www.BDTIC.com/ON/ Test Procedure for the LV8498CTGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... Check if pull-up resistors have been connected to the lines. If not, mount R1 and R2 on the evaluation board. ・ The USB adapter we provided has built-in resistors. Therefore, you do not need to mount any resistor. ・ Check the ENA pin is not OPEN. And supply power. After powered, if the ENA pin is pu ...
... Check if pull-up resistors have been connected to the lines. If not, mount R1 and R2 on the evaluation board. ・ The USB adapter we provided has built-in resistors. Therefore, you do not need to mount any resistor. ・ Check the ENA pin is not OPEN. And supply power. After powered, if the ENA pin is pu ...
Course summary for Unit 3 "Electronics and photonics"
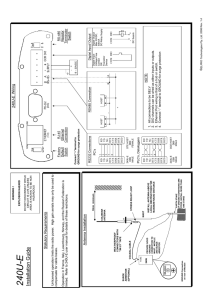
... variable DC voltage that can range from a maximum value set by the DC power supply to zero. They are often used with transducers such as LDRs and thermistors as one of the components. A typical voltage divider circuit is drawn below. The output voltage is V0ut = [ R2 / (R1 + R2)] VIn ...
... variable DC voltage that can range from a maximum value set by the DC power supply to zero. They are often used with transducers such as LDRs and thermistors as one of the components. A typical voltage divider circuit is drawn below. The output voltage is V0ut = [ R2 / (R1 + R2)] VIn ...
OP290 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... High-performance portable equipment and instruments frequently use lithium cells because of their long shelf-life, light weight, and high energy density relative to older primary cells. Most lithium cells have a nominal output voltage of 3 V and are noted for a flat discharge characteristic. The low ...
... High-performance portable equipment and instruments frequently use lithium cells because of their long shelf-life, light weight, and high energy density relative to older primary cells. Most lithium cells have a nominal output voltage of 3 V and are noted for a flat discharge characteristic. The low ...
AD633 Low Cost Analog Multiplier
... 100 µV rms in a 10 Hz to 10 kHz bandwidth. A 1 MHz bandwidth, 20 V/µs slew rate, and the ability to drive capacitive loads make the AD633 useful in a wide variety of applications where simplicity and cost are key concerns. The AD633’s versatility is not compromised by its simplicity. The Z-input pro ...
... 100 µV rms in a 10 Hz to 10 kHz bandwidth. A 1 MHz bandwidth, 20 V/µs slew rate, and the ability to drive capacitive loads make the AD633 useful in a wide variety of applications where simplicity and cost are key concerns. The AD633’s versatility is not compromised by its simplicity. The Z-input pro ...
SGA1263Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... DCto4000MHz SILICON GERMANIUM HBT CASCADABLE GAIN BLOCK Package: SOT-363 ...
... DCto4000MHz SILICON GERMANIUM HBT CASCADABLE GAIN BLOCK Package: SOT-363 ...
L4947 L4947R 5V-0.5A VERY LOW DROP REGULATOR WITH RESET
... Since the purpose of a voltage regulator is to supply and load variations, the open loop gain of the regulator must be very high at low frequencies. This may cause instability as a result of the various poles present in the loop. To avoid this instability dominant pole compensation is used to reduce ...
... Since the purpose of a voltage regulator is to supply and load variations, the open loop gain of the regulator must be very high at low frequencies. This may cause instability as a result of the various poles present in the loop. To avoid this instability dominant pole compensation is used to reduce ...
HMC842LC4B 数据资料DataSheet下载
... GHz. During normal operation, input data (or clock) is transferred to both output channels. Differential input and output signals of the HMC842LC4B are terminated with 50 Ohms to ground on-chip, and may be either AC or DC coupled. The Outputs can be connected directly to a 50 Ohms-to-ground terminat ...
... GHz. During normal operation, input data (or clock) is transferred to both output channels. Differential input and output signals of the HMC842LC4B are terminated with 50 Ohms to ground on-chip, and may be either AC or DC coupled. The Outputs can be connected directly to a 50 Ohms-to-ground terminat ...
5 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... – examples are: adders, subtractors, decoders, encoders, multiplexers and demultiplexers. – The results are based on the truth table ...
... – examples are: adders, subtractors, decoders, encoders, multiplexers and demultiplexers. – The results are based on the truth table ...
AD537
... first is trimmed by adjustment of the scaling resistor R and the second by the (optional) potentiometer connected to +VS and the VOS pins (“D” package only). Precise calibration requires the use of an accurate voltage standard set to the desired FS value and a frequency meter; a scope is useful for ...
... first is trimmed by adjustment of the scaling resistor R and the second by the (optional) potentiometer connected to +VS and the VOS pins (“D” package only). Precise calibration requires the use of an accurate voltage standard set to the desired FS value and a frequency meter; a scope is useful for ...
TDE1747
... This device is essentially blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to safe values. Adjustment only requires one external resistor. In addition, thermal shut down is provided to keep the IC from overheating. If internal dissipation becomes too high, the driver w ...
... This device is essentially blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to safe values. Adjustment only requires one external resistor. In addition, thermal shut down is provided to keep the IC from overheating. If internal dissipation becomes too high, the driver w ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.