LT1764A - 3A, Fast Transient Response, Low
... Note 6: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout, the output voltage will be equal to: VIN – VDROPOUT. Note 7: GND pin current is tested with VIN = VOUT(NOMINAL) + 1V or VIN = 2.7V (E grade) or VIN = 2 ...
... Note 6: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout, the output voltage will be equal to: VIN – VDROPOUT. Note 7: GND pin current is tested with VIN = VOUT(NOMINAL) + 1V or VIN = 2.7V (E grade) or VIN = 2 ...
AT10.1 SERIES CHARGERS AT10.1 SERIES CHARGERS
... markings on: A) this equipment, B) battery, and C) any other equipment to be used in conjunction with this equipment. ...
... markings on: A) this equipment, B) battery, and C) any other equipment to be used in conjunction with this equipment. ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
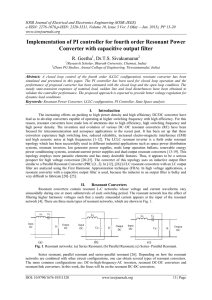
... Fig. 3 Voltage conversion ratio of a series-parallel resonant converter independency on the load and on the normalized switching frequency The voltage conversion ratio curves also show that the output voltage can be regulated at no load. Thus, the main disadvantage of the series resonant converter i ...
... Fig. 3 Voltage conversion ratio of a series-parallel resonant converter independency on the load and on the normalized switching frequency The voltage conversion ratio curves also show that the output voltage can be regulated at no load. Thus, the main disadvantage of the series resonant converter i ...
MAX5721 10-Bit, Low-Power, Dual, Voltage-Output DAC with Serial Interface General Description
... The MAX5721 digital interface is a standard 3-wire connection compatible with SPI/QSPI/MICROWIRE/DSP interfaces. The chip-select input (CS) frames the serial data loading at DIN. Immediately following CS high-tolow transition, the data is shifted synchronously and latched into the input register on ...
... The MAX5721 digital interface is a standard 3-wire connection compatible with SPI/QSPI/MICROWIRE/DSP interfaces. The chip-select input (CS) frames the serial data loading at DIN. Immediately following CS high-tolow transition, the data is shifted synchronously and latched into the input register on ...
MAX5722 12-Bit, Low-Power, Dual, Voltage-Output DAC with Serial Interface General Description
... 112µA supply current accommodates low-power and low-voltage applications. DAC outputs employ on-chip precision output amplifiers that swing Rail-to-Rail®. The MAX5722’s reference input accepts a voltage range from 0 to VDD. In power-down, the reference input is high impedance, further reducing the s ...
... 112µA supply current accommodates low-power and low-voltage applications. DAC outputs employ on-chip precision output amplifiers that swing Rail-to-Rail®. The MAX5722’s reference input accepts a voltage range from 0 to VDD. In power-down, the reference input is high impedance, further reducing the s ...
BQ24751B 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... AC adapter to system-switch driver output. Connect directly to the gate of the ACFET P-channel power MOSFET and the reverse conduction blocking P-channel power MOSFET. Connect both FETs as common-source. Connect the ACFET drain to the system-load side. The PVCC should be connected to the common-sour ...
... AC adapter to system-switch driver output. Connect directly to the gate of the ACFET P-channel power MOSFET and the reverse conduction blocking P-channel power MOSFET. Connect both FETs as common-source. Connect the ACFET drain to the system-load side. The PVCC should be connected to the common-sour ...
Voltage-Series Feedback
... Stabilization of the gain of an amplifier against changes in the components (e.g., with temperature, frequency) If you represent the gain without feedback (the open loop gain) by Ao, then the system gain with negative feedback is ...
... Stabilization of the gain of an amplifier against changes in the components (e.g., with temperature, frequency) If you represent the gain without feedback (the open loop gain) by Ao, then the system gain with negative feedback is ...
ECE 469 Power Electronics Lab Manual
... components such as motors, batteries, magnetic devices, and power semiconductors. The course has a significant design component. The final weeks of the term are devoted to a power converter design project. The equipment and instrumentation for ECE 469 were updated substantially in 2011, and our comp ...
... components such as motors, batteries, magnetic devices, and power semiconductors. The course has a significant design component. The final weeks of the term are devoted to a power converter design project. The equipment and instrumentation for ECE 469 were updated substantially in 2011, and our comp ...
ICL7106/ICL7107 3 ⁄ Digit A/D Converters
... Versatility and accuracy are inherent features of these converters. The dual-slope conversion technique automatically rejects interference signals common in industrial environments. The true differential input and reference are particularly useful when making ratiometric measurements (ohms or bridge ...
... Versatility and accuracy are inherent features of these converters. The dual-slope conversion technique automatically rejects interference signals common in industrial environments. The true differential input and reference are particularly useful when making ratiometric measurements (ohms or bridge ...
UNIT I
... • For a transistor circuit to amplify it must be properly biased with dc voltages. • The dc operating point between saturation and cutoff is called the Q-point. • The goal is to set the Q-point such that that it does not go into saturation or cutoff when an a ac signal is applied. ...
... • For a transistor circuit to amplify it must be properly biased with dc voltages. • The dc operating point between saturation and cutoff is called the Q-point. • The goal is to set the Q-point such that that it does not go into saturation or cutoff when an a ac signal is applied. ...
LT1764A - 3A, Fast Transient Response, Low Noise, LDO Regulators
... Note 6: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout, the output voltage will be equal to: VIN – VDROPOUT. Note 7: GND pin current is tested with VIN = VOUT(NOMINAL) + 1V or VIN = 2.7V (E grade) or VIN = 2 ...
... Note 6: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout, the output voltage will be equal to: VIN – VDROPOUT. Note 7: GND pin current is tested with VIN = VOUT(NOMINAL) + 1V or VIN = 2.7V (E grade) or VIN = 2 ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).