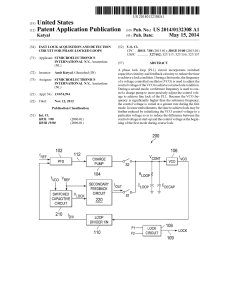
FEATURES HIGH LEVEL BLOCK DIAGRAM
... The low quiescent current, low dropout voltage, and wide input voltage range of the ADP5042 LDOs extend the battery life of portable devices. The two LDOs maintain power supply rejection greater than 60 dB for frequencies as high as 10 kHz while operating with a low headroom voltage. Each regulator ...
... The low quiescent current, low dropout voltage, and wide input voltage range of the ADP5042 LDOs extend the battery life of portable devices. The two LDOs maintain power supply rejection greater than 60 dB for frequencies as high as 10 kHz while operating with a low headroom voltage. Each regulator ...
MAX5037 VRM 9.0, Dual-Phase, Parallelable, Average Current-Mode Controller General Description
... The MAX5037 dual-phase, PWM controller provides high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5037 utilizes a dual-phase, average current-mode control that enables optimal use of low R DS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsi ...
... The MAX5037 dual-phase, PWM controller provides high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5037 utilizes a dual-phase, average current-mode control that enables optimal use of low R DS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsi ...
Highest accuracy & precision WT3000E Precision Power Analyzer
... Accuracy – The WT3000E is the world’s most trusted power analyzer thanks to its unmatched power accuracy. Reliability – With proven high stability, the WT3000E not only provides the best power measurement accuracy but also the ability to repeat these results time and time ...
... Accuracy – The WT3000E is the world’s most trusted power analyzer thanks to its unmatched power accuracy. Reliability – With proven high stability, the WT3000E not only provides the best power measurement accuracy but also the ability to repeat these results time and time ...
ADP2147 Compact, 800 mA, 3 MHz, Simple DVS, Buck Regulator
... The ADP2147 is a step-down dc-to-dc regulator that uses a fixed frequency and high speed current-mode architecture. The high switching frequency and tiny 6-ball WLCSP package enable a small step-down dc-to-dc regulator solution. The ADP2147 operates with an input voltage of 2.3 V to 5.5 V and regula ...
... The ADP2147 is a step-down dc-to-dc regulator that uses a fixed frequency and high speed current-mode architecture. The high switching frequency and tiny 6-ball WLCSP package enable a small step-down dc-to-dc regulator solution. The ADP2147 operates with an input voltage of 2.3 V to 5.5 V and regula ...
Omnia.11 - Media
... was typically unnatural. This wasn’t much of an issue ten to fifteen years ago when CD mastering was much more relaxed. In today’s world, it isn’t unusual to have CD’s that are just as processed (if not more) than a typical radio station. When an audio processor that used weighted peak control is us ...
... was typically unnatural. This wasn’t much of an issue ten to fifteen years ago when CD mastering was much more relaxed. In today’s world, it isn’t unusual to have CD’s that are just as processed (if not more) than a typical radio station. When an audio processor that used weighted peak control is us ...
A TWO STAGE OF CONCURRENT DUAL
... (CS) amplifier stages to provide high gain as shown in Figure 4(a). At the same time, this technique also supports low noise figures and capable to achieved high performance with low power consumption. In such a design approach, transistors M1and M2 is connected a cascade structure by means of coupl ...
... (CS) amplifier stages to provide high gain as shown in Figure 4(a). At the same time, this technique also supports low noise figures and capable to achieved high performance with low power consumption. In such a design approach, transistors M1and M2 is connected a cascade structure by means of coupl ...
AP3440 Description Pin Assignments
... An open drain power good signal indicates the output is within 93% to 107% of its nominal voltage. The AP3440 is available in U-QFN3030-16 package. ...
... An open drain power good signal indicates the output is within 93% to 107% of its nominal voltage. The AP3440 is available in U-QFN3030-16 package. ...
MAX17535 Evaluation Kit Evaluates: General Description Features
... If a window is not seen that is similar to the one described above after 30s, remove the USB cable from the board and reconnect it. Administrator privileges are required to install the USB device driver on Windows. 10) Follow the directions of the Add New Hardware Wizard to install the USB device d ...
... If a window is not seen that is similar to the one described above after 30s, remove the USB cable from the board and reconnect it. Administrator privileges are required to install the USB device driver on Windows. 10) Follow the directions of the Add New Hardware Wizard to install the USB device d ...
MAX3430 ±80V Fault-Protected, Fail-Safe, 1/4-Unit Load, +3.3V RS-485 Transceiver General Description
... ±80V protection from overvoltage signal faults on communication bus lines. Each device contains one driver and one receiver, and the output pins can withstand faults, with respect to ground, of up to ±80V. Even if the faults occur when the transceiver is active, shut down, or powered off, the device ...
... ±80V protection from overvoltage signal faults on communication bus lines. Each device contains one driver and one receiver, and the output pins can withstand faults, with respect to ground, of up to ±80V. Even if the faults occur when the transceiver is active, shut down, or powered off, the device ...
Noise - UniMAP Portal
... either end of a resistor to vary randomly and thereby varies the resistor’s potential difference. That is the direction of current flow is random and has a zero mean value. ...
... either end of a resistor to vary randomly and thereby varies the resistor’s potential difference. That is the direction of current flow is random and has a zero mean value. ...
PC-Based Data Acquisition Unit
... • Ten-Channel Universal Input Module: 120 Vrms/Vdc (continuous) • Four-Channel Universal Input Module: 250 Vrms/Vdc (continuous) ...
... • Ten-Channel Universal Input Module: 120 Vrms/Vdc (continuous) • Four-Channel Universal Input Module: 250 Vrms/Vdc (continuous) ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).