EO323_04-05 - University of Brighton
... a) Explain the main functions of semiconductor devices within any power electronic systems and identify other essential components for such systems. ...
... a) Explain the main functions of semiconductor devices within any power electronic systems and identify other essential components for such systems. ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... When the horizontal axis is time, as in Figure 2.3, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in space as a function of time With the horizontal axis in space, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in time as a function of distance ...
... When the horizontal axis is time, as in Figure 2.3, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in space as a function of time With the horizontal axis in space, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in time as a function of distance ...
View File
... Modern Digital Electronic Circuits Play an Important Role in Our Lives Practically, Each Everyday-use Product is a Digital System or at Least Incorporates One In Order to Better Understand The Operation of Digital Circuits, and be Able to Design, Verify and Test Them, It is Very Crucial to Reach to ...
... Modern Digital Electronic Circuits Play an Important Role in Our Lives Practically, Each Everyday-use Product is a Digital System or at Least Incorporates One In Order to Better Understand The Operation of Digital Circuits, and be Able to Design, Verify and Test Them, It is Very Crucial to Reach to ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... When the horizontal axis is time, as in Figure 2.3, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in space as a function of time With the horizontal axis in space, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in time as a function of distance ...
... When the horizontal axis is time, as in Figure 2.3, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in space as a function of time With the horizontal axis in space, graphs display the value of a signal at a given point in time as a function of distance ...
OpAmp Output Protection (posted 16 June, 2016)
... Operational Amplifiers are often used as output drivers and can be subject to output overload, especially when driving loads outside the box. This overload may damage the output driver of the op-amp. An often used circuit includes an output resistor placed between the op amp and the feedback loop as ...
... Operational Amplifiers are often used as output drivers and can be subject to output overload, especially when driving loads outside the box. This overload may damage the output driver of the op-amp. An often used circuit includes an output resistor placed between the op amp and the feedback loop as ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... Common-source JFET amplifier Using the same transistor, build the circuit below with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. For a good operating point, the drain voltage should be between 3 V and 7 V. Measure the quiescent drain voltage fo ...
... Common-source JFET amplifier Using the same transistor, build the circuit below with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. For a good operating point, the drain voltage should be between 3 V and 7 V. Measure the quiescent drain voltage fo ...
Lab 2 - Full wave rectifier
... Plot the R-C circuit phase vs frequency over the same range 10Hz to 100kHz. Setup the CRO to plot input Amplitude on the X axis and Output amplitude on the Y axis. What angle on the CRO is represented as 0 degrees? Find the frequency where the phase is 15 degrees? 30 degrees? 45 degrees? 60 degrees? ...
... Plot the R-C circuit phase vs frequency over the same range 10Hz to 100kHz. Setup the CRO to plot input Amplitude on the X axis and Output amplitude on the Y axis. What angle on the CRO is represented as 0 degrees? Find the frequency where the phase is 15 degrees? 30 degrees? 45 degrees? 60 degrees? ...
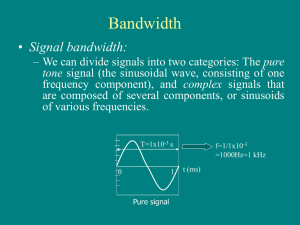
Bandwidth - Studyeland
... signals. The HDTV screen is normally a ratio of 16 : 9. There are 1920 by 1080 pixels per screen, and the screen is renewed 30 times per second. Twenty-four bits represents one color pixel. ...
... signals. The HDTV screen is normally a ratio of 16 : 9. There are 1920 by 1080 pixels per screen, and the screen is renewed 30 times per second. Twenty-four bits represents one color pixel. ...
Dec 2002 2500V/µs Slew Rate Op Amps Process Large Signals with Low Distortion at High Frequencies
... bandwidth product and 2500V/µs slew rate. The parts operate with supplies from ±2V to ±6V and draw a typical supply current of only 9mA per amplifier. The amplifiers can drive 100Ω loads with a low distortion of –85dBc relative to a 5MHz, 2VP–P signal. In single 5V supply applications, the output sw ...
... bandwidth product and 2500V/µs slew rate. The parts operate with supplies from ±2V to ±6V and draw a typical supply current of only 9mA per amplifier. The amplifiers can drive 100Ω loads with a low distortion of –85dBc relative to a 5MHz, 2VP–P signal. In single 5V supply applications, the output sw ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).