Chapter 8 – The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs What did the pharaohs
... enjoyed many great achievements in literature, art, and architecture. The New Kingdom (about 1600 to 1100 B.C.E.) is often called Egypt’s Golden Age. During this time of peace and stability, ancient Egypt’s power reached its height. Pharaohs increased trade and had huge monuments built. As in Mesopo ...
... enjoyed many great achievements in literature, art, and architecture. The New Kingdom (about 1600 to 1100 B.C.E.) is often called Egypt’s Golden Age. During this time of peace and stability, ancient Egypt’s power reached its height. Pharaohs increased trade and had huge monuments built. As in Mesopo ...
WHICh2Egypt-Sec1-2Ancient Egypt-2015
... built by slave labor. However, now historians have determined that they were built by free Egyptian citizens who were drafted by the government to spend a certain time building pyramids. • They were organized into work-groups and lived in a village set up near the pyramid. • Some groups even had nic ...
... built by slave labor. However, now historians have determined that they were built by free Egyptian citizens who were drafted by the government to spend a certain time building pyramids. • They were organized into work-groups and lived in a village set up near the pyramid. • Some groups even had nic ...
Ancient Egypt Travel Brochure
... The Rosetta Stone was inscribed with a law made in 196BC, written in two forms of hieroglyphics and in ancient Greek. A French scholar named Jean François Champollion translated the Egyptian into Greek. Champollion also found out that hieroglyphs had originally been pictographs, but they stood ...
... The Rosetta Stone was inscribed with a law made in 196BC, written in two forms of hieroglyphics and in ancient Greek. A French scholar named Jean François Champollion translated the Egyptian into Greek. Champollion also found out that hieroglyphs had originally been pictographs, but they stood ...
Egyptian Vocabulary Worksheet
... with the dead in order to help them pass through the d____________ of the underworld and attain an afterlife of bliss in the Field of Reeds. Some of the texts are also found on the w_____________ of tombs and on c_______________ or written on papyrus, linen or vellum. Slide #3: Ra or Re: The Egyptia ...
... with the dead in order to help them pass through the d____________ of the underworld and attain an afterlife of bliss in the Field of Reeds. Some of the texts are also found on the w_____________ of tombs and on c_______________ or written on papyrus, linen or vellum. Slide #3: Ra or Re: The Egyptia ...
The Egyptian Empire
... These small shafts extend out from the rooms in the pyramid to the outer surface of the pyramid. Some experts believe that they were built to provide ventilation for the people working inside the pyramid while it was being built. Other experts believe that these shafts had a religious purpose becau ...
... These small shafts extend out from the rooms in the pyramid to the outer surface of the pyramid. Some experts believe that they were built to provide ventilation for the people working inside the pyramid while it was being built. Other experts believe that these shafts had a religious purpose becau ...
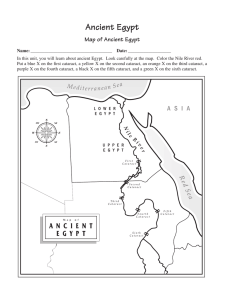
Egypt and the Nile River Valley System
... god of the sun, Ra, to become Amon-Ra. • During the “reign” and worship of Amon-Ra, the Egyptian people were very polytheistic. ...
... god of the sun, Ra, to become Amon-Ra. • During the “reign” and worship of Amon-Ra, the Egyptian people were very polytheistic. ...
Exploring Ancient Egypt Unit Summary
... beginning in 2649 BC to 2150 BC. The pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom. Next was the Middle Kingdom which was when Egypt’s Pharaohs were at their most powerful. Lastly, we move into the New Kingdom, which is when Egypt began to expand to other countries. Also, the capital was moved to ...
... beginning in 2649 BC to 2150 BC. The pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom. Next was the Middle Kingdom which was when Egypt’s Pharaohs were at their most powerful. Lastly, we move into the New Kingdom, which is when Egypt began to expand to other countries. Also, the capital was moved to ...
Egyptian Civilization
... chroniclers and inscribed on the walls of tombs (the Pyramid Texts) or painted on the outside of coffins or sarcophagi (the Coffin Texts). Later, they were copied ...
... chroniclers and inscribed on the walls of tombs (the Pyramid Texts) or painted on the outside of coffins or sarcophagi (the Coffin Texts). Later, they were copied ...
Feather of Maat
... it would return to the tomb. At this time, it would look for the person to which it belonged. This would be the mummy, however, often the egyptians would supply the Ba with a statue in the likeness of the deceased in case the mummy was lost or damaged. ...
... it would return to the tomb. At this time, it would look for the person to which it belonged. This would be the mummy, however, often the egyptians would supply the Ba with a statue in the likeness of the deceased in case the mummy was lost or damaged. ...
