Document
... brain signals of different frequency and amplitude and it will convert these signals into packets and transmit through Bluetooth medium in to the level splitter section to check the attention level. Level splitter section (LSS) analyse the level and gives the drowsy driving alert and keeps the vehic ...
... brain signals of different frequency and amplitude and it will convert these signals into packets and transmit through Bluetooth medium in to the level splitter section to check the attention level. Level splitter section (LSS) analyse the level and gives the drowsy driving alert and keeps the vehic ...
ICT implants in the human body : a review
... The micro-electro mechanical systems device (MEMS) is an implantable micro-sensor that can send data to a hand-held receiver outside the body, alerting doctors to a potential medical crisis, without using any wires or batteries. Brain prosthesis 9 artificial hippocampus: an implantable brain chip th ...
... The micro-electro mechanical systems device (MEMS) is an implantable micro-sensor that can send data to a hand-held receiver outside the body, alerting doctors to a potential medical crisis, without using any wires or batteries. Brain prosthesis 9 artificial hippocampus: an implantable brain chip th ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... lobes helps us to judge, plan, and process new memories. ...
... lobes helps us to judge, plan, and process new memories. ...
ORAL SCIENCE I
... 3. 4 Basic Processes of the Nervous System • Reception- stimuli • Transmission- Sensory input- from area to brain Afferent • Integration- sums up input to allow brain to make decision • Motor output- efferent- cause response ...
... 3. 4 Basic Processes of the Nervous System • Reception- stimuli • Transmission- Sensory input- from area to brain Afferent • Integration- sums up input to allow brain to make decision • Motor output- efferent- cause response ...
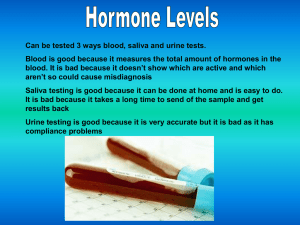
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... Measures the electronic activity of the brain by using electrodes attached to the scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity ha ...
... Measures the electronic activity of the brain by using electrodes attached to the scalp. The electrical pulses are know as EEG and show an electrical signal caused by the neurones in the brain EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity ha ...
Anikeeva
... In the Bioelectronics Group, we envision integration of biology and electronics with devices that incorporate biologically inspired components and technologies that seamlessly interface biological and electronic systems. We are currently focused on developing methods to manipulate nerve cells. The a ...
... In the Bioelectronics Group, we envision integration of biology and electronics with devices that incorporate biologically inspired components and technologies that seamlessly interface biological and electronic systems. We are currently focused on developing methods to manipulate nerve cells. The a ...
Inner Ear
... cells. Each ear contains thousands of hair cells. The hair cells are arranged by frequency (pitch) just like the keyboard of a piano. Nerves are attached to the bottom of these hair cells so when the hair cells move, electrical impulses are passed to specific parts of the auditory nerve. These elect ...
... cells. Each ear contains thousands of hair cells. The hair cells are arranged by frequency (pitch) just like the keyboard of a piano. Nerves are attached to the bottom of these hair cells so when the hair cells move, electrical impulses are passed to specific parts of the auditory nerve. These elect ...
Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... If the axon cannot reestablish contact with a target, the neuron eventually dies ...
... If the axon cannot reestablish contact with a target, the neuron eventually dies ...
Nerves and the brain
... changing. Sense organs such as the ear and the eye detect these changes and send information to the brain. The brain then interprets the information and sends an impulse to an effector organ such as a muscle. It is essential that the brain interpret signals from the sense organs correctly. ...
... changing. Sense organs such as the ear and the eye detect these changes and send information to the brain. The brain then interprets the information and sends an impulse to an effector organ such as a muscle. It is essential that the brain interpret signals from the sense organs correctly. ...
Biopsychology
... Skin Conductance Response (SCR; formerly GSR) Measurement of electricity passed between two surface electrodes placed on the ...
... Skin Conductance Response (SCR; formerly GSR) Measurement of electricity passed between two surface electrodes placed on the ...
CS 160 * Comparative Cognition * Spring 02
... - Motor Programs, esp for rapid, co-ord’d movements that require precise timing and/or aiming - i.e. “Procedural Memory” for well-practiced moves, simple to complex athletic/manual acts - Receives from sensory (visual, acoustic, vestibular for balance, etc) & from/to motor centers - Also involved in ...
... - Motor Programs, esp for rapid, co-ord’d movements that require precise timing and/or aiming - i.e. “Procedural Memory” for well-practiced moves, simple to complex athletic/manual acts - Receives from sensory (visual, acoustic, vestibular for balance, etc) & from/to motor centers - Also involved in ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Some injuries harm nerve cells, but the brain often recovers from stress, damage, or disease. ...
... Some injuries harm nerve cells, but the brain often recovers from stress, damage, or disease. ...
SompolinskyAug09
... accelerated or distorted manner. However, the neuronal mechanisms that enable our brain to perceive a word correctly, for example, that is pronounced in different ways by different speakers or to understand a heavy accent, was a mystery to scientists until now. Research associate Dr. Robert Gütig an ...
... accelerated or distorted manner. However, the neuronal mechanisms that enable our brain to perceive a word correctly, for example, that is pronounced in different ways by different speakers or to understand a heavy accent, was a mystery to scientists until now. Research associate Dr. Robert Gütig an ...
BRAIN COMPUTER INTERFACE
... and allows electrode placement in the specific area of the brain where the appropriate signals are generated. ...
... and allows electrode placement in the specific area of the brain where the appropriate signals are generated. ...
Neurons
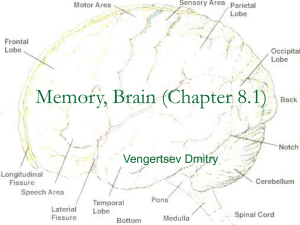
... Each cerebral hemisphere divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital ...
... Each cerebral hemisphere divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital ...
The Nervous System
... Severed spinal cord – could cause the loss of bodily movement Paralysis – loss of neurological communication (movement, feeling, etc) Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immun ...
... Severed spinal cord – could cause the loss of bodily movement Paralysis – loss of neurological communication (movement, feeling, etc) Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immun ...
05-First 2 years - Biosocial
... Blood vessels rupture in the brain Neural connections beak “Abusive Head Trauma” ...
... Blood vessels rupture in the brain Neural connections beak “Abusive Head Trauma” ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... substitution treatments used for a range of human ...
... substitution treatments used for a range of human ...
The Structures of the Brain
... frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
... frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
the central nervous system
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
The Nervous System
... neurons Found in brain, spinal cord and nerves Approximately 100 billion neurons in human brain Neurons conduct electrical signals (nerve impulses) ...
... neurons Found in brain, spinal cord and nerves Approximately 100 billion neurons in human brain Neurons conduct electrical signals (nerve impulses) ...
outline28002
... c. Photoreceptors-Subretinal Space d. Ganglion Cells-Epiretinal Space C. Three Physiologic Principles a. Electric currents can substitute light photons in producing visual sensations (phosphene). b. Most etiologies of blindness leave upstream structure intact. c. Retinotopic organization of target n ...
... c. Photoreceptors-Subretinal Space d. Ganglion Cells-Epiretinal Space C. Three Physiologic Principles a. Electric currents can substitute light photons in producing visual sensations (phosphene). b. Most etiologies of blindness leave upstream structure intact. c. Retinotopic organization of target n ...