NTE74LS624 Integrated Circuit TTL − Voltage Controlled Oscillator
... is provided fo the enable, synchronization−gating, and output sections, and a separate set (OSC VCC and OSC GND) is provided for the oscillator and associated frequency−control circuits so that effective isolation can be accomplished in the system. For operation of frequencies greater than 10Mhz, it ...
... is provided fo the enable, synchronization−gating, and output sections, and a separate set (OSC VCC and OSC GND) is provided for the oscillator and associated frequency−control circuits so that effective isolation can be accomplished in the system. For operation of frequencies greater than 10Mhz, it ...
AD7470 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled using standard control inputs, allowing easy interfacing to microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal is sampled on the falling edge of CONVST, and conversion is also initiated at this point. BUSY goes high at the start of conversion and goe ...
... The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled using standard control inputs, allowing easