Chapter 5 Low-Noise Design Methodology
... • The diode current then consists of a constant component I, due to the local oscillator, and a small component i, due to the input signal. The diode current is described by iD I s exp Vd / VT where Vd is the voltage drop across the diode and VT=kT/q • The input signal Vi causes a signal curre ...
... • The diode current then consists of a constant component I, due to the local oscillator, and a small component i, due to the input signal. The diode current is described by iD I s exp Vd / VT where Vd is the voltage drop across the diode and VT=kT/q • The input signal Vi causes a signal curre ...
AND8026/D Solving EMI and ESD Problems with Integrated Passive
... Figure 9. Measurement Conditions Cut–off (f–3dB) Frequency ...
... Figure 9. Measurement Conditions Cut–off (f–3dB) Frequency ...
LC Quadrature Generation in Integrated Circuits
... Figure 3. Symmetrical resistance reciprocal network Allpass filters can be realized in a number of different manners. These include single ended LC networks using ideal transformers or center tapped inductors, active circuits exploiting negative feedback and symmetrical cross coupled resistance reci ...
... Figure 3. Symmetrical resistance reciprocal network Allpass filters can be realized in a number of different manners. These include single ended LC networks using ideal transformers or center tapped inductors, active circuits exploiting negative feedback and symmetrical cross coupled resistance reci ...
SGL0622Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
Problems to resolve:
... deal with this in the short term would be to get the programming kit in and samples, and program our parameters into the part via EEPROM. If we could rig in the new part in place of the old (and disconnect the 3-wire interface that previously controlled it), via white wires, etc. then we could demon ...
... deal with this in the short term would be to get the programming kit in and samples, and program our parameters into the part via EEPROM. If we could rig in the new part in place of the old (and disconnect the 3-wire interface that previously controlled it), via white wires, etc. then we could demon ...
A Review of Digital Techniques for Modeling Vacuum
... professional guitar amplifiers. A major reason for this is that electric-guitar amplifiers are typically overdriven, that is, operated in such a way that the output saturates. Vacuum tubes distort the signal in a different manner compared to solid-state electronics, and human listeners tend to prefe ...
... professional guitar amplifiers. A major reason for this is that electric-guitar amplifiers are typically overdriven, that is, operated in such a way that the output saturates. Vacuum tubes distort the signal in a different manner compared to solid-state electronics, and human listeners tend to prefe ...
WAN_0209 Wolfson Frequency Locked Loop
... output as the system clock. Some devices support automatic configuration of the FLL, where a single register is set according to the FLL input reference frequency only. Other devices require the frequency ratios to be commanded using a small number of control registers. It is important that the FLL ...
... output as the system clock. Some devices support automatic configuration of the FLL, where a single register is set according to the FLL input reference frequency only. Other devices require the frequency ratios to be commanded using a small number of control registers. It is important that the FLL ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... The differential difference current conveyors (DDCC) [1] or differential voltage current conveyors (DVCC) [2] have received considerable attention due to they enjoy the advantages of second-generation current conveyor (CCII) and differential difference amplifier (DDA) such as larger signal bandwidth ...
... The differential difference current conveyors (DDCC) [1] or differential voltage current conveyors (DVCC) [2] have received considerable attention due to they enjoy the advantages of second-generation current conveyor (CCII) and differential difference amplifier (DDA) such as larger signal bandwidth ...
AD8072
... outputs of each amplifier swing to within 1.3 volts of either supply rail to accommodate video signals on a single 5 V supply. The high bandwidth of 100 MHz, 500 V/µs of slew rate, along with settling to 0.1% in 25 ns, make the AD8072 and AD8073 useful in many general purpose, high speed application ...
... outputs of each amplifier swing to within 1.3 volts of either supply rail to accommodate video signals on a single 5 V supply. The high bandwidth of 100 MHz, 500 V/µs of slew rate, along with settling to 0.1% in 25 ns, make the AD8072 and AD8073 useful in many general purpose, high speed application ...
1E6 Electricity and Magnetism
... this can generate heat. For high power applications means of cooling the amplifier may be required. ...
... this can generate heat. For high power applications means of cooling the amplifier may be required. ...
SiGe BiCMOS LNA`S AND TUNABLE ACTIVE FILTER FOR
... Due to the mere fact that the single-stage LNA does not provide a sufficiently high gain at frequencies above X-band we have also designed a two-stage cascaded CE based LNA (see Fig. 2a for circuit schematic). In this design the first stage (stage 1) is designed for low noise and the second stage (s ...
... Due to the mere fact that the single-stage LNA does not provide a sufficiently high gain at frequencies above X-band we have also designed a two-stage cascaded CE based LNA (see Fig. 2a for circuit schematic). In this design the first stage (stage 1) is designed for low noise and the second stage (s ...
MAX442 - elektrOnline
... To prevent oscillation and unwanted signal coupling, minimize trace area at the circuit’s critical high-impedance nodes, especially the amplifier summing junction (the amplifier’s inverting input). Surround these critical nodes with a ground trace, and include ground traces between all signal traces ...
... To prevent oscillation and unwanted signal coupling, minimize trace area at the circuit’s critical high-impedance nodes, especially the amplifier summing junction (the amplifier’s inverting input). Surround these critical nodes with a ground trace, and include ground traces between all signal traces ...
Filters and Impedance Matching
... E7B07 -- Which of the following is a likely result when a Class C amplifier is used to amplify a single-sideband phone signal? A. Reduced intermodulation products B. Increased overall intelligibility C. Signal inversion D. Signal distortion and excessive bandwidth ...
... E7B07 -- Which of the following is a likely result when a Class C amplifier is used to amplify a single-sideband phone signal? A. Reduced intermodulation products B. Increased overall intelligibility C. Signal inversion D. Signal distortion and excessive bandwidth ...
4.2.3 – Resonant Filters
... both inductors and capacitors. Inductors also have a small resistance from the wire used to make the coil. The formula will always give a value of resonant frequency slightly higher than the actual value as the formula assumes that rL is negligible. In practice rL effectively lowers the resonant fre ...
... both inductors and capacitors. Inductors also have a small resistance from the wire used to make the coil. The formula will always give a value of resonant frequency slightly higher than the actual value as the formula assumes that rL is negligible. In practice rL effectively lowers the resonant fre ...
Section H7: Frequency Response of Op-Amp Circuits
... fed back to the input in phase with the input. This changes the feedback mechanism from negative to positive (which we will get into in the next section) and the amplifier may become unstable or marginally stable (in the marginally stable case, it exhibits behavioral characteristics of an oscillator ...
... fed back to the input in phase with the input. This changes the feedback mechanism from negative to positive (which we will get into in the next section) and the amplifier may become unstable or marginally stable (in the marginally stable case, it exhibits behavioral characteristics of an oscillator ...
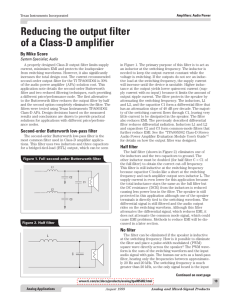
Reducing the output filter of a Class-D amplifier
... Class-D with half filter Class-D with a half filter had a lower quiescent current and performed as good as or better than the Class-D with full filter in THD+N and IMD. The quiescent current lowers as the inductor of the half filter increases. As inductance increases, peaking occurs at the corner fr ...
... Class-D with half filter Class-D with a half filter had a lower quiescent current and performed as good as or better than the Class-D with full filter in THD+N and IMD. The quiescent current lowers as the inductor of the half filter increases. As inductance increases, peaking occurs at the corner fr ...
Audio crossover

Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and absence of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a combination of multiple loudspeaker drivers, each catering to a different frequency band. Crossovers split the audio signal into separate frequency bands that can be separately routed to loudspeakers optimized for those bands.Active crossovers are distinguished from passive crossovers in that they divide the audio signal prior to amplification. Active crossovers come in both digital and analog varieties. Digital active crossovers often include additional signal processing, such as limiting, delay, and equalization.Signal crossovers allow the audio signal to be split into bands that are processed separately before they are mixed together again. Some examples are: multiband dynamics (compression, limiting, de-essing), multiband distortion, bass enhancement, high frequency exciters, and noise reduction such as Dolby A noise reduction.