Fully Integrated 8-Channel DC/DC Converter for
... topology and single inductor supports. These channels achieve higher efficiency in spite of input/output voltage conditions. CH7 has a brightness control and drives white LED by constant current. Also, CH7 supports overvoltage protection (OVP) for open load. CH1/2/3 have a power ON/OFF sequence suit ...
... topology and single inductor supports. These channels achieve higher efficiency in spite of input/output voltage conditions. CH7 has a brightness control and drives white LED by constant current. Also, CH7 supports overvoltage protection (OVP) for open load. CH1/2/3 have a power ON/OFF sequence suit ...
XGT Analog Output Module - Ana
... 4) Conversion process at high speed Conversion speed is 250 ㎲/channel. 5) Various output ranges available XGF-DV4A: 1~5V, 0~5V, 0~10V, -10~10V XGF-DC4A: 4~20mA, 0~20mA 6) The number of modules used for one base is not limited. (However, it should be within the capacity of the power module.) ...
... 4) Conversion process at high speed Conversion speed is 250 ㎲/channel. 5) Various output ranges available XGF-DV4A: 1~5V, 0~5V, 0~10V, -10~10V XGF-DC4A: 4~20mA, 0~20mA 6) The number of modules used for one base is not limited. (However, it should be within the capacity of the power module.) ...
0160-5.9 - Rockwell Automation
... control precautions are required when installing, testing, servicing or repairing this assembly. Component damage may result if ESD control procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar with static control procedures, reference A-B Publication ...
... control precautions are required when installing, testing, servicing or repairing this assembly. Component damage may result if ESD control procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar with static control procedures, reference A-B Publication ...
expCpid_EDIT
... The DC Power Supply is used to create step input response to the controller. The input values are changed to create different DC levels that simulate a step change. Set the Current knob to minimum and the current selector to ‘LO’ Adjust the voltage knob ‘FINE’ centre position. Change the voltage out ...
... The DC Power Supply is used to create step input response to the controller. The input values are changed to create different DC levels that simulate a step change. Set the Current knob to minimum and the current selector to ‘LO’ Adjust the voltage knob ‘FINE’ centre position. Change the voltage out ...
1.1 Special Diodes PN junction diodes are the most
... region, it starts conducting around 0.7 V, just like an ordinary silicon diode. In the leakage region between zero and breakdown, it has only a small reverse current. In a Zener diode, the breakdown has a very sharp knee, followed by an almost vertical increase in current. Note that the voltage is a ...
... region, it starts conducting around 0.7 V, just like an ordinary silicon diode. In the leakage region between zero and breakdown, it has only a small reverse current. In a Zener diode, the breakdown has a very sharp knee, followed by an almost vertical increase in current. Note that the voltage is a ...
Crosstalk Circuit 2
... When multiple outputs switch simultaneously, it is difficult for power distribution to keep up. The ground potential for the device briefly raises compared with the system ground. This effect is known as simultaneous switching noise, or ground bounce. Induction in the board, traces, and components k ...
... When multiple outputs switch simultaneously, it is difficult for power distribution to keep up. The ground potential for the device briefly raises compared with the system ground. This effect is known as simultaneous switching noise, or ground bounce. Induction in the board, traces, and components k ...
Cascaded Multilevel Inverter for PV Cell Application
... When the switch is off as shown in Fig. 7 the output stage receives energy from the inductor as well as from the input. In the steady-state analysis, the output filter capacitor is assumed to be very large to ensure a constant output voltage vo(t) = Vo. Fig. 8 shows the switch state, voltage and cur ...
... When the switch is off as shown in Fig. 7 the output stage receives energy from the inductor as well as from the input. In the steady-state analysis, the output filter capacitor is assumed to be very large to ensure a constant output voltage vo(t) = Vo. Fig. 8 shows the switch state, voltage and cur ...
74LCXH16245 Low Voltage 16-Bit Bidirectional Transceiver with Bushold 7
... oriented applications. The device is designed for low voltage (2.5V or 3.3V) VCC applications with capability of interfacing to a 5V signal environment. The device is byte controlled. Each byte has separate control inputs which could be shorted together for full 16-bit operation. The T/R inputs dete ...
... oriented applications. The device is designed for low voltage (2.5V or 3.3V) VCC applications with capability of interfacing to a 5V signal environment. The device is byte controlled. Each byte has separate control inputs which could be shorted together for full 16-bit operation. The T/R inputs dete ...
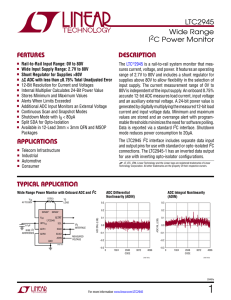
LTC2945 Wide Range I C Power Monitor
... placed between SCL and VDD or INTVCC. The voltage at SCL is internally clamped to 6.4V (5.9V minimum) SDAI: I2C Bus Data Input. Used for shifting in address, command or data bits. This pin is driven by an opencollector output from a master controller. An external pull-up resistor or current source i ...
... placed between SCL and VDD or INTVCC. The voltage at SCL is internally clamped to 6.4V (5.9V minimum) SDAI: I2C Bus Data Input. Used for shifting in address, command or data bits. This pin is driven by an opencollector output from a master controller. An external pull-up resistor or current source i ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).