Biofeedback Tension Monitor
... potential divider comprising R2, VR2 and R3. VR1 adjusts the input current to pin3. Feed back is provided through VR3 which adjusts the gain of the amplifier. With this arrangement- R1 and VR3- the amplifier can give very high gain. Thus the skin resistance is converted by the amplifier into corresp ...
... potential divider comprising R2, VR2 and R3. VR1 adjusts the input current to pin3. Feed back is provided through VR3 which adjusts the gain of the amplifier. With this arrangement- R1 and VR3- the amplifier can give very high gain. Thus the skin resistance is converted by the amplifier into corresp ...
EUP6514 5V/12V Synchronous Buck PWM Controller
... Upper gate driver output. Connect to the gate of high-side power N-Channel MOSEFT. This pin is monitored by the adaptive shoot-through protection circuitry to determine when the upper MOSFET has turned off. Both signal and power ground for the IC. All voltage levels are measured with respect to this ...
... Upper gate driver output. Connect to the gate of high-side power N-Channel MOSEFT. This pin is monitored by the adaptive shoot-through protection circuitry to determine when the upper MOSFET has turned off. Both signal and power ground for the IC. All voltage levels are measured with respect to this ...
ada03
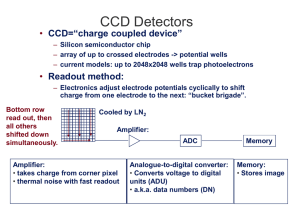
... Cosmic-ray hits limit exposure times Saturation via wells filling up and limited ADC range Charge “bleeding” down columns, then across rows Blemishes (charge traps, hot pixels) Gaps between pixels ...
... Cosmic-ray hits limit exposure times Saturation via wells filling up and limited ADC range Charge “bleeding” down columns, then across rows Blemishes (charge traps, hot pixels) Gaps between pixels ...
Lecture 7 Overview - University of Delaware
... • The amplifier measures voltage across RIN, then generates a voltage which is larger by a factor A • This voltage generator, in series with the output resistance ROUT, is connected to the output port. • A should be a constant (i.e. gain is linear) ...
... • The amplifier measures voltage across RIN, then generates a voltage which is larger by a factor A • This voltage generator, in series with the output resistance ROUT, is connected to the output port. • A should be a constant (i.e. gain is linear) ...
Lecture 15 - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... words, the source VIN only needs to supply a little power (since IIN = 0), whereas the output can drive a powerhungry load (with the op-amp providing the power). EECS40, Fall 2004 ...
... words, the source VIN only needs to supply a little power (since IIN = 0), whereas the output can drive a powerhungry load (with the op-amp providing the power). EECS40, Fall 2004 ...
ADS7815 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... into a microcontroller or DSP even if the ADS7815 is not connected to shared bus. The reason for this is that during a conversion, the ADS7815 outputs are tri-stated. The only chance to read the outputs are during the acquisition period. And, this is not recommended if the data will be read just pri ...
... into a microcontroller or DSP even if the ADS7815 is not connected to shared bus. The reason for this is that during a conversion, the ADS7815 outputs are tri-stated. The only chance to read the outputs are during the acquisition period. And, this is not recommended if the data will be read just pri ...
MAX107 Dual, 6-Bit, 400Msps ADC with On-Chip, Wideband Input Amplifier General Description
... bandwidth. Matching channel-to-channel performance is typically 0.04dB gain, 0.1LSB offset, and 0.2 degrees phase. Dynamic performance is 36.7dB signal-to-noise plus distortion (SINAD) with a 125MHz analog input signal and a sampling speed of 400MHz. A fully differential comparator design and encodi ...
... bandwidth. Matching channel-to-channel performance is typically 0.04dB gain, 0.1LSB offset, and 0.2 degrees phase. Dynamic performance is 36.7dB signal-to-noise plus distortion (SINAD) with a 125MHz analog input signal and a sampling speed of 400MHz. A fully differential comparator design and encodi ...
MOS Inverter: Static Characteristics
... The inverter is the most fundamental logic gate that performs a Boolean operation on a single input variable. Many basic principles employed in the design and analysis of MOS inverters can be directly applied to more complex circuits such as NAND, NOR and XOR, XNOR gates. The inverter operation is s ...
... The inverter is the most fundamental logic gate that performs a Boolean operation on a single input variable. Many basic principles employed in the design and analysis of MOS inverters can be directly applied to more complex circuits such as NAND, NOR and XOR, XNOR gates. The inverter operation is s ...
B. Front end electronics - GAE
... time structure is becoming more extended. This is because the measuring instrument can see only the lower part of the shower where the e-e+ have few times lower energy than in those high-up and correspondingly they can undergo scattering under larger angles, i.e. the lower part has larger lateral ex ...
... time structure is becoming more extended. This is because the measuring instrument can see only the lower part of the shower where the e-e+ have few times lower energy than in those high-up and correspondingly they can undergo scattering under larger angles, i.e. the lower part has larger lateral ex ...
AdaptaBeacon® PLC Compatible Strobe Light
... Designed for indoor or outdoor installation. May be direct, 1/2” (13mm) conduit, or box mounted on a 4” (102mm) octagon box. For weatherproof installation, units must be mounted ...
... Designed for indoor or outdoor installation. May be direct, 1/2” (13mm) conduit, or box mounted on a 4” (102mm) octagon box. For weatherproof installation, units must be mounted ...
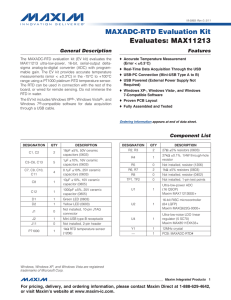
General Description Features
... a USB cable. The MAXADC-RTD provides accurate temperature-measurement readings in the -15NC to +100NC range and does not require an external power supply or a USB device driver. The RTD is soldered on a stick, which can be connected to the rest of the PCB or broken off for remote monitoring. The RTD ...
... a USB cable. The MAXADC-RTD provides accurate temperature-measurement readings in the -15NC to +100NC range and does not require an external power supply or a USB device driver. The RTD is soldered on a stick, which can be connected to the rest of the PCB or broken off for remote monitoring. The RTD ...
ad515a data sheet
... internal compensation, which minimize required external components and eliminate the need for adjustments to the device itself. The major considerations in applying this device are the external problems of layout and heat control which have already been discussed. In circuit situations employing the ...
... internal compensation, which minimize required external components and eliminate the need for adjustments to the device itself. The major considerations in applying this device are the external problems of layout and heat control which have already been discussed. In circuit situations employing the ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).