Domain 4: Waves, Electricity, and Magnetism
... If one bulb in circuit A goes out, what happens to the other? If one bulb in circuit B goes out, what happens to the other? If I add a 3rd bulb to circuit A, what happens to the brightness of the other two? If I add a 3rd bulb to circuit B, what happens to the brightness of the other two? ...
... If one bulb in circuit A goes out, what happens to the other? If one bulb in circuit B goes out, what happens to the other? If I add a 3rd bulb to circuit A, what happens to the brightness of the other two? If I add a 3rd bulb to circuit B, what happens to the brightness of the other two? ...
Inteli-PowerTM
... for Positive and Negative outputs are provided as are permanent, “organ appropriate” mounting provisions. A three foot line cord can plug into a Peterson Console AC Control System* or Single Outlet Control Box for conveniently switching the power supply on and off. An external chassis grounding term ...
... for Positive and Negative outputs are provided as are permanent, “organ appropriate” mounting provisions. A three foot line cord can plug into a Peterson Console AC Control System* or Single Outlet Control Box for conveniently switching the power supply on and off. An external chassis grounding term ...
ExIIrev05ans
... B: The electric field might be zero, or it might be non-zero and perpendicular to the line ab. D: The electric field can vary along the line ab, but it must have the same value at points a and b. E: You can conclude absolutely nothing about the electric field. Answer: The electric field might be zer ...
... B: The electric field might be zero, or it might be non-zero and perpendicular to the line ab. D: The electric field can vary along the line ab, but it must have the same value at points a and b. E: You can conclude absolutely nothing about the electric field. Answer: The electric field might be zer ...
Presentation - IEEE Standards working groups
... • 6.3.1.1 Hand Held Detector • 6.3.1.2 Mobile E-field Detector • 6.3.1.3 Hand Held E-field Detector • 6.3.1.4 Voltmeter • 6.3.1.5 Ground Lead • 6.3.1.6 Switchable Shunt Resistor • 6.3.1.7 Ground Rod • 6.3.2 Safety Equipment ...
... • 6.3.1.1 Hand Held Detector • 6.3.1.2 Mobile E-field Detector • 6.3.1.3 Hand Held E-field Detector • 6.3.1.4 Voltmeter • 6.3.1.5 Ground Lead • 6.3.1.6 Switchable Shunt Resistor • 6.3.1.7 Ground Rod • 6.3.2 Safety Equipment ...
RC Time Constant
... The maximal frequency we can transmit through this "wire " then would be νmax = 1/RC = 1.36 GHz. This may appear a bit "handwaving" or just a rough estimation; nevertheless, the problem should be clear. On a real chip, signals travel through many wires; possibly far shorter then 1 cm, and possibly n ...
... The maximal frequency we can transmit through this "wire " then would be νmax = 1/RC = 1.36 GHz. This may appear a bit "handwaving" or just a rough estimation; nevertheless, the problem should be clear. On a real chip, signals travel through many wires; possibly far shorter then 1 cm, and possibly n ...
Lesson 13
... vibration results in more collisions between the atoms and the free-flowing electrons in the current. Since greater vibrations cause more collisions, resistance increases with temperature. • type of material: depends on the material’s conductivity. Conductivity up, resistance down. ...
... vibration results in more collisions between the atoms and the free-flowing electrons in the current. Since greater vibrations cause more collisions, resistance increases with temperature. • type of material: depends on the material’s conductivity. Conductivity up, resistance down. ...
Chapter 17 & 18
... Breakers are switches that automatically open with the current is too high. If there is not a connection, current cannot flow. Therefore it prevents electrical fires as well. 30. How are loads connected in a series circuit? In a single loop or straight line. ...
... Breakers are switches that automatically open with the current is too high. If there is not a connection, current cannot flow. Therefore it prevents electrical fires as well. 30. How are loads connected in a series circuit? In a single loop or straight line. ...
Week 2
... These are true RMS to DC converters. This will convert the input signals into a DC waveform which will be fed to the computer for data analysis. There are 2 TRMS in the circuit because one will be the voltage coming out from the crystal and the other will be the input current of crystal. TRM 1 has a ...
... These are true RMS to DC converters. This will convert the input signals into a DC waveform which will be fed to the computer for data analysis. There are 2 TRMS in the circuit because one will be the voltage coming out from the crystal and the other will be the input current of crystal. TRM 1 has a ...
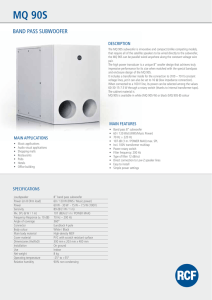
MQ 90S
... that require all of the satellite speakers to be wired directly to the subwoofer, the MQ 90S can be parallel wired anywhere along the constant voltage wire pair. The high power transducer is a unique 8” woofer design that achieves truly impressive performance for its size when matched with the speci ...
... that require all of the satellite speakers to be wired directly to the subwoofer, the MQ 90S can be parallel wired anywhere along the constant voltage wire pair. The high power transducer is a unique 8” woofer design that achieves truly impressive performance for its size when matched with the speci ...
Solved_Problems_to_Chapter_11
... 11.5 An a.c. full-wave voltage controller operating in integral cycle mode feeds a resistive load of 10W from a single phase a.c. voltage source related at 230 V, 50 Hz. The thyristor switch is ON for 25 cycles followed by 75 cycles of extinction period. Determine: (a) rms value of load voltage and ...
... 11.5 An a.c. full-wave voltage controller operating in integral cycle mode feeds a resistive load of 10W from a single phase a.c. voltage source related at 230 V, 50 Hz. The thyristor switch is ON for 25 cycles followed by 75 cycles of extinction period. Determine: (a) rms value of load voltage and ...
START-DET PMT-Base-H..
... Therefore, this number is to be used as a figure of merit of what is the accuracy of this setup. The leakage current presented in figure 4 also includes the leaks in the SHV connectors, RG59 cables and other components of the setup. The uncertainty introduced by the additional leakage currents due t ...
... Therefore, this number is to be used as a figure of merit of what is the accuracy of this setup. The leakage current presented in figure 4 also includes the leaks in the SHV connectors, RG59 cables and other components of the setup. The uncertainty introduced by the additional leakage currents due t ...
IMT4
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
BJT and MOS Class AB Output Stages: Comparison and
... In case of constant bias current from M3, the LHS is constant, so increasing Vgs1 decreases Vsg2 and vice versa. ...
... In case of constant bias current from M3, the LHS is constant, so increasing Vgs1 decreases Vsg2 and vice versa. ...
here
... Electric circuits: the need for a complete circuit, electrical symbols (battery, cell, switch, fuse, voltmeter, ammeter, resistor, filament lamp), current, voltage, resistance, construct simple series and parallel circuits, measure current and voltage using meters, use the equation: V = IR, direct c ...
... Electric circuits: the need for a complete circuit, electrical symbols (battery, cell, switch, fuse, voltmeter, ammeter, resistor, filament lamp), current, voltage, resistance, construct simple series and parallel circuits, measure current and voltage using meters, use the equation: V = IR, direct c ...
AEEE531CO
... The lecturer introduces the computer simulation software through illustrations in the class room and the students using the knowledge gained, having the assistance of the lecturer familiarise themselves with the software. Furthermore as this subject combines knowledge from many areas of power system ...
... The lecturer introduces the computer simulation software through illustrations in the class room and the students using the knowledge gained, having the assistance of the lecturer familiarise themselves with the software. Furthermore as this subject combines knowledge from many areas of power system ...
DTB143TK
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).