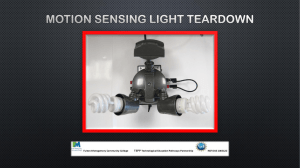
Product Sheet MKV-D1X-15-75
... Rated Urms (V): 750 Rated voltage UN (V): 1060 Voltage UNDC (V): 1400 Peak voltage Us (V): 2100 Max current (Arms): 31 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,5 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,8 Self inductance (nH): 120 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 137 Weight (kg): 820 Creepage between term ...
... Rated Urms (V): 750 Rated voltage UN (V): 1060 Voltage UNDC (V): 1400 Peak voltage Us (V): 2100 Max current (Arms): 31 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,5 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,8 Self inductance (nH): 120 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 137 Weight (kg): 820 Creepage between term ...
Brochure
... which the voltage stability of the system is to be evaluated. This is achieved by scaling up all the loads in user-defined steps for a given network, base case and all defined contingencies, either by bus, areas, zones or globally. The steady-state P-V approach dictates that for each load increase, ...
... which the voltage stability of the system is to be evaluated. This is achieved by scaling up all the loads in user-defined steps for a given network, base case and all defined contingencies, either by bus, areas, zones or globally. The steady-state P-V approach dictates that for each load increase, ...
2-port EtherCAT P junction with feed-in
... The 2-port EK1322 EtherCAT P junction enables configuration of EtherCAT P star topologies. The ports can be used to connect individual EtherCAT P devices or whole EtherCAT P strands. The EK1322 can be installed at any point in an EtherCAT strand between the EtherCAT Terminals (ELxxxx). The front ter ...
... The 2-port EK1322 EtherCAT P junction enables configuration of EtherCAT P star topologies. The ports can be used to connect individual EtherCAT P devices or whole EtherCAT P strands. The EK1322 can be installed at any point in an EtherCAT strand between the EtherCAT Terminals (ELxxxx). The front ter ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
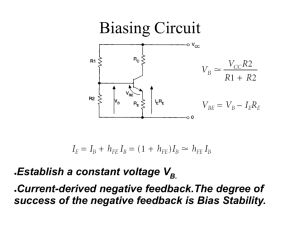
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
Physics_A2_37_GeneratingElectricity
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
IRP Presentation - Iowa State University
... turbine, as well as a RPM sensor that may be used for a plethora of different projects in the future. Our only objective that we expected to deliver upon and failed was the full utilization of available wind power. Throughout this semester, many different solutions for this problem were brought up, ...
... turbine, as well as a RPM sensor that may be used for a plethora of different projects in the future. Our only objective that we expected to deliver upon and failed was the full utilization of available wind power. Throughout this semester, many different solutions for this problem were brought up, ...
Aim: The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential
... Note: An error known as ’zero error’ is present in some differential transformer i.e. a nonzero reading at the null position. The main reasons for the zero error are non-uniformities in the windings, harmonic components in the primary signal, and non linearity in the device. The LVDT is a transduce ...
... Note: An error known as ’zero error’ is present in some differential transformer i.e. a nonzero reading at the null position. The main reasons for the zero error are non-uniformities in the windings, harmonic components in the primary signal, and non linearity in the device. The LVDT is a transduce ...
plans - Warren Mar
... diodes, convert the AC into bumps, which gets smoothed out by large capacitors. This smoothed out bumping signal then gets further regulated into a stable supply. Noise in the power supply can couple into noise in the output. A stable power supply is a must. A dual-polarity power supply will give us ...
... diodes, convert the AC into bumps, which gets smoothed out by large capacitors. This smoothed out bumping signal then gets further regulated into a stable supply. Noise in the power supply can couple into noise in the output. A stable power supply is a must. A dual-polarity power supply will give us ...
- Emicro Technologies
... there are enormous applications of there in FACTS and industrial drives etc., Although there are many topologies of multilevel inverters in literature, popular among them are cascaded H-bridge. In general the control methods of these cascaded inverters are designed an assumption of having all dc sou ...
... there are enormous applications of there in FACTS and industrial drives etc., Although there are many topologies of multilevel inverters in literature, popular among them are cascaded H-bridge. In general the control methods of these cascaded inverters are designed an assumption of having all dc sou ...
Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... voltages. A cost function is chosen for the selection of the appropriate switching state such that the square of error between the actual and reference voltages is minimized. Simulation and experimental results confirm the feasibility and usefulness of the proposed scheme. ...
... voltages. A cost function is chosen for the selection of the appropriate switching state such that the square of error between the actual and reference voltages is minimized. Simulation and experimental results confirm the feasibility and usefulness of the proposed scheme. ...
Dynamic Volt-Amp Reactive (D-VAR®) Compensation
... D-VAR systems stabilize and regulate voltage and power factor on T&D networks and at industrial operations. The system detects and rapidly compensates for voltage disturbances by injecting leading or lagging reactive power at key points on transmission and distribution grids. Each D-VAR solution is ...
... D-VAR systems stabilize and regulate voltage and power factor on T&D networks and at industrial operations. The system detects and rapidly compensates for voltage disturbances by injecting leading or lagging reactive power at key points on transmission and distribution grids. Each D-VAR solution is ...
Download T2100 Datasheet
... excitation in a synchronous generator. T2100 detects the high-inductive current running into a generator in case of low excitation. The faulty generator breaker is tripped, thus protecting the generator, and avoiding undervoltage on the busbar with a possible blackout of the system. The T2100 calcul ...
... excitation in a synchronous generator. T2100 detects the high-inductive current running into a generator in case of low excitation. The faulty generator breaker is tripped, thus protecting the generator, and avoiding undervoltage on the busbar with a possible blackout of the system. The T2100 calcul ...
Voltage/current dividers
... Referring back to the original circuit, iR13 divides between R2 and R3. ...
... Referring back to the original circuit, iR13 divides between R2 and R3. ...
CT-CATVPS60/90 CATV Power Supply 60/90VAC, 15A
... The CableTronix CT-CATVPS60/90 is a CATV power supply designed to provide conditioned power to remote active devices over a hardline CATV cable distribution plant. This unit is designed to work with either 120VAC or 220VAC input voltages with a 60VAC or 90VAC selectable output. The enclosure is buil ...
... The CableTronix CT-CATVPS60/90 is a CATV power supply designed to provide conditioned power to remote active devices over a hardline CATV cable distribution plant. This unit is designed to work with either 120VAC or 220VAC input voltages with a 60VAC or 90VAC selectable output. The enclosure is buil ...
EGN 3373 Week 4 – Caps and Ind Explained - Help-A-Bull
... Capacitors in parallel Capacitors in a parallel configuration each have the same applied voltage. Their capacitances are added. Charge is apportioned among them by size. ...
... Capacitors in parallel Capacitors in a parallel configuration each have the same applied voltage. Their capacitances are added. Charge is apportioned among them by size. ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).