Page 1 6483 0939 Tannoy United Kingdom T: +44 (0) 1236 420199
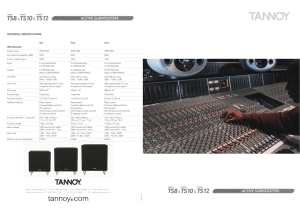
... TS12 respectively) ensuring there is ample power to reproduce dynamic movie scores. ...
... TS12 respectively) ensuring there is ample power to reproduce dynamic movie scores. ...
06 lecture #6
... Labs 12-13 Pspice Analysis • Pspice is a circuit simulator program • It uses libraries of components to define circuits and simulate them. • Probe provides graphical output for the results • Pspice includes transient, dc, transfer function, and other simulations modes ...
... Labs 12-13 Pspice Analysis • Pspice is a circuit simulator program • It uses libraries of components to define circuits and simulate them. • Probe provides graphical output for the results • Pspice includes transient, dc, transfer function, and other simulations modes ...
Capacitor Self
... is very hard to measure the value of this inductance but it can be accurately estimated from the oscillation frequency. Also, the Q of the circuit (and therefore the resistance) can be estimated from the level of the first peak. One should always try to maintain a Q of less than 1.5 to keep the over ...
... is very hard to measure the value of this inductance but it can be accurately estimated from the oscillation frequency. Also, the Q of the circuit (and therefore the resistance) can be estimated from the level of the first peak. One should always try to maintain a Q of less than 1.5 to keep the over ...
The Case for Active Speakers - Precision Transducer Engineering
... Music contains many frequencies simultaneously. In the passive system the power amplifier must produce all of these, while in the active system the load is shared between two amplifiers. I note here that there will be much less intermodulation distortion in the active speaker’s amplifiers. The stand ...
... Music contains many frequencies simultaneously. In the passive system the power amplifier must produce all of these, while in the active system the load is shared between two amplifiers. I note here that there will be much less intermodulation distortion in the active speaker’s amplifiers. The stand ...
EL6413 Catalog Description
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
Lecture 1 - Digilent Learn site
... absolutely remove all components outside the passband. • Also point out that these cannot be implemented in the real world (turns out that they would need to respond to the input before the input is applied – they need to see into the future) ...
... absolutely remove all components outside the passband. • Also point out that these cannot be implemented in the real world (turns out that they would need to respond to the input before the input is applied – they need to see into the future) ...
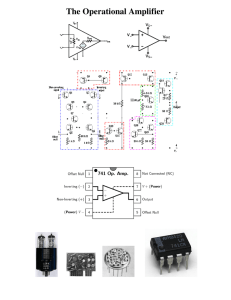
The Operational Amplifier
... - Which Op-Amp design would you choose Non-Inverting or Inverting, what will be the difference - What will be the significance if the input impedance is low? - Design an Op Amp to reach line level voltages - How would you use your 10k resistors to get the desired values - Series or Parallel connect ...
... - Which Op-Amp design would you choose Non-Inverting or Inverting, what will be the difference - What will be the significance if the input impedance is low? - Design an Op Amp to reach line level voltages - How would you use your 10k resistors to get the desired values - Series or Parallel connect ...
In this project, you are going to design an active Low
... A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a certain cut-off frequency and preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter ...
... A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a certain cut-off frequency and preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter ...
Signal Processing revision notes
... Most noise in digital filters is caused by rounding errors. Multiplications in filters increase the wordlength, but at some point this must be rounded off. The rounding only usually affects the recursive part of the filter and is coloured by it. This can be avoided by applying a noise shaping techni ...
... Most noise in digital filters is caused by rounding errors. Multiplications in filters increase the wordlength, but at some point this must be rounded off. The rounding only usually affects the recursive part of the filter and is coloured by it. This can be avoided by applying a noise shaping techni ...
(minimum-delay or zero
... Calibration of Digitizers Digitizers normally don’t need to be calibrated if the manufacturer’s specifications are clear and complete. You may want to check the scale factor, normally in microvolts per count, by connecting a battery and a digital voltmeter to the input. Forget about the filter coef ...
... Calibration of Digitizers Digitizers normally don’t need to be calibrated if the manufacturer’s specifications are clear and complete. You may want to check the scale factor, normally in microvolts per count, by connecting a battery and a digital voltmeter to the input. Forget about the filter coef ...
ee221_3
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
HFAM - 26 - Photonic Solutions
... Detector Overload Current (Imax, please specify) Detector Overload Warning Current Warning Response Time ...
... Detector Overload Current (Imax, please specify) Detector Overload Warning Current Warning Response Time ...
The Response of Measuring Systems
... In contrast to the filter, a well-designed sensor or transducer should respond to all frequencies equally. Unfortunately, most actual sensors and transducers do not. Instead, such devices are characterized by an upper or lower frequency beyond which response is attenuated (much like a filter) or by ...
... In contrast to the filter, a well-designed sensor or transducer should respond to all frequencies equally. Unfortunately, most actual sensors and transducers do not. Instead, such devices are characterized by an upper or lower frequency beyond which response is attenuated (much like a filter) or by ...
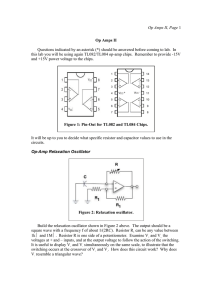
Op Amps II
... versus ωτ for four different values of x. It can be shown (you do not have to do this) that ...
... versus ωτ for four different values of x. It can be shown (you do not have to do this) that ...
Audio crossover

Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and absence of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a combination of multiple loudspeaker drivers, each catering to a different frequency band. Crossovers split the audio signal into separate frequency bands that can be separately routed to loudspeakers optimized for those bands.Active crossovers are distinguished from passive crossovers in that they divide the audio signal prior to amplification. Active crossovers come in both digital and analog varieties. Digital active crossovers often include additional signal processing, such as limiting, delay, and equalization.Signal crossovers allow the audio signal to be split into bands that are processed separately before they are mixed together again. Some examples are: multiband dynamics (compression, limiting, de-essing), multiband distortion, bass enhancement, high frequency exciters, and noise reduction such as Dolby A noise reduction.