Filterless, High Efficiency, Mono 3 W Class-D Audio Amplifier SSM2335
... filtering of the speaker and human ear to fully recover the audio component of the square wave output. Most Class-D amplifiers use some variation of pulse-width modulation (PWM), but the SSM2335 uses Σ-Δ modulation to determine the switching pattern of the output devices, resulting in a number of im ...
... filtering of the speaker and human ear to fully recover the audio component of the square wave output. Most Class-D amplifiers use some variation of pulse-width modulation (PWM), but the SSM2335 uses Σ-Δ modulation to determine the switching pattern of the output devices, resulting in a number of im ...
Studying Characteristic Curves with LabVIEW
... and one labeled Resistor Value (ohms). The term shunt resistor is another name for a sensing resistor. LabVIEW knows that to measure current, we’ll be playing our little trick of inserting a sensing resistor. When we run this VI, LabVIEW will take the measured voltage across this sensing resistor an ...
... and one labeled Resistor Value (ohms). The term shunt resistor is another name for a sensing resistor. LabVIEW knows that to measure current, we’ll be playing our little trick of inserting a sensing resistor. When we run this VI, LabVIEW will take the measured voltage across this sensing resistor an ...
PLUS+1® Controller Family Technical Information Manual
... debounce is defined as an input being in a given state for three samples before a state change is reported. The sample time is a function of application loop time. Multifunction pins that are configured to be DIN are subject to the same update rates as the analog input function for that pin. Debounc ...
... debounce is defined as an input being in a given state for three samples before a state change is reported. The sample time is a function of application loop time. Multifunction pins that are configured to be DIN are subject to the same update rates as the analog input function for that pin. Debounc ...
AL8807B Description Pin Assignments
... the LEDs and the Schottky diode D1, and back to the supply rail, but it decays, with the rate of decay determined by the forward voltage drop of the LEDs and the Schottky diode. This decaying current produces a falling voltage at R1, which is sensed by the AL8807B. A voltage proportional to the sens ...
... the LEDs and the Schottky diode D1, and back to the supply rail, but it decays, with the rate of decay determined by the forward voltage drop of the LEDs and the Schottky diode. This decaying current produces a falling voltage at R1, which is sensed by the AL8807B. A voltage proportional to the sens ...
MAX15038 4A, 2MHz Step-Down Regulator General Description Features
... voltage-error amplifier. The voltage-mode control architecture and the voltage-error amplifier permit a type III compensation scheme to be utilized to achieve maximum loop bandwidth, up to 20% of the switching frequency. High loop bandwidth provides fast transient response, resulting in less require ...
... voltage-error amplifier. The voltage-mode control architecture and the voltage-error amplifier permit a type III compensation scheme to be utilized to achieve maximum loop bandwidth, up to 20% of the switching frequency. High loop bandwidth provides fast transient response, resulting in less require ...
AN2844
... This information is used to change the set point of the pulse-by-pulse current limitation. In the standard application circuit with L6565 as U1, an OFF-time limitation circuit with a Q3 transistor has been added. This transistor limits the maximum switching frequency of the converter to approximatel ...
... This information is used to change the set point of the pulse-by-pulse current limitation. In the standard application circuit with L6565 as U1, an OFF-time limitation circuit with a Q3 transistor has been added. This transistor limits the maximum switching frequency of the converter to approximatel ...
PLUS+1 Controller Family Technical Information ©2010 Sauer
... What information is in this manual?................................................................................................... 5 What information is in individual module product data sheets?............................................. 5 What information is in individual module API specifica ...
... What information is in this manual?................................................................................................... 5 What information is in individual module product data sheets?............................................. 5 What information is in individual module API specifica ...
LT1363 - 70MHz, 1000V/µs Op Amp
... typical performance curves.The photo of the small-signal response with 200pF load shows 62% peaking. The largesignal response with a 10,000pF load shows the output slew rate being limited to 10V/µs by the short-circuit current. Coaxial cable can be driven directly, but for best pulse fidelity a resi ...
... typical performance curves.The photo of the small-signal response with 200pF load shows 62% peaking. The largesignal response with a 10,000pF load shows the output slew rate being limited to 10V/µs by the short-circuit current. Coaxial cable can be driven directly, but for best pulse fidelity a resi ...
MIDRANGE INPUT SYNCHRONOUS BUCK CONTROLLER WITH ADVANCED SEQUENCING AND OUTPUT MARGINING TPS40100 FEATURES
... the amount of current feedback providing greater application flexibility. Likewise, the overcurrent function has user programmable integration to eliminate nuisance tripping and allow the user to tailor the response to application requirements. The controller provides an integrated method to margin ...
