SolarEdge Three Phase Inverters for
... P/N of inverter with automatic rapid shutdown: SE33.3K-USR48NNF4 ...
... P/N of inverter with automatic rapid shutdown: SE33.3K-USR48NNF4 ...
Transformer problems (Due Tuesday 25th March (PAYDAY
... EASY (10 points) A transformer has 10 turns on its primary coil and 30 turns on the secondary. 1. If the primary voltage is 2 V, what is the secondary voltage? 2. A transformer has 20 turns on the primary coil and 2 turns on the secondary. If the primary voltage is 100 V, what is the secondary volta ...
... EASY (10 points) A transformer has 10 turns on its primary coil and 30 turns on the secondary. 1. If the primary voltage is 2 V, what is the secondary voltage? 2. A transformer has 20 turns on the primary coil and 2 turns on the secondary. If the primary voltage is 100 V, what is the secondary volta ...
1E6 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING [5 credits]
... Module description, aims and contribution to programme This is a one semester module which intends to impart a basic understanding of the concepts and laws of electricity and magnetism to Junior Freshman Engineering students. Fundamental laws will be established from physical principles and then use ...
... Module description, aims and contribution to programme This is a one semester module which intends to impart a basic understanding of the concepts and laws of electricity and magnetism to Junior Freshman Engineering students. Fundamental laws will be established from physical principles and then use ...
Circuit Components
... A component must be considered as distributed when the physical dimensions of an element become significant with respect to the propagation time of a signal across the element A component can be considered as lumped when the physical dimensions of the component are of little significance. Assuming l ...
... A component must be considered as distributed when the physical dimensions of an element become significant with respect to the propagation time of a signal across the element A component can be considered as lumped when the physical dimensions of the component are of little significance. Assuming l ...
LAB 3 Basic CMOS Inverter
... Lab 2: The CMOS Inverter This lab shows the basic layout and electrical characteristics of the CMOS inverter which is the fundamental component of integrated MOS logic circuits. 1 Get a copy of the hand-out, Design of a CMOS Inverter. The instructions in this hand-out are from an older version of th ...
... Lab 2: The CMOS Inverter This lab shows the basic layout and electrical characteristics of the CMOS inverter which is the fundamental component of integrated MOS logic circuits. 1 Get a copy of the hand-out, Design of a CMOS Inverter. The instructions in this hand-out are from an older version of th ...
Chapter 22 Outline
... A battery, in the form of DC AC powers most of our lights and household appliances through wall outlets. ...
... A battery, in the form of DC AC powers most of our lights and household appliances through wall outlets. ...
RG2 Recessed Gimball Emergency Light
... Perfect for commercial or architectural applications where the aesthetics of a fully recessed unit are essential. The slim profile of the RG Series is ideal for low ceilings and blends inconspicuously with existing recessed installations. The gimbal mounted lamp provides directional aiming (optional ...
... Perfect for commercial or architectural applications where the aesthetics of a fully recessed unit are essential. The slim profile of the RG Series is ideal for low ceilings and blends inconspicuously with existing recessed installations. The gimbal mounted lamp provides directional aiming (optional ...
So how does an electricity generator work
... An electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, a scientific law that was discovered by British scientist Michael Faraday and American scientist Joseph Henry in 1831. The principle states that when an electric conduc ...
... An electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, a scientific law that was discovered by British scientist Michael Faraday and American scientist Joseph Henry in 1831. The principle states that when an electric conduc ...
Physical Science Test Electromagnetism Multiple Choice 1
... 1. Materials that allow the charges of an electric current to move freely through them are called A. conductors. B. resistors. C. insulators. D. magnets. 2. According to Ohm’s law, what is the resistance of a light if the voltage is 9.0 volts and the current is 0.30 amps? A. 2.7 ohms. B. 30 ohms. C. ...
... 1. Materials that allow the charges of an electric current to move freely through them are called A. conductors. B. resistors. C. insulators. D. magnets. 2. According to Ohm’s law, what is the resistance of a light if the voltage is 9.0 volts and the current is 0.30 amps? A. 2.7 ohms. B. 30 ohms. C. ...
Technology Selection - Sunrator Technologies LLP
... voltage levels for transmission across the site and export to the grid. Transformers can also loose energy through magnetising currents in the core. These losses are known as iron and cooper losses. Minimising the losses will increase the energy supplied to the grid and thus enhance the revenue of t ...
... voltage levels for transmission across the site and export to the grid. Transformers can also loose energy through magnetising currents in the core. These losses are known as iron and cooper losses. Minimising the losses will increase the energy supplied to the grid and thus enhance the revenue of t ...
Design Note - Texas Instruments
... The Single Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC) can convert an input voltage to an output voltage that is higher, lower or equal to the input. Conversion is performed without the use of expensive transformers, making this a good choice for low cost, non-isolated applications. The UC2577 provid ...
... The Single Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC) can convert an input voltage to an output voltage that is higher, lower or equal to the input. Conversion is performed without the use of expensive transformers, making this a good choice for low cost, non-isolated applications. The UC2577 provid ...
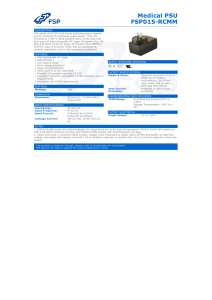
Medical PSU FSP015-RCMM
... Medical PSU FSP015-RCMM DESCRIPTION This series of AC /DC wall mount switching power supplies are for 15 watts of continuous output power. They are enclosed in a 94V-1 rated polyphenylene-oxide case with four types of interchangeable AC plugs: European plug, UK plug and North American plugs. All mod ...
... Medical PSU FSP015-RCMM DESCRIPTION This series of AC /DC wall mount switching power supplies are for 15 watts of continuous output power. They are enclosed in a 94V-1 rated polyphenylene-oxide case with four types of interchangeable AC plugs: European plug, UK plug and North American plugs. All mod ...
Transformers - Sackville School
... on each side of a transformer by the following equation: primary voltage secondary voltage ...
... on each side of a transformer by the following equation: primary voltage secondary voltage ...
BLTC-I Cutsheet
... shunt device. It is designed to allow switching of designated Non-Dimmed emergency lighting fixtures. The BLTC - I contains low voltage circuitry to safely bypass and shunt switches and relays in the event of a power failure thus providing the emergency lighting power access to alternate power syste ...
... shunt device. It is designed to allow switching of designated Non-Dimmed emergency lighting fixtures. The BLTC - I contains low voltage circuitry to safely bypass and shunt switches and relays in the event of a power failure thus providing the emergency lighting power access to alternate power syste ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).




![1E6 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING [5 credits]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008172045_1-b416785fd6305cc783c87ea745442b53-300x300.png)