10~Chapter 10_Functi.. - Programming Assignment 0
... • if the current state and next input symbol match the first element of a pair, then the finite automaton enters the state given by the second element of the pair Copyright © 2009 Elsevier ...
... • if the current state and next input symbol match the first element of a pair, then the finite automaton enters the state given by the second element of the pair Copyright © 2009 Elsevier ...
15A NCAC 02D .0533 STACK HEIGHT (a) For the purpose of this
... the height demonstrated by a fluid model or a field study approved by the Director, which ensures that the emissions from a stack do not result in excessive concentrations of any air pollutant as a result of atmospheric downwash, wakes, or eddy effects created by the source itself, nearby structures ...
... the height demonstrated by a fluid model or a field study approved by the Director, which ensures that the emissions from a stack do not result in excessive concentrations of any air pollutant as a result of atmospheric downwash, wakes, or eddy effects created by the source itself, nearby structures ...
Logic Programming
... if null(x) then raise Nomatch else if a = hd(x) then x else member(a,tl(x)) ...
... if null(x) then raise Nomatch else if a = hd(x) then x else member(a,tl(x)) ...
review of haskell
... Polymorphic Functions A function is called polymorphic (“of many forms”) if its type contains one or more type variables. length :: [a] Int ...
... Polymorphic Functions A function is called polymorphic (“of many forms”) if its type contains one or more type variables. length :: [a] Int ...
4on1 - FSU Computer Science
... Unstructured flow: the use of goto statements and statement labels to obtain control flow Merit or evil? Generally considered bad, but sometimes useful for jumping out of nested loops and for programming errors and exceptions Java has no goto statement Structured flow: Sequencing: the subsequent exe ...
... Unstructured flow: the use of goto statements and statement labels to obtain control flow Merit or evil? Generally considered bad, but sometimes useful for jumping out of nested loops and for programming errors and exceptions Java has no goto statement Structured flow: Sequencing: the subsequent exe ...
Common Lisp - cse.sc.edu
... his scientific goal -- artificial intelligence. • McCarthy desired for an algebraic list processing language for artificial intelligence work on the IBM 704 computer ...
... his scientific goal -- artificial intelligence. • McCarthy desired for an algebraic list processing language for artificial intelligence work on the IBM 704 computer ...
Miranda * A Functional Language
... Basic Themes of Miranda • Miranda is purely functional - there are no side effects or imperative features of any kind • A program, called a “script”, contains a collection of equations defining various functions and data structures • Changing the order of equations in the script does not change the ...
... Basic Themes of Miranda • Miranda is purely functional - there are no side effects or imperative features of any kind • A program, called a “script”, contains a collection of equations defining various functions and data structures • Changing the order of equations in the script does not change the ...
Higher-order functions
... 60, whose call-by-name parameter passing mechanism provides a form of lazy evaluation. Some modern functional languages have lazy evaluation, most notably Clean and Haskell. This provides for concise programs, extreme modularization, and very powerful and general functions, especially when working w ...
... 60, whose call-by-name parameter passing mechanism provides a form of lazy evaluation. Some modern functional languages have lazy evaluation, most notably Clean and Haskell. This provides for concise programs, extreme modularization, and very powerful and general functions, especially when working w ...
ppt
... when the method is called, an activation record is pushed onto the stack when the method terminates, its activation record is popped note that the currently executing method is always at the top of the stack ...
... when the method is called, an activation record is pushed onto the stack when the method terminates, its activation record is popped note that the currently executing method is always at the top of the stack ...
Lambda-calculus. - UT Computer Science
... while ((l < h) && (a[l] <= p)) l = l+1; while ((h > l) && (a[h] >= p)) h = h-1; if (l < h) { t = a[l]; a[l] = a[h]; a[h] = t; } } while (l < h); t = a[l]; a[l] = a[hi]; a[hi] = t; qsort( a, lo, l-1 ); qsort( a, l+1, hi ); ...
... while ((l < h) && (a[l] <= p)) l = l+1; while ((h > l) && (a[h] >= p)) h = h-1; if (l < h) { t = a[l]; a[l] = a[h]; a[h] = t; } } while (l < h); t = a[l]; a[l] = a[hi]; a[hi] = t; qsort( a, lo, l-1 ); qsort( a, l+1, hi ); ...
Lisp vs Scheme
... • “It differs from most current dialects of LISP in that it closes all lambdaexpressions in the environment of their definition [...], rather than in the execution environment [..., and in] that tail-recursions execute without net growth of the interpreter stack.” ...
... • “It differs from most current dialects of LISP in that it closes all lambdaexpressions in the environment of their definition [...], rather than in the execution environment [..., and in] that tail-recursions execute without net growth of the interpreter stack.” ...
LISP
... In imperative programming an expression is evaluated and the result is stored in memory location which is represented as a variable in the program. A purely functional programming language does not use variables and assignment statements. Without variables iterative constructs are not possible. Repe ...
... In imperative programming an expression is evaluated and the result is stored in memory location which is represented as a variable in the program. A purely functional programming language does not use variables and assignment statements. Without variables iterative constructs are not possible. Repe ...
Lect 1
... A predicate is a procedure that always returns a boolean value (#t or #f). By convention, predicates usually have names that end in `?'. A mutation procedure is a procedure that alters a data structure. By convention, mutation procedures usually have names that end in `!'. ...
