Wave Optics
... Remember that mλ is simply the extra path length to point P. It is labelled Delta in the picture. You can use the same equation for dark bands. However, there you have half wavelengths. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Remember that mλ is simply the extra path length to point P. It is labelled Delta in the picture. You can use the same equation for dark bands. However, there you have half wavelengths. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Sample Problems for Final
... illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxima for both colors occur on the screen straight ahead of the slits. How far away fr ...
... illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxima for both colors occur on the screen straight ahead of the slits. How far away fr ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
Interference, Diffraction and Polarization
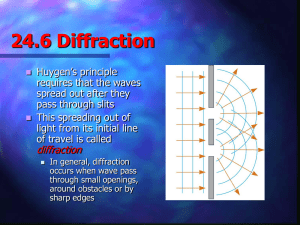
... buildings, hills, etc. (AM radio) • Visible light diffracted by objects around 10-7 m; determines limit of optical microscope • Electron beam has shorter wavelength so electron microscopes can resolve much smaller objects ...
... buildings, hills, etc. (AM radio) • Visible light diffracted by objects around 10-7 m; determines limit of optical microscope • Electron beam has shorter wavelength so electron microscopes can resolve much smaller objects ...
Optics-Diffraction - The Wave Nature of Light
... where virtually all information about the cosmos arrives in the form of electromagnetic radiation observed with telescopes or specialized instruments located on the Earth’s surface or aboard satellites in earth orbit. Similarly, much of what is known about atomic structure—the arrangement of electro ...
... where virtually all information about the cosmos arrives in the form of electromagnetic radiation observed with telescopes or specialized instruments located on the Earth’s surface or aboard satellites in earth orbit. Similarly, much of what is known about atomic structure—the arrangement of electro ...
Ultrafast holographic Stokesmeter for polarization imaging in real time Mark Kleinschmit
... B 苷 tFSk 2 uk 2 tESk 2 . This equation shows the Stokes vector that is diffracted from one grating. The second grating will produce an equation of the same form but with different grating coeff icients u. Both equations have the same Stokes vector as input, but because grating parameters u differ, t ...
... B 苷 tFSk 2 uk 2 tESk 2 . This equation shows the Stokes vector that is diffracted from one grating. The second grating will produce an equation of the same form but with different grating coeff icients u. Both equations have the same Stokes vector as input, but because grating parameters u differ, t ...
Resolution questions with solutions
... IB PHYSICS UNIT 11 RESOLUTION SOLUTIONS 1. (a) central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
... IB PHYSICS UNIT 11 RESOLUTION SOLUTIONS 1. (a) central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
... deviate from the actual behaviour whenever the hologram is thin or the refractive index is high. In these cases, it is necessary to use a more general Coupled Wave Theory (CW) or the Rigorous Coupled Wave Theory (RCW). Both of these theories allow for more than two orders propagating inside the holo ...
optical design of an echelle grating based atomic emission
... and 175 mm focal length respectively with aluminium high reflection coatings. The Littrow prism is 35 X 70 X 40 mm3 made of fused silica with aluminium high reflection coating. The mirrors and the prism, which were fabricated in-house have a surface accuracy of λ/8 and angle accuracies of 30 arc-sec ...
... and 175 mm focal length respectively with aluminium high reflection coatings. The Littrow prism is 35 X 70 X 40 mm3 made of fused silica with aluminium high reflection coating. The mirrors and the prism, which were fabricated in-house have a surface accuracy of λ/8 and angle accuracies of 30 arc-sec ...
Spectroscopy – I. Gratings and Prisms
... If we could see the whole spectrum (radio to γ–ray), then every order would completely overlap with every other order. In reality, of course, many effects limit what we can see/measure. For example, the atmosphere will eliminate most photons at shorter wavelengths than about 340nm – as well as large ...
... If we could see the whole spectrum (radio to γ–ray), then every order would completely overlap with every other order. In reality, of course, many effects limit what we can see/measure. For example, the atmosphere will eliminate most photons at shorter wavelengths than about 340nm – as well as large ...
