Voltage Reference - Elettronica INFN Lecce
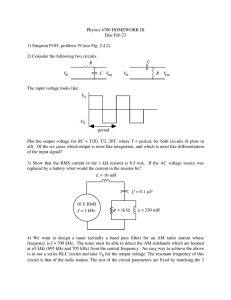
... The current from VREF master ADC is 0.6 mA About -0.2% or -2mV on 1V ...
... The current from VREF master ADC is 0.6 mA About -0.2% or -2mV on 1V ...
ADC slides
... resistor values Resisters need to have a tolerance less than the resolution. E.g. 8-bit resolution = 1:28 = 1/256 = 0.00390625 resolution = 0.390625% Alternative is R-2R ladder arrangement R-2R ...
... resistor values Resisters need to have a tolerance less than the resolution. E.g. 8-bit resolution = 1:28 = 1/256 = 0.00390625 resolution = 0.390625% Alternative is R-2R ladder arrangement R-2R ...
Moving coil meters for DC measurements
... how many parts the maximum signal can be divided into. The formula to calculate resolution is 2^n. For example, a 12 bit ADC has a resolution of 2^12 = 4,096. Therefore, our best resolution is 1 part out of 4,096, or 0.0244% of the full scale. An ADC takes an analog signal and turns it into a binar ...
... how many parts the maximum signal can be divided into. The formula to calculate resolution is 2^n. For example, a 12 bit ADC has a resolution of 2^12 = 4,096. Therefore, our best resolution is 1 part out of 4,096, or 0.0244% of the full scale. An ADC takes an analog signal and turns it into a binar ...
The Criterion for the Tangential Sensitivity Measurement Application
... the pulse (Figure 1). Although the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio depends on many system factors, the generally accepted ratio of 8 dB at the output correlates well with the tangential appearance on the oscilloscope for practical systems. PULSED SIGNAL AT RECEIVER OUTPUT ...
... the pulse (Figure 1). Although the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio depends on many system factors, the generally accepted ratio of 8 dB at the output correlates well with the tangential appearance on the oscilloscope for practical systems. PULSED SIGNAL AT RECEIVER OUTPUT ...
ADC
... • Example: In an 8-bit resolution system, a value of 236.4 will be stored as the digital value 236. • Signal to noise ratio measures the noise level by the ...
... • Example: In an 8-bit resolution system, a value of 236.4 will be stored as the digital value 236. • Signal to noise ratio measures the noise level by the ...
Analog to Digital (A/D) Conversion
... counter that drives the D/A converter. – When the D/A output is larger than the input then the count is reduced otherwise it is increased using an algorithm to home in on the matching value. – When the counter step size is within the tolerance ...
... counter that drives the D/A converter. – When the D/A output is larger than the input then the count is reduced otherwise it is increased using an algorithm to home in on the matching value. – When the counter step size is within the tolerance ...
Chapter 12 - UNT College of Engineering
... the actual from the ideal output voltage as a fraction of the full-scale voltage. • Settling time is the time required for the outputs to switch and settle within ½ LSB when the input switches form all 0s to all 1s. ...
... the actual from the ideal output voltage as a fraction of the full-scale voltage. • Settling time is the time required for the outputs to switch and settle within ½ LSB when the input switches form all 0s to all 1s. ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... that can be used as an alternative to a dual device in very high performance systems. The absolute value of R is flexible, but it must be chosen to achieve the desired bandwidth of the op amp. ...
... that can be used as an alternative to a dual device in very high performance systems. The absolute value of R is flexible, but it must be chosen to achieve the desired bandwidth of the op amp. ...
AN-1131 APPLICATION NOTE
... are joined. Within an integrated circuit such as an ADC, there are numerous sources of internal offset errors, such as offset due to the instrumentation amplifier, charge injection onto the sampling capacitor when a sampling switch is closed, or interference from EMI radiation. These offsets are gen ...
... are joined. Within an integrated circuit such as an ADC, there are numerous sources of internal offset errors, such as offset due to the instrumentation amplifier, charge injection onto the sampling capacitor when a sampling switch is closed, or interference from EMI radiation. These offsets are gen ...
ADC interfacing with Microcontrollers
... The successive approximation ADC is much faster than the digital ramp ADC because it uses digital logic to converge on the value closest to the input voltage. A comparator and a DAC are used in the process. A flowchart explaning the working is shown in the figure below. ...
... The successive approximation ADC is much faster than the digital ramp ADC because it uses digital logic to converge on the value closest to the input voltage. A comparator and a DAC are used in the process. A flowchart explaning the working is shown in the figure below. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - OSU Physics
... ADS5281 (Texas Instr.) 3.3V analog, 1.8V digital, 2Vpp range ...
... ADS5281 (Texas Instr.) 3.3V analog, 1.8V digital, 2Vpp range ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... isoPower technology, based on Analog Devices, Inc., iCoupler® technology. It is used to provide isolation between the field side and the system microcontroller, with an isolation rating of 2.5 kV rms. The ADuM5401 also has an integrated dc-to-dc converter, which can provide 500 mW of regulated isola ...
... isoPower technology, based on Analog Devices, Inc., iCoupler® technology. It is used to provide isolation between the field side and the system microcontroller, with an isolation rating of 2.5 kV rms. The ADuM5401 also has an integrated dc-to-dc converter, which can provide 500 mW of regulated isola ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).