DN110 - Micropower Buck/Boost Circuits, Part 2: Converting Four
... Two combinations of cell count and output voltage are to be strictly avoided: three cells converted to 3.3V and four cells converted to 5V. These combinations are troublesome because no ordinary regulator (boost, buck or linear) can accommodate a situation where the input voltage range overlaps the ...
... Two combinations of cell count and output voltage are to be strictly avoided: three cells converted to 3.3V and four cells converted to 5V. These combinations are troublesome because no ordinary regulator (boost, buck or linear) can accommodate a situation where the input voltage range overlaps the ...
Getting Started with X13 Rev1
... motor output. If available, an ECM development box may be used to provide the pwm signal by connecting pin #1 to the X13 Common and pin #10 to Tap #1. Note that the development box may be limited to only 98-99% of full output. Signal Connection – Discrete Control for OEM production: Common to C, 24V ...
... motor output. If available, an ECM development box may be used to provide the pwm signal by connecting pin #1 to the X13 Common and pin #10 to Tap #1. Note that the development box may be limited to only 98-99% of full output. Signal Connection – Discrete Control for OEM production: Common to C, 24V ...
Controlling the Speed of the Motor
... The solution to this problem is to use a different analog reference for full range. Luckily, the Atmega chip has a built-in analog reference pin, which can be used to specify a different full-scale analog voltage than the default 5V. The way this works is shown in the diagram above. The Atmega chip ...
... The solution to this problem is to use a different analog reference for full range. Luckily, the Atmega chip has a built-in analog reference pin, which can be used to specify a different full-scale analog voltage than the default 5V. The way this works is shown in the diagram above. The Atmega chip ...
iC-NVH 6-bit Sin/D Flash Converter - iC-Haus
... This specification is for a newly developed product. iC-Haus therefore reserves the right to change or update, without notice, any information contained herein, design and specification; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product versions. Please contact iC-Haus to ascerta ...
... This specification is for a newly developed product. iC-Haus therefore reserves the right to change or update, without notice, any information contained herein, design and specification; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product versions. Please contact iC-Haus to ascerta ...
CD54HC160/3A CD54HCT160/3A Synchronous Presettable Counters Functional Diagram
... P3 inputs to be loaded into the counter (provided that the setup and hold requirements for SPE are met.) ...
... P3 inputs to be loaded into the counter (provided that the setup and hold requirements for SPE are met.) ...
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
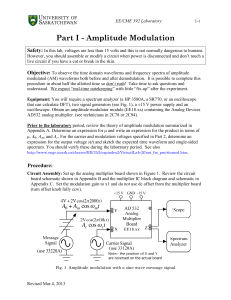
... Appendix C AD532 Multiplier A functional block diagram for the AD532 is shown in Figure 3, and a simplified schematic is shown in Figure 4. In the multiplying mode, Z is connected to the OUTPUT to close the feedback around the output op-amp. The X and Y are inputs to high-impedance, lowdistortion di ...
... Appendix C AD532 Multiplier A functional block diagram for the AD532 is shown in Figure 3, and a simplified schematic is shown in Figure 4. In the multiplying mode, Z is connected to the OUTPUT to close the feedback around the output op-amp. The X and Y are inputs to high-impedance, lowdistortion di ...
Document
... superior to an analog signal. The tendency today is to change an analog signal to digital data. In this section we describe two techniques, pulse code modulation and delta modulation. Topics discussed in this section: Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) Delta Modulation (DM) ...
... superior to an analog signal. The tendency today is to change an analog signal to digital data. In this section we describe two techniques, pulse code modulation and delta modulation. Topics discussed in this section: Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) Delta Modulation (DM) ...
Application Note #1435 100
... Application Note #1435 Protecting Encoder Input Circuitry If there are voltage spikes which are damaging the line receiver inputs of the Galil controller, the input circuit may be protected by placing 2 diodes on every encoder input that is used on the controller (CHA, CHB, CHA-, CHB-). The procedur ...
... Application Note #1435 Protecting Encoder Input Circuitry If there are voltage spikes which are damaging the line receiver inputs of the Galil controller, the input circuit may be protected by placing 2 diodes on every encoder input that is used on the controller (CHA, CHB, CHA-, CHB-). The procedur ...
Pressure sensors and thermistors
... circuitry is added for easy data processing. • The input impedance of R-DAS is 1kΩ, so a unity gain buffer is required for loading. • Low pass filter before ADC. • All power supplies should be bypassed to reduce noises. ...
... circuitry is added for easy data processing. • The input impedance of R-DAS is 1kΩ, so a unity gain buffer is required for loading. • Low pass filter before ADC. • All power supplies should be bypassed to reduce noises. ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION Since the AD7190 provides an integrated solution for weigh scales, it interfaces directly to the load cell. The only external components required are some filters on the analog inputs and capacitors on the reference pins for EMC purposes. The low level signal from the load cell ...
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION Since the AD7190 provides an integrated solution for weigh scales, it interfaces directly to the load cell. The only external components required are some filters on the analog inputs and capacitors on the reference pins for EMC purposes. The low level signal from the load cell ...
physical.pdf
... Digital Transmission: ReceiverSide Issues Clocking: determining the beginning and end of each bit. Transmitting long sequences of 0’s or 1’s can cause synchronization problems. Signal level: determining whether the signal represents the high (logic 1) or low (logic 0) ...
... Digital Transmission: ReceiverSide Issues Clocking: determining the beginning and end of each bit. Transmitting long sequences of 0’s or 1’s can cause synchronization problems. Signal level: determining whether the signal represents the high (logic 1) or low (logic 0) ...
raise - lower (set-point) / ramp generator
... indiviually programmble. Output options Four ramp types are available each of which may be set to generate a single period waveform or, using the repeat option, a continuous waveform. Other options enable the ramp to start when power is applied and set maximum and minimum values of the ramp (range 0 ...
... indiviually programmble. Output options Four ramp types are available each of which may be set to generate a single period waveform or, using the repeat option, a continuous waveform. Other options enable the ramp to start when power is applied and set maximum and minimum values of the ramp (range 0 ...
V in - WSU EECS - Washington State University
... the low output, is a feature required by all useful logic gates to reject noise in the system. The input range is very large while the output range is small for the ideal inverter. The range refers to the voltage interval over which a signal is considered to be a logic 0 or logic 1 ...
... the low output, is a feature required by all useful logic gates to reject noise in the system. The input range is very large while the output range is small for the ideal inverter. The range refers to the voltage interval over which a signal is considered to be a logic 0 or logic 1 ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).