CHAPTER 7 “The Indus Valley Civilization” - SEXTO
... 6.- Who conquered Egypt when the Middle Kingdom ended? The Hyksos from Canaan conquered Egypt when the Middle Kingdom ended. 7.- Which Kingdom was considered a great period in Egyptian history? The New Kingdom was considered the great period in Egyptian history. 8.- What was the purpose of the pyram ...
... 6.- Who conquered Egypt when the Middle Kingdom ended? The Hyksos from Canaan conquered Egypt when the Middle Kingdom ended. 7.- Which Kingdom was considered a great period in Egyptian history? The New Kingdom was considered the great period in Egyptian history. 8.- What was the purpose of the pyram ...
Ancient Egyptian Leadership - Ms Bergman's Class Website
... 2) Do you think Egypt would be so well known today if Pharaohs did not exist? 3) In ancient Egypt all property belonged to the Pharaohs, would our society be successful if this was true today about the ...
... 2) Do you think Egypt would be so well known today if Pharaohs did not exist? 3) In ancient Egypt all property belonged to the Pharaohs, would our society be successful if this was true today about the ...
APWH Chapter 3: Early African Societies and the Bantu
... • Aten and Monotheism – Amenhotep IV (Akhenaten) started a new religion based on Aten, the “one, true god” of Egypt. While Akhenaten lived, the cult flourished. When he died, the cult was destroyed by the rival Amon-Re cult. • Mummification – Egyptians believed in an afterlife. During the Old Kingdo ...
... • Aten and Monotheism – Amenhotep IV (Akhenaten) started a new religion based on Aten, the “one, true god” of Egypt. While Akhenaten lived, the cult flourished. When he died, the cult was destroyed by the rival Amon-Re cult. • Mummification – Egyptians believed in an afterlife. During the Old Kingdo ...
Nile—Egypt
... --”Book of the Dead” – aided the dead in the afterlife; contains ideas borrowed from outsiders; details how Isis & Nephthys brought Osiris back to life after being killed by his brother Set --mummification --ka (life force); ba (soul/personality); ren (name); ib (heart); sheut (shadow) f. Bronze Age ...
... --”Book of the Dead” – aided the dead in the afterlife; contains ideas borrowed from outsiders; details how Isis & Nephthys brought Osiris back to life after being killed by his brother Set --mummification --ka (life force); ba (soul/personality); ren (name); ib (heart); sheut (shadow) f. Bronze Age ...
Name: Cohort: ______ Date: Before you start the Do Now complete
... Directions: Highlight the passage as you read, use your highlights to help you complete the outline on the back. You WILL be checked for accurate highlighting. Who were the pharaohs? Ancient Egyptian government was dominated by a single person, the pharaoh. The people believed that the pharaoh was m ...
... Directions: Highlight the passage as you read, use your highlights to help you complete the outline on the back. You WILL be checked for accurate highlighting. Who were the pharaohs? Ancient Egyptian government was dominated by a single person, the pharaoh. The people believed that the pharaoh was m ...
Ancient Africa - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... when it was written, there were three scripts being used in Egypt. • The first was hieroglyphic which was the script used for important or religious documents. • The second was demotic which was the common script of Egypt. • The third was Greek which was the language of the rulers of Egypt at that t ...
... when it was written, there were three scripts being used in Egypt. • The first was hieroglyphic which was the script used for important or religious documents. • The second was demotic which was the common script of Egypt. • The third was Greek which was the language of the rulers of Egypt at that t ...
Ancient Egypt Review - 6th Grade Social Studies
... was left in the body. The ancient Egyptians believed that the heart was the organ of life force and intellect and that the person would need it in the afterlife. After the organs were removed, the body was covered in a kind of salt called natron. This salt drew even more moisture from the body. Afte ...
... was left in the body. The ancient Egyptians believed that the heart was the organ of life force and intellect and that the person would need it in the afterlife. After the organs were removed, the body was covered in a kind of salt called natron. This salt drew even more moisture from the body. Afte ...
Old and Middle Kingdoms
... Obverse of a Narmer Palette facsimileBelow the bovine heads thought to represent the cow goddess Bat, who was the patron deity of the seventh nome of Upper Egypt, flanking the serekh of Narmer.[11] Below that is what appears to be a procession, with Narmer depicted at almost the full height of the r ...
... Obverse of a Narmer Palette facsimileBelow the bovine heads thought to represent the cow goddess Bat, who was the patron deity of the seventh nome of Upper Egypt, flanking the serekh of Narmer.[11] Below that is what appears to be a procession, with Narmer depicted at almost the full height of the r ...
Ancient Egypt Practice Test
... Egyptian traders to trade with people outside of Egypt. She used the wealth gained from trade to support the arts. She built monuments during her reign, such as her temple near the city of Thebes. 4. Sample answer: Religion was very important to the Egyptians. They built temples as homes for the god ...
