ADR391 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... references provides a stable output voltage from a minimum supply of 300 mV above the output. Their advanced design eliminates the need for external capacitors, which further reduces board space and system cost. The combination of low power operation, small size, and ease of use makes the ADR39x pre ...
... references provides a stable output voltage from a minimum supply of 300 mV above the output. Their advanced design eliminates the need for external capacitors, which further reduces board space and system cost. The combination of low power operation, small size, and ease of use makes the ADR39x pre ...
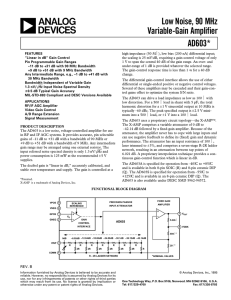
MAX16993 Step-Down Controller with Dual 2.1MHz Step-Down DC-DC Converters General Description
... OUT1. Under no-load conditions, the MAX16993 consumes only 30µA of quiescent current, making it ideal for automotive applications. The high-voltage synchronous step-down DC-DC controller (OUT1) operates from a voltage up to 36V continuous and is protected from load-dump transients up to 42V. There i ...
... OUT1. Under no-load conditions, the MAX16993 consumes only 30µA of quiescent current, making it ideal for automotive applications. The high-voltage synchronous step-down DC-DC controller (OUT1) operates from a voltage up to 36V continuous and is protected from load-dump transients up to 42V. There i ...
LTC3701 - 2-Phase, Low Input Voltage, Dual Step
... The LTC3701 uses a constant frequency, current mode architecture with the two controller channels operating 180 degrees out of phase. During normal operation, each external P-channel power MOSFET is turned on when the clock for that channel sets the RS latch, and turned off when the current comparat ...
... The LTC3701 uses a constant frequency, current mode architecture with the two controller channels operating 180 degrees out of phase. During normal operation, each external P-channel power MOSFET is turned on when the clock for that channel sets the RS latch, and turned off when the current comparat ...
ELEC7770 Advanced VLSI Design Spring 2007
... A true linear device is an idealization. Most electronic devices are nonlinear. Nonlinearity in amplifier is undesirable and causes distortion of signal. Nonlinearity in mixer or frequency converter is essential. Copyright 2008, Agrawal ...
... A true linear device is an idealization. Most electronic devices are nonlinear. Nonlinearity in amplifier is undesirable and causes distortion of signal. Nonlinearity in mixer or frequency converter is essential. Copyright 2008, Agrawal ...
TPS40040 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... amplifier. The voltage reference is trimmed with the error amplifier in a unity gain configuration to remove amplifier offset from the final regulation voltage. ...
... amplifier. The voltage reference is trimmed with the error amplifier in a unity gain configuration to remove amplifier offset from the final regulation voltage. ...
74LCX16374 Low Voltage 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flop with 5V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... state of their individual D inputs that meet the setup and hold time requirements on the LOW-to-HIGH Clock (CPn) transition. With the Output Enable (OEn) LOW, the contents of the flip-flops are available at the outputs. When OEn is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operation of the ...
... state of their individual D inputs that meet the setup and hold time requirements on the LOW-to-HIGH Clock (CPn) transition. With the Output Enable (OEn) LOW, the contents of the flip-flops are available at the outputs. When OEn is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operation of the ...
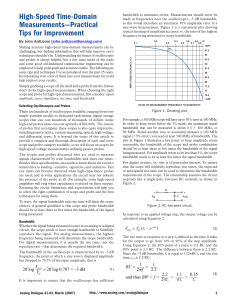
LT1801/LT1802 - Dual/Quad 80MHz, 25V/µs Low Power Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Precision Op Amps
... Note 1: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to any Absolute Maximum Rating condition for extended periods may affect device reliability and lifetime. Note 2: The inputs are protected by back-to-back diodes. If the differentia ...
... Note 1: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to any Absolute Maximum Rating condition for extended periods may affect device reliability and lifetime. Note 2: The inputs are protected by back-to-back diodes. If the differentia ...
AD7858 数据手册DataSheet下载
... and remains high until conversion is completed. BUSY is also used to indicate when the AD7858/ AD7858L has completed its on-chip calibration sequence. Sleep Input/Low-Power Mode. A Logic 0 initiates a sleep, and all circuitry is powered down including the internal voltage reference provided there is ...
... and remains high until conversion is completed. BUSY is also used to indicate when the AD7858/ AD7858L has completed its on-chip calibration sequence. Sleep Input/Low-Power Mode. A Logic 0 initiates a sleep, and all circuitry is powered down including the internal voltage reference provided there is ...
Octal Channel Protectors ADG467 FEATURES
... the output of the channel protector (no load) is clamped at these threshold voltages. However, the channel protector output clamps at a voltage value that is inside these thresholds if the output is loaded. For example, with an output load of 1 kΩ, VDD = 15 V, and a positive overvoltage on the input ...
... the output of the channel protector (no load) is clamped at these threshold voltages. However, the channel protector output clamps at a voltage value that is inside these thresholds if the output is loaded. For example, with an output load of 1 kΩ, VDD = 15 V, and a positive overvoltage on the input ...
AN2123
... turn-off. Both the level and duration of the intermediate off level are adjustable. The duration is set by an external resistor/capacitor in conjunction with the integrated voltage reference for accurate timing. The level can be easily set by an external Zener diode, and its value is chosen dependin ...
... turn-off. Both the level and duration of the intermediate off level are adjustable. The duration is set by an external resistor/capacitor in conjunction with the integrated voltage reference for accurate timing. The level can be easily set by an external Zener diode, and its value is chosen dependin ...
BD63536FJ
... The GATE pin is used to drive the external FET gate. Since output H voltage is “VCC voltage 0.05V (typ)” and output L voltage is “VCC voltage 5.4V (typ)”, the pin is able to directly drive the external FET gate. Provide thick, short and low impedance wiring from this pin. The GATE pin has a buil ...
... The GATE pin is used to drive the external FET gate. Since output H voltage is “VCC voltage 0.05V (typ)” and output L voltage is “VCC voltage 5.4V (typ)”, the pin is able to directly drive the external FET gate. Provide thick, short and low impedance wiring from this pin. The GATE pin has a buil ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).