Name________________________________ STUDY GUIDE FOR
... The Egyptian religion was based on a belief in the afterlife. To prepare for this, a body was mummified to protect it from decay. Many everyday objects went into the tomb along with the body, including food, drink, jewelry, and games. Egyptians were polytheistic, believing in many gods, such as Osir ...
... The Egyptian religion was based on a belief in the afterlife. To prepare for this, a body was mummified to protect it from decay. Many everyday objects went into the tomb along with the body, including food, drink, jewelry, and games. Egyptians were polytheistic, believing in many gods, such as Osir ...
скачати
... Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous machine that helps the king go through the wall of the dead, achieve resurrection and live forever in the happiness of ...
... Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous machine that helps the king go through the wall of the dead, achieve resurrection and live forever in the happiness of ...
Ancient Egypt A Time Of The Pyramid
... Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous machine that helps the king go through the wall of the dead, achieve resurrection and live forever in the happiness of ...
... Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous machine that helps the king go through the wall of the dead, achieve resurrection and live forever in the happiness of ...
New Kingdom: Pharaohs King Tut Tutankhamun was nine years old
... Thutmose III was the sixth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. During the first twenty-two years of Thutmose's reign he was co-regent with his aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh. While she is shown first on surviving monuments, both were assigned the usual royal names and insignia and neithe ...
... Thutmose III was the sixth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. During the first twenty-two years of Thutmose's reign he was co-regent with his aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh. While she is shown first on surviving monuments, both were assigned the usual royal names and insignia and neithe ...
Notes Ancient Egypt - Mr. Meier`s Daily Class Info
... -to begin with Egypt had little chance to defeat the Hittites because Egypt had Bronze and Hittites had Iron AND Hittites had 3 man chariots -the Hittites did break through Egyptian lines and did surround Ramses and a small group of ...
... -to begin with Egypt had little chance to defeat the Hittites because Egypt had Bronze and Hittites had Iron AND Hittites had 3 man chariots -the Hittites did break through Egyptian lines and did surround Ramses and a small group of ...
Document
... • Those responsible for creation were the most important gods (Atum is the creator God) • They later developed national gods around the Middle Kingdom (Amon- local god of Thebes; gods of Dead: Osiris, Anubis, Horus and Thoth) ...
... • Those responsible for creation were the most important gods (Atum is the creator God) • They later developed national gods around the Middle Kingdom (Amon- local god of Thebes; gods of Dead: Osiris, Anubis, Horus and Thoth) ...
Ancient Egypt Vocabulary
... 4. Pharaoh-the title used by the rulers of Egypt. 5. Dynasty-a series of rulers form the same family. 6. Old kingdom-the period from about 2700 to 2200 BC in Egyptian history that began shortly after Egypt was unified. 7. Khufu-Egyptian pharaoh, he ruled during Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is known for t ...
... 4. Pharaoh-the title used by the rulers of Egypt. 5. Dynasty-a series of rulers form the same family. 6. Old kingdom-the period from about 2700 to 2200 BC in Egyptian history that began shortly after Egypt was unified. 7. Khufu-Egyptian pharaoh, he ruled during Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is known for t ...
Egypt_Notes - Groupfusion.net
... What happened in each kingdom Understand the geography of Ancient Egypt - Upper and Lower Egypt - The Nile River - Where the best farming was located ...
... What happened in each kingdom Understand the geography of Ancient Egypt - Upper and Lower Egypt - The Nile River - Where the best farming was located ...
Life in Ancient Egypt - 6th Grade Social Studies
... balanced with a divine feather. The scale weighed your good and 700 gods and goddesses, in fact. The most important god bad deeds on Earth. If you had more good in your life, your spirit to the Egyptians was probably the sun god, Ra. The sun is would have an eternity of happiness. Too many bad deeds ...
... balanced with a divine feather. The scale weighed your good and 700 gods and goddesses, in fact. The most important god bad deeds on Earth. If you had more good in your life, your spirit to the Egyptians was probably the sun god, Ra. The sun is would have an eternity of happiness. Too many bad deeds ...
Lesson 2 Study Guide The Kingdoms of Egypt
... B. A massive structure built of stone, usually having a square base and four triangular sides that slope upward. C. The process of preserving a dead body through embalming and drying. D. An Egyptian pharaoh who built the Great Pyramid at Giza. E. The title used by the rulers of ancient Egypt. F. A F ...
... B. A massive structure built of stone, usually having a square base and four triangular sides that slope upward. C. The process of preserving a dead body through embalming and drying. D. An Egyptian pharaoh who built the Great Pyramid at Giza. E. The title used by the rulers of ancient Egypt. F. A F ...
Memphis gained great importance during the early dynastic period
... eventually developed into the Great Pyramid of Khufu at Giza. Saqqara, just to the southwest of Memphis, was the royal burial site of the city. As the capital of the Old Kingdom, Memphis was the heart of Egypt, serving as the home of the pharaoh, chief priests, and nobles. Pharaohs ruled from Memphi ...
... eventually developed into the Great Pyramid of Khufu at Giza. Saqqara, just to the southwest of Memphis, was the royal burial site of the city. As the capital of the Old Kingdom, Memphis was the heart of Egypt, serving as the home of the pharaoh, chief priests, and nobles. Pharaohs ruled from Memphi ...
Egyptian Society
... Egyptians from all social classes were mummified to prepare for the afterlife. ...
... Egyptians from all social classes were mummified to prepare for the afterlife. ...
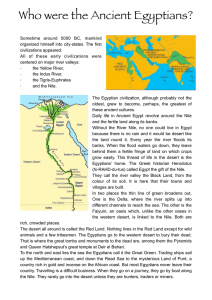
Who were the Ancient Egyptians?
... part of their everyday lives. Many Egyptians religious customs focused on what happened after people died. Like Mesopotamians, Egyptians practiced polytheism. Before the Firs Dynasty, each village worshipped its own gods. During the Old Kingdom, however, Egyptian officials tried to give some sort of ...
... part of their everyday lives. Many Egyptians religious customs focused on what happened after people died. Like Mesopotamians, Egyptians practiced polytheism. Before the Firs Dynasty, each village worshipped its own gods. During the Old Kingdom, however, Egyptian officials tried to give some sort of ...
Jeopardy (powerpoint
... - Imhotep is one of the few individuals whose life achievements were recorded by the Egyptians; historians believe he was a genius - Imhotep served at the right hand of Pharaoh Djoser, was a priest, a builder, a sculptor and much more - He created the system of medicine, one that was highly honoure ...
... - Imhotep is one of the few individuals whose life achievements were recorded by the Egyptians; historians believe he was a genius - Imhotep served at the right hand of Pharaoh Djoser, was a priest, a builder, a sculptor and much more - He created the system of medicine, one that was highly honoure ...
Unit 2 day 10 World - River Mill Academy
... Floods every year, predictable Prevented invasion: flowed through cataracts (rocky stretches with swift currents) Too dangerous to navigate boats Delta Area at mouth of river (triangle shaped) Most fertile soil in Egypt ...
... Floods every year, predictable Prevented invasion: flowed through cataracts (rocky stretches with swift currents) Too dangerous to navigate boats Delta Area at mouth of river (triangle shaped) Most fertile soil in Egypt ...
Social Classes in Ancient Egypt
... medicine through years of training at the temples. I knew a lot about the human body, even though there were no medical schools. My knowledge came through the process of mummification, in which I removed and examined different parts of the body after death. I was able to learn about the various flui ...
... medicine through years of training at the temples. I knew a lot about the human body, even though there were no medical schools. My knowledge came through the process of mummification, in which I removed and examined different parts of the body after death. I was able to learn about the various flui ...
egypt 2, tombs temples r.pdf
... receive offerings . Sometimes a small slot or a peephole was included so visitors could see the statue. ...
... receive offerings . Sometimes a small slot or a peephole was included so visitors could see the statue. ...
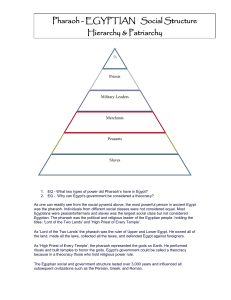
r EQ - What two types of power did Pharaoh`s have in Egypt? EQ
... As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy those who hold religious power rule. The Egyptian social and government structure lasted over 3 ...
... As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy those who hold religious power rule. The Egyptian social and government structure lasted over 3 ...
Ancient Egyptian Art
... told her where it was. Isis mourned for her dead husband. Then she hid the body, while she went back to look after her son Horus, still a baby. Seth was terrified that Isis might be able to bring Osiris back from the dead, since she was a great magician. So Seth found where she had hidden the body a ...
... told her where it was. Isis mourned for her dead husband. Then she hid the body, while she went back to look after her son Horus, still a baby. Seth was terrified that Isis might be able to bring Osiris back from the dead, since she was a great magician. So Seth found where she had hidden the body a ...
Ancient Egyptians Activity Sheet
... A. A form of writing using pictures. B. Stone figure with human head and lion’s body. C. A kind of paper used by ancient Egyptians. D. Kept the written record of the Egyptian people. E. Stretches of rocky rapids or waterfalls in a river. F. The pharaoh’s chief minister and official. G. ...
... A. A form of writing using pictures. B. Stone figure with human head and lion’s body. C. A kind of paper used by ancient Egyptians. D. Kept the written record of the Egyptian people. E. Stretches of rocky rapids or waterfalls in a river. F. The pharaoh’s chief minister and official. G. ...
Unit 1 EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION (OLD, MIDDLE, AND NEW
... - pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army - traded agricultural surplus: wheat, barley (from Nile floods which provided silt) - mining of large mineral deposits of copper which used for bronze tools. Gold and copper were mined by slaves which greatly enriched the royal treasury. - ...
... - pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army - traded agricultural surplus: wheat, barley (from Nile floods which provided silt) - mining of large mineral deposits of copper which used for bronze tools. Gold and copper were mined by slaves which greatly enriched the royal treasury. - ...
Reading Like a Historian: Pyramids
... areas around the pyramids. Below is an excerpt from an article that appeared in many newspapers and magazines around the world reporting some of Hawass’s recent findings. Egypt displayed on Monday newly discovered tombs more than 4,000 years old and said they belonged to people who worked on the Gre ...
... areas around the pyramids. Below is an excerpt from an article that appeared in many newspapers and magazines around the world reporting some of Hawass’s recent findings. Egypt displayed on Monday newly discovered tombs more than 4,000 years old and said they belonged to people who worked on the Gre ...
Ancient Egypt ABC Book
... and agricultural practices and products flourished as a result of favorable geographic characteristics. The cultural practices and products of these early civilizations can be used to help understand the Eastern Hemisphere ...
... and agricultural practices and products flourished as a result of favorable geographic characteristics. The cultural practices and products of these early civilizations can be used to help understand the Eastern Hemisphere ...
Ancient Egypt (The Old Kingdom) - History-13-14
... They observed enthusiastic observations of the natural world. They painted and carved on the walls of temples and tombs. Their aim in the Old Kingdom was developing a connection with the Egyptian concept of kingship and religion. ...
... They observed enthusiastic observations of the natural world. They painted and carved on the walls of temples and tombs. Their aim in the Old Kingdom was developing a connection with the Egyptian concept of kingship and religion. ...
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death (the after life). These rituals and protocols included mummifying the body, casting of magic spells, and burial with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the Egyptian afterlife.The burial process used by the ancient Egyptians evolved throughout time as old customs were discarded and new ones adopted, but several important elements of the process persisted. Although specific details changed over time, the preparation of the body, the magic rituals involved, and the grave goods provided were all essential parts of a proper Egyptian funeral.