... Egyptian traders to trade with people outside of Egypt. She used the wealth gained from trade to support the arts. She built monuments during her reign, such as her temple near the city of Thebes. 4. Sample answer: Religion was very important to the Egyptians. They built temples as homes for the god ...
Egypt/Kush - Mrs. Blackwell Social Studies
... (write out) Which statement best explains why Tutankhamen’s tomb was special? A) Tutankhamen ruled Egypt longer than any other pharaoh. B) Little had been known about this period in Egyptian history. C) Egyptian historians had not mentioned the location of this tomb. D) This tomb still contained eve ...
... (write out) Which statement best explains why Tutankhamen’s tomb was special? A) Tutankhamen ruled Egypt longer than any other pharaoh. B) Little had been known about this period in Egyptian history. C) Egyptian historians had not mentioned the location of this tomb. D) This tomb still contained eve ...
How Was the Great Pyramid Built?
... For centuries, people have wondered how the ancient Egyptians were able to build the Great Pyramid. Remember, the Great Pyramid is over 450 feet tall, and it is constructed of more than 2 million huge blocks, many of which weigh 3 tons or more. And yet most scientists agree that it was likely built ...
... For centuries, people have wondered how the ancient Egyptians were able to build the Great Pyramid. Remember, the Great Pyramid is over 450 feet tall, and it is constructed of more than 2 million huge blocks, many of which weigh 3 tons or more. And yet most scientists agree that it was likely built ...
Egypt: Engineering an Empire
... place to another almost like a system of highways. Initially the tombs of pharaohs were simple one story structures called __mastaba_. Egyptians built more than _100_pyramids. In Saqqara, Pharaoh Djoser would have his architect, vizier, and high priest Imhotep build his tomb. Different from other st ...
... place to another almost like a system of highways. Initially the tombs of pharaohs were simple one story structures called __mastaba_. Egyptians built more than _100_pyramids. In Saqqara, Pharaoh Djoser would have his architect, vizier, and high priest Imhotep build his tomb. Different from other st ...
TOPIC 2 READING GUIDE
... Where was Nubia located? What region was Nubia later called? Why was Egypt willing to trade with Kerma? List the many Egyptian cultural attributes Nubians adopted during Egypt’s occupation of Nubia. Explain the historical importance of Kashta and Piye. How did iron tools and weapons impact the kingd ...
... Where was Nubia located? What region was Nubia later called? Why was Egypt willing to trade with Kerma? List the many Egyptian cultural attributes Nubians adopted during Egypt’s occupation of Nubia. Explain the historical importance of Kashta and Piye. How did iron tools and weapons impact the kingd ...
WHICh2Egypt-Sec1-2Ancient Egypt-2016
... built by slave labor. However, now historians have determined that they were built by free Egyptian citizens who were drafted by the government to spend a certain time building pyramids. • They were organized into work-groups and lived in a village set up near the pyramid. • Some groups even had nic ...
... built by slave labor. However, now historians have determined that they were built by free Egyptian citizens who were drafted by the government to spend a certain time building pyramids. • They were organized into work-groups and lived in a village set up near the pyramid. • Some groups even had nic ...
ancient Egyptian houses
... Egypt. The two construction materials that the ancient land of Egypt seemed capable of producing in multitude was sand and papyrus reeds; with some stone quarries. Therefore, for the most part, the majority of ancient Egyptian houses were constructed of mud brick. • Ancient mud houses in Egypt were ...
... Egypt. The two construction materials that the ancient land of Egypt seemed capable of producing in multitude was sand and papyrus reeds; with some stone quarries. Therefore, for the most part, the majority of ancient Egyptian houses were constructed of mud brick. • Ancient mud houses in Egypt were ...
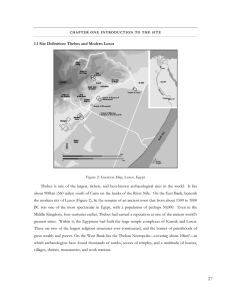
1.1 Site Definition: Thebes and Modern Luxor Thebes is one of the
... afterglow give Thebes the appearance of an over-imagined painting. Europeans were certain that here was the landscape in which God had created the Garden of Eden. The close proximity of limestone cliffs and the richness and extent of adjacent agricultural land helped maintain the wealth and prestige ...
... afterglow give Thebes the appearance of an over-imagined painting. Europeans were certain that here was the landscape in which God had created the Garden of Eden. The close proximity of limestone cliffs and the richness and extent of adjacent agricultural land helped maintain the wealth and prestige ...
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death (the after life). These rituals and protocols included mummifying the body, casting of magic spells, and burial with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the Egyptian afterlife.The burial process used by the ancient Egyptians evolved throughout time as old customs were discarded and new ones adopted, but several important elements of the process persisted. Although specific details changed over time, the preparation of the body, the magic rituals involved, and the grave goods provided were all essential parts of a proper Egyptian funeral.