Numerical simulation of diffraction grating alignment and phase noise
... More work on verifying what is seen in FDTD simulations to the RCWA method used by A.Bunkowski et al. (2006) Measure the more relevant reflection coefficient for waveguide coatings and determine if it is immune to phase noises from ...
... More work on verifying what is seen in FDTD simulations to the RCWA method used by A.Bunkowski et al. (2006) Measure the more relevant reflection coefficient for waveguide coatings and determine if it is immune to phase noises from ...
Abstract - University of Dayton
... Ujitha Abeywickrema University of Dayton Abstract Materials exhibiting effective nonlinearity through refractive index modulation at relatively low optical powers can be exploited for various applications. Examples of such materials include liquids where the refractive index is modified through heat ...
... Ujitha Abeywickrema University of Dayton Abstract Materials exhibiting effective nonlinearity through refractive index modulation at relatively low optical powers can be exploited for various applications. Examples of such materials include liquids where the refractive index is modified through heat ...
Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by space
... Singularities in optical fields have received much attention lately.1 Such singularities appear at points or lines where the phase or the amplitude of the wave is undef ined or changes abruptly. One class of dislocation is vortices, which are spiral phase ramps about a singularity. Vortices are H ch ...
... Singularities in optical fields have received much attention lately.1 Such singularities appear at points or lines where the phase or the amplitude of the wave is undef ined or changes abruptly. One class of dislocation is vortices, which are spiral phase ramps about a singularity. Vortices are H ch ...
Efficiency enhancement in a light
... electrode was formed on the contact layer. Around this, triangular lattice airholes were formed by electron beam 共EB兲 lithography and Cl2 /Xe inductively coupled plasma etching.8,9 The etching was stopped in the middle of the InP layer beneath the contact layer. The substrate was lapped and polished ...
... electrode was formed on the contact layer. Around this, triangular lattice airholes were formed by electron beam 共EB兲 lithography and Cl2 /Xe inductively coupled plasma etching.8,9 The etching was stopped in the middle of the InP layer beneath the contact layer. The substrate was lapped and polished ...
Titel
... Gratings Transmission gratings The incident light is transmitted through the slits Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is Transmission transmitted in all direction gratings Each slit becomes a secondary source of light A constructive interference will be created on the image plane o ...
... Gratings Transmission gratings The incident light is transmitted through the slits Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is Transmission transmitted in all direction gratings Each slit becomes a secondary source of light A constructive interference will be created on the image plane o ...
Interference
... • By the early 19th century the wave model was becoming accepted and the French Physicist Fresnel had worked out an elaborate mathematical theory of light. However, the famous physicist Poisson claimed to have found a fatal flaw in the ...
... • By the early 19th century the wave model was becoming accepted and the French Physicist Fresnel had worked out an elaborate mathematical theory of light. However, the famous physicist Poisson claimed to have found a fatal flaw in the ...
Powerpoint Slides
... The maximas in intensity occur when the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
... The maximas in intensity occur when the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... As shown in Fig. 5, we extended the slit interference concept and considered a great amount of slits that were extremely narrow. When multiple-slit apparatus is illuminated by a ray, the resulting interference can be considered to be produced by numerous light point sources. Constructive interferenc ...
... As shown in Fig. 5, we extended the slit interference concept and considered a great amount of slits that were extremely narrow. When multiple-slit apparatus is illuminated by a ray, the resulting interference can be considered to be produced by numerous light point sources. Constructive interferenc ...
Classical Optics
... for 0 ≤ sinθ ≤ 2λ/a for systems containing two, three and four slits. 11. Using Lloyd's mirror (as shown below), X-ray fringes were observed, the spacing of which was found to be 0.0025 cm. The wavelength used was 0.833 nm. (a) If the source-screen distance was 300 cm, how high above the mirror plan ...
