contrast.In the last several years, a variety of phase-contrast X-ray imaging techniques have been developed, all of which are based on the observation of interference patterns between diffracted and undiffracted waves. The most common techniques are crystal interferometry, propagation-based imaging, analyzer-based imaging, edge-illumination and grating-based imaging (see below).