... A predicate is a procedure that always returns a boolean value (#t or #f). By convention, predicates usually have names that end in `?'. A mutation procedure is a procedure that alters a data structure. By convention, mutation procedures usually have names that end in `!'. ...
Document
... A predicate is a procedure that always returns a boolean value (#t or #f). By convention, predicates usually have names that end in `?'. A mutation procedure is a procedure that alters a data structure. By convention, mutation procedures usually have names that end in `!'. ...
... A predicate is a procedure that always returns a boolean value (#t or #f). By convention, predicates usually have names that end in `?'. A mutation procedure is a procedure that alters a data structure. By convention, mutation procedures usually have names that end in `!'. ...
Functionalprogramming
... • the top level loop (“ear”) evaluates an expression for its value or for its side-effects such as I/O (this expression may invoke a function that implements a large and complex algorithm), • a Lisp program is a collection of functions that may be called (directly or indirectly) from the top level ...
... • the top level loop (“ear”) evaluates an expression for its value or for its side-effects such as I/O (this expression may invoke a function that implements a large and complex algorithm), • a Lisp program is a collection of functions that may be called (directly or indirectly) from the top level ...
CS112 Lecture: Recursion Last revised 3/20/08 1. Von Koch curve images
... list, rather than modifying the existing list. The latter would be more efficient in this case, but this example has been constructed in a way that will be helpful to you as you work on Lab 10. ...
... list, rather than modifying the existing list. The latter would be more efficient in this case, but this example has been constructed in a way that will be helpful to you as you work on Lab 10. ...
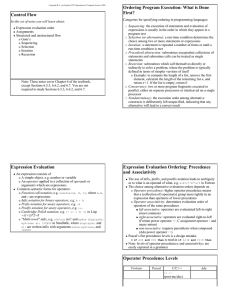
Control Flow - FSU Computer Science
... iterations is changed compared to the iterations set by the loop bounds GOTOs can jump out of the loop and also from outside into the loop The value of counter i after the loop is implementation dependent The body of the loop will be executed at least once (no empty bounds) COP4020 Spring 2014 ...
... iterations is changed compared to the iterations set by the loop bounds GOTOs can jump out of the loop and also from outside into the loop The value of counter i after the loop is implementation dependent The body of the loop will be executed at least once (no empty bounds) COP4020 Spring 2014 ...
D16/B330/3C11 Functional Programming Lecture 5
... Tuple patterns (x,y,z) = (3, “hello”, (34,True,[3])) ...
... Tuple patterns (x,y,z) = (3, “hello”, (34,True,[3])) ...
3. Functional Programming
... Referential transparency means that “equals can be replaced by equals”. In a pure functional language, all functions are referentially transparent, and therefore always yield the same result no ...
... Referential transparency means that “equals can be replaced by equals”. In a pure functional language, all functions are referentially transparent, and therefore always yield the same result no ...
Chapter 14a - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... In pure lambda calculus, expressions like (( x . x2)5) = 52 are uninterpreted. In a functional language, (( x . x2)5) is interpreted normally (25). ...
... In pure lambda calculus, expressions like (( x . x2)5) = 52 are uninterpreted. In a functional language, (( x . x2)5) is interpreted normally (25). ...
PPTX - cs.Virginia
... (define (mlist-append! p q) (if (null? p) (error “Cannot append to empty list!”) (if (null? (mcdr p)) (set-mcdr! p q) (mlist-append! (mcdr p) q)))) Running time in (Np), number of elements in p Number of new cons cells: 0 ...
... (define (mlist-append! p q) (if (null? p) (error “Cannot append to empty list!”) (if (null? (mcdr p)) (set-mcdr! p q) (mlist-append! (mcdr p) q)))) Running time in (Np), number of elements in p Number of new cons cells: 0 ...
Functional Programming
... can discard the current activation record, push record for new recursive call thus, no limit on recursion depth (each recursive call reuses the same memory) Scheme interpreters are required to perform this tail-recursion optimization ...
... can discard the current activation record, push record for new recursive call thus, no limit on recursion depth (each recursive call reuses the same memory) Scheme interpreters are required to perform this tail-recursion optimization ...
CSC 533: Programming Languages Spring 2017
... unlike arrays, lists do not have to store items of same type/size do not have to be stored contiguously do not have to provide random access § all computation is performed by applying functions to arguments in pure LISP: no variables, no assignments, no iteration § functions and function calls are ...
... unlike arrays, lists do not have to store items of same type/size do not have to be stored contiguously do not have to provide random access § all computation is performed by applying functions to arguments in pure LISP: no variables, no assignments, no iteration § functions and function calls are ...
4.1 Characteristics of Functional Programming Languages Chapter
... 4.1 Characteristics of Functional Programming Languages Chapter 3 examined imperative languages, those languages with a design that is an abstraction of the underlying von Neumann architecture. While imperative languages continue to be the most widely used languages, renewed interested in functional ...
... 4.1 Characteristics of Functional Programming Languages Chapter 3 examined imperative languages, those languages with a design that is an abstraction of the underlying von Neumann architecture. While imperative languages continue to be the most widely used languages, renewed interested in functional ...