... the amount of current feedback providing greater application flexibility. Likewise, the overcurrent function has user programmable integration to eliminate nuisance tripping and allow the user to tailor the response to application requirements. The controller provides an integrated method to margin ...
J. Phinney and D.J. Perreault, “Filters with Active Tuning for Power Applications,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics , Vol. 18, No. 2, March 2003, pp. 636-647.
... To take advantage of high-Q resonant filters, one must ensure that the converter switching frequency remains aligned with the filter resonance across all component tolerances and operating conditions. Resonant excitation is equivalent to maintaining a resistive phase relationship (0 ) between resona ...
... To take advantage of high-Q resonant filters, one must ensure that the converter switching frequency remains aligned with the filter resonance across all component tolerances and operating conditions. Resonant excitation is equivalent to maintaining a resistive phase relationship (0 ) between resona ...
Low Distortion 1.0 GHz Differential Amplifier
... of the ac-coupling capacitors, CAC, should be negligible if 100 nF capacitors are used and the lowest signal frequency is greater than 1 MHz. If the series reactance of the matching network inductor is defined to be XS = 2 π f LS, and the shunt reactance of the matching capacitor to be XP = (2 π f C ...
... of the ac-coupling capacitors, CAC, should be negligible if 100 nF capacitors are used and the lowest signal frequency is greater than 1 MHz. If the series reactance of the matching network inductor is defined to be XS = 2 π f LS, and the shunt reactance of the matching capacitor to be XP = (2 π f C ...
ADG781 数据手册DataSheet下载
... 5. –3 dB Bandwidth >200 MHz. 6. Low Power Dissipation. CMOS construction ensures low power dissipation. 7. Fast tON/tOFF. 8. Break-Before-Make Switching. This prevents channel shorting when the switches are configured as a multiplexer (ADG783 only). ...
... 5. –3 dB Bandwidth >200 MHz. 6. Low Power Dissipation. CMOS construction ensures low power dissipation. 7. Fast tON/tOFF. 8. Break-Before-Make Switching. This prevents channel shorting when the switches are configured as a multiplexer (ADG783 only). ...
solar disconnects flyer
... F100 (100A fuse) F275 (250A fuse) F125 (125A fuse) F300 (300A fuse) F150 (150A fuse) F325 (300A fuse) F175 (175A fuse) F350 (350A fuse) F200 (200A fuse) F375 (350A fuse) F225 (250A fuse) F400 (400A fuse) F250 (250A fuse) ...
... F100 (100A fuse) F275 (250A fuse) F125 (125A fuse) F300 (300A fuse) F150 (150A fuse) F325 (300A fuse) F175 (175A fuse) F350 (350A fuse) F200 (200A fuse) F375 (350A fuse) F225 (250A fuse) F400 (400A fuse) F250 (250A fuse) ...
Hot Swap Controller and Digital Power Monitor with ALERTB Output ADM1178
... The ADM1178 limits the current through this resistor by controlling the gate voltage (via the GATE pin) of an external N-channel FET in the power path. The voltage across the sense resistor (and therefore the inrush current) is kept below a preset maximum. ...
... The ADM1178 limits the current through this resistor by controlling the gate voltage (via the GATE pin) of an external N-channel FET in the power path. The voltage across the sense resistor (and therefore the inrush current) is kept below a preset maximum. ...
4.5V to 28V Input, Synchronous PWM Buck Controllers
... The controllers operate in synchronous-rectification mode to ensure balanced current sourcing and sinking capability of up to 25A. The MAX8553/MAX8554 also provide up to 95% efficiency, making them ideal for server and pointof-load applications. Additionally, a low 5µA shutdown current allows for lo ...
... The controllers operate in synchronous-rectification mode to ensure balanced current sourcing and sinking capability of up to 25A. The MAX8553/MAX8554 also provide up to 95% efficiency, making them ideal for server and pointof-load applications. Additionally, a low 5µA shutdown current allows for lo ...
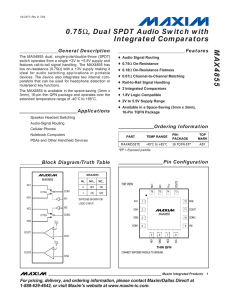
MAX4855 0.75 Integrated Comparators , Dual SPDT Audio Switch with
... low on-resistance (0.75Ω) with a +3V supply making it ideal for audio switching applications in portable devices. The device also integrates two internal comparators that can be used for headphone detection or mute/send key functions. The MAX4855 is available in the space-saving (3mm x 3mm), 16-pin ...
... low on-resistance (0.75Ω) with a +3V supply making it ideal for audio switching applications in portable devices. The device also integrates two internal comparators that can be used for headphone detection or mute/send key functions. The MAX4855 is available in the space-saving (3mm x 3mm), 16-pin ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).