... for 0 ≤ sinθ ≤ 2λ/a for systems containing two, three and four slits. 11. Using Lloyd's mirror (as shown below), X-ray fringes were observed, the spacing of which was found to be 0.0025 cm. The wavelength used was 0.833 nm. (a) If the source-screen distance was 300 cm, how high above the mirror plan ...
'א דעומ Classical Optics
... process. (a) What are the conditions for constructive interference for this interferometer? Describe each variable. (b) If the device is illuminated with 500-nm light, how far was the mirror moved? (c) What is the purpose of the optical element that is labeled C in the figure on the right? 10. Consi ...
... process. (a) What are the conditions for constructive interference for this interferometer? Describe each variable. (b) If the device is illuminated with 500-nm light, how far was the mirror moved? (c) What is the purpose of the optical element that is labeled C in the figure on the right? 10. Consi ...
'א דעומ Classical Optics
... process. (a) What are the conditions for constructive interference for this interferometer? Describe each variable. (b) If the device is illuminated with 500-nm light, how far was the mirror moved? (c) What is the purpose of the optical element that is labeled C in the figure on the right? 10. Consi ...
... process. (a) What are the conditions for constructive interference for this interferometer? Describe each variable. (b) If the device is illuminated with 500-nm light, how far was the mirror moved? (c) What is the purpose of the optical element that is labeled C in the figure on the right? 10. Consi ...
Electroholographic tunable volume grating in the g44
... (i.e., polarized in the y direction), and the angle of incidence is chosen so that Eq. (2b) is fulfilled. In general, upon the application of Eo, the 2K gratings that arise from the diagonal terms in Eq. (3) do not fulfill the Bragg condition and therefore cannot cause diffraction. The K grating t ...
... (i.e., polarized in the y direction), and the angle of incidence is chosen so that Eq. (2b) is fulfilled. In general, upon the application of Eo, the 2K gratings that arise from the diagonal terms in Eq. (3) do not fulfill the Bragg condition and therefore cannot cause diffraction. The K grating t ...
Light Sources
... PhotolithographyDiffraction • Rayleigh suggested that a reasonable criterion for resolution (R = distance between A and B) is that the central maximum of one point source lies at the first minimum of the Airy pattern of the other point (R = diameter of circle) • The numerical aperture (NA) of a len ...
... PhotolithographyDiffraction • Rayleigh suggested that a reasonable criterion for resolution (R = distance between A and B) is that the central maximum of one point source lies at the first minimum of the Airy pattern of the other point (R = diameter of circle) • The numerical aperture (NA) of a len ...
Lateral shearing interferometry for EUV optical testing
... Spatial frequencies incident upon a periodic grating will diffract based on the grating equation: ...
... Spatial frequencies incident upon a periodic grating will diffract based on the grating equation: ...
Diffraction grating

In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as the dispersive element. Because of this, gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers.For practical applications, gratings generally have ridges or rulings on their surface rather than dark lines. Such gratings can be either transmissive or reflective. Gratings which modulate the phase rather than the amplitude of the incident light are also produced, frequently using holography.The principles of diffraction gratings were discovered by James Gregory, about a year after Newton's prism experiments, initially with items such as bird feathers. The first man-made diffraction grating was made around 1785 by Philadelphia inventor David Rittenhouse, who strung hairs between two finely threaded screws. This was similar to notable German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer's wire diffraction grating in 1821.Diffraction can create ""rainbow"" colors when illuminated by a wide spectrum (e.g., continuous) light source. The sparkling effects from the closely spaced narrow tracks on optical storage disks such as CD's or DVDs are an example, while the similar rainbow effects caused by thin layers of oil (or gasoline, etc.) on water are not caused by a grating, but rather by interference effects in reflections from the closely spaced transmissive layers (see Examples, below). A grating has parallel lines, while a CD has a spiral of finely-spaced data tracks. Diffraction colors also appear when one looks at a bright point source through a translucent fine-pitch umbrella-fabric covering. Decorative patterned plastic films based on reflective grating patches are very inexpensive, and are commonplace.