Geometry Vocabulary
... dimension one, a plane dimension two, and space dimension three. The points of n-dimensional space have n coordinates ( x1, x2 , …, xn ). ...
... dimension one, a plane dimension two, and space dimension three. The points of n-dimensional space have n coordinates ( x1, x2 , …, xn ). ...
Triangles in Hyperbolic Geometry
... It took a long time for people to accept the existence of a Non-Euclidean geometry, particularly because of the strong belief in Kantian philosophy in the late 18th and early 19th century. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) believed that geometry, because it existed in space, was an absolute science. He beli ...
... It took a long time for people to accept the existence of a Non-Euclidean geometry, particularly because of the strong belief in Kantian philosophy in the late 18th and early 19th century. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) believed that geometry, because it existed in space, was an absolute science. He beli ...
Chapter 4
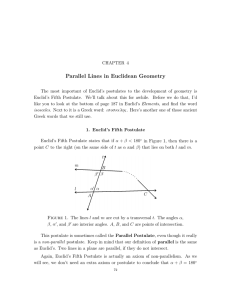
... Let a be any line and A a point not on it. Then there is at most one line in the plane, determined by a and A, that passes through A and does not intersect a. This is pretty much the same as Euclid’s Fifth Postulate, which states that for all cases except when α + β = 180◦ the lines are not parallel ...
... Let a be any line and A a point not on it. Then there is at most one line in the plane, determined by a and A, that passes through A and does not intersect a. This is pretty much the same as Euclid’s Fifth Postulate, which states that for all cases except when α + β = 180◦ the lines are not parallel ...
Algebraic geometry

Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics, classically studying zeros of multivariate polynomials. Modern algebraic geometry is based on the use of abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, for solving geometrical problems about these sets of zeros.The fundamental objects of study in algebraic geometry are algebraic varieties, which are geometric manifestations of solutions of systems of polynomial equations. Examples of the most studied classes of algebraic varieties are: plane algebraic curves, which include lines, circles, parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, cubic curves like elliptic curves and quartic curves like lemniscates, and Cassini ovals. A point of the plane belongs to an algebraic curve if its coordinates satisfy a given polynomial equation. Basic questions involve the study of the points of special interest like the singular points, the inflection points and the points at infinity. More advanced questions involve the topology of the curve and relations between the curves given by different equations.Algebraic geometry occupies a central place in modern mathematics and has multiple conceptual connections with such diverse fields as complex analysis, topology and number theory. Initially a study of systems of polynomial equations in several variables, the subject of algebraic geometry starts where equation solving leaves off, and it becomes even more important to understand the intrinsic properties of the totality of solutions of a system of equations, than to find a specific solution; this leads into some of the deepest areas in all of mathematics, both conceptually and in terms of technique.In the 20th century, algebraic geometry has split into several subareas. The main stream of algebraic geometry is devoted to the study of the complex points of the algebraic varieties and more generally to the points with coordinates in an algebraically closed field. The study of the points of an algebraic variety with coordinates in the field of the rational numbers or in a number field became arithmetic geometry (or more classically Diophantine geometry), a subfield of algebraic number theory. The study of the real points of an algebraic variety is the subject of real algebraic geometry. A large part of singularity theory is devoted to the singularities of algebraic varieties. With the rise of the computers, a computational algebraic geometry area has emerged, which lies at the intersection of algebraic geometry and computer algebra. It consists essentially in developing algorithms and software for studying and finding the properties of explicitly given algebraic varieties.Much of the development of the main stream of algebraic geometry in the 20th century occurred within an abstract algebraic framework, with increasing emphasis being placed on ""intrinsic"" properties of algebraic varieties not dependent on any particular way of embedding the variety in an ambient coordinate space; this parallels developments in topology, differential and complex geometry. One key achievement of this abstract algebraic geometry is Grothendieck's scheme theory which allows one to use sheaf theory to study algebraic varieties in a way which is very similar to its use in the study of differential and analytic manifolds. This is obtained by extending the notion of point: In classical algebraic geometry, a point of an affine variety may be identified, through Hilbert's Nullstellensatz, with a maximal ideal of the coordinate ring, while the points of the corresponding affine scheme are all prime ideals of this ring. This means that a point of such a scheme may be either a usual point or a subvariety. This approach also enables a unification of the language and the tools of classical algebraic geometry, mainly concerned with complex points, and of algebraic number theory. Wiles's proof of the longstanding conjecture called Fermat's last theorem is an example of the power of this approach.








![arXiv:0706.3441v1 [math.AG] 25 Jun 2007](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017784481_1-dd1160ad974ad834977ad61a663d12c3-300x300.png)