Mars Land Rover ASTEROID BELT
... something you can hold in your hand, unlike a meteor (shooting star), which burns up in the atmosphere. The fall of a meteorite is almost always a very spectacular affair, so that there is a bright fireball, sonic booms, a dust trail and, if the meteorite was big enough, an impact crater. ...
... something you can hold in your hand, unlike a meteor (shooting star), which burns up in the atmosphere. The fall of a meteorite is almost always a very spectacular affair, so that there is a bright fireball, sonic booms, a dust trail and, if the meteorite was big enough, an impact crater. ...
Astronomy Chapter 11 – Meteors, Comets and Asteroids A. Main
... ⇒ Most comets cone from the Oort cloud, the swarm of trillions of icy bodies believed to lie far beyond the orbit of Pluto ⇒ Some comets may come a region called the Kuiper belt which begins about the orbit of Neptune and extends for an unknown distance beyond ⇒ In order for us to see a comet its or ...
... ⇒ Most comets cone from the Oort cloud, the swarm of trillions of icy bodies believed to lie far beyond the orbit of Pluto ⇒ Some comets may come a region called the Kuiper belt which begins about the orbit of Neptune and extends for an unknown distance beyond ⇒ In order for us to see a comet its or ...
Science 9: Space Practice Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following
... 14. If you called a friend in China at 2pm from Miramichi, what time is it in China? a. 3pm b. 2am c. 2pm 15. During the winter the Earth is tilted in which direction to the sun? a. Towards b. up c. down ...
... 14. If you called a friend in China at 2pm from Miramichi, what time is it in China? a. 3pm b. 2am c. 2pm 15. During the winter the Earth is tilted in which direction to the sun? a. Towards b. up c. down ...
Earth, Sun and Moon
... • By measuring the ages of lunar rocks, we know that the moon is about 4.6 billion years old, or about the same age as Earth. • The distance between the Earth and its moon averages about 238,900 miles (384,000 kilometers). The diameter of the moon is 2,160 miles (3,476 kilometers). The moon's mass—t ...
... • By measuring the ages of lunar rocks, we know that the moon is about 4.6 billion years old, or about the same age as Earth. • The distance between the Earth and its moon averages about 238,900 miles (384,000 kilometers). The diameter of the moon is 2,160 miles (3,476 kilometers). The moon's mass—t ...
GEOLOGIC TIME
... • Based on fossil evidence and mass extinctions • Life forms have evolved over time • 4 MAJOR ERAS ...
... • Based on fossil evidence and mass extinctions • Life forms have evolved over time • 4 MAJOR ERAS ...
34_alone
... could kill all nearby life. • No known defense except to move far away. • Low density of stars near sun suggest that a very close supernova is very rare! • Also worry about gamma ray burst (collapse of very massive star to form black hole). • Gamma Ray bursts would kill anything that happened to be ...
... could kill all nearby life. • No known defense except to move far away. • Low density of stars near sun suggest that a very close supernova is very rare! • Also worry about gamma ray burst (collapse of very massive star to form black hole). • Gamma Ray bursts would kill anything that happened to be ...
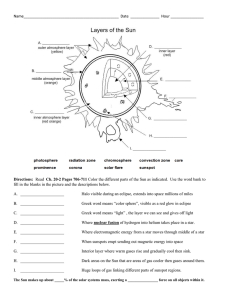
Ch. 20-2 Sun Study Gd. Revised
... 4. When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, friction causes it to burn up and produce a streak of light called a(n) __________________________________________________ . 5. A chunk of ice and dust whose orbit is usually a long, narrow ellipse is a(n) __________________ . 6. If a meteoroid hits Ear ...
... 4. When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, friction causes it to burn up and produce a streak of light called a(n) __________________________________________________ . 5. A chunk of ice and dust whose orbit is usually a long, narrow ellipse is a(n) __________________ . 6. If a meteoroid hits Ear ...
Microsoft Word - students_diffe
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
Potential Meteorite Impact - Albert
... through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are termed meteorites. ...
... through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are termed meteorites. ...
Potential meteorite impact - Albert
... are heated to incandescence by the friction of the air. The bright trails that are coming through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are ter ...
... are heated to incandescence by the friction of the air. The bright trails that are coming through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are ter ...
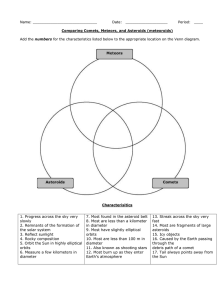
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors
... numerous to be considered planets • Rocky – 75% of all asteroids • Iron (metals) – 7% of all asteroids • Mixed (rock and iron blended) – 18% of all asteroids ...
... numerous to be considered planets • Rocky – 75% of all asteroids • Iron (metals) – 7% of all asteroids • Mixed (rock and iron blended) – 18% of all asteroids ...
Can we detect asteroid impacts with rocky extrasolar planets?
... also calculated the detectability of giant impacts with planets like Neptune. Building on this work, let us consider the effects of a Chicxulub-size impact with planets similar to the Earth. Impact frequency The Earth suffers a Chicxulub-size impact every 100 million years or so. There are four rock ...
... also calculated the detectability of giant impacts with planets like Neptune. Building on this work, let us consider the effects of a Chicxulub-size impact with planets similar to the Earth. Impact frequency The Earth suffers a Chicxulub-size impact every 100 million years or so. There are four rock ...
Ch. 3 Sec. 5 Notes
... *More than 100,000 asteroids have been discovered *The largest asteroid, Ceres, was recently classified as a dwarf planet *Some asteroids have an extremely elliptical orbit that crosses paths with Earth -Someday, one of these asteroids could hit Earth and wipe out our entire planet *An asteroid did ...
... *More than 100,000 asteroids have been discovered *The largest asteroid, Ceres, was recently classified as a dwarf planet *Some asteroids have an extremely elliptical orbit that crosses paths with Earth -Someday, one of these asteroids could hit Earth and wipe out our entire planet *An asteroid did ...
Comets, Asteroids, Meteoroids
... • A comet’s tail will point away from the sun as it gets closer to the sun. ...
... • A comet’s tail will point away from the sun as it gets closer to the sun. ...
a naturally occuring object in space such as a star, planet, moon
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
the Moon? The Moon has no wind or water to erode the craters
... different amounts of time. Mars is closer to the Sun, travels faster, and in a smaller orbit. Saturn moves more slowly and has a longer orbit. 11. How does Earth rotation on its axis help keep the planet at proper temperature for life? The Earth rotates quickly ...
... different amounts of time. Mars is closer to the Sun, travels faster, and in a smaller orbit. Saturn moves more slowly and has a longer orbit. 11. How does Earth rotation on its axis help keep the planet at proper temperature for life? The Earth rotates quickly ...
Solar System - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Too small to be planets Believed to be leftover pieces from the birth of the Solar System that never merged into planets. ...
... Too small to be planets Believed to be leftover pieces from the birth of the Solar System that never merged into planets. ...
Meteoroids-Asteroids-Comets
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
Meteroroids! Asteroids! Comets!
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
Meteoroids! Asteroids! Comets!
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
... How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain ...
tail can extend millions of kilometers into space
... sometimes called a shooting star Meteor showers are large numbers of small meteors usually caused by Earth passing by dusty debris left by a comet ...
... sometimes called a shooting star Meteor showers are large numbers of small meteors usually caused by Earth passing by dusty debris left by a comet ...
document
... Tails (105 km to 1 AU long), always points away from the Sun. Solar wind (steady stream of solar particles) pushes gas away; dust continues to orbit Sun. ...
... Tails (105 km to 1 AU long), always points away from the Sun. Solar wind (steady stream of solar particles) pushes gas away; dust continues to orbit Sun. ...
Lecture 1 Review Sheet
... Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Explain the nebular theory of planet formation Why is the Earth a sphere? List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean wh ...
... Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Explain the nebular theory of planet formation Why is the Earth a sphere? List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean wh ...
Impact event

An impact event is a collision between celestial objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal impact. When large objects impact terrestrial planets like the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped Earth's history, have been implicated in the formation of the Earth–Moon system, the evolutionary history of life, the origin of water on Earth and several mass extinctions. Notable impact events include the Chicxulub impact, 66 million years ago, believed to be the cause of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.Throughout recorded history, hundreds of Earth impacts (and exploding bolides) have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage, or other significant localised consequences. One of the best-known recorded impacts in modern times was the Tunguska event, which occurred in Siberia, Russia, in 1908. The 2013 Chelyabinsk meteor event is the only known such event to result in a large number of injuries, and the Chelyabinsk meteor is the largest recorded object to have encountered the Earth since the Tunguska event.The most notable non-terrestrial event is the Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 impact, which provided the first direct observation of an extraterrestrial collision of Solar System objects, when the comet broke apart and collided with Jupiter in July 1994. Most of the observed extrasolar impacts are the slow collision of galaxies; however, in 2014, one of the first massive terrestrial impacts observed was detected around the star NGC 2547 ID8 by NASA's Spitzer space telescope and confirmed by ground observations. Impact events have been a plot and background element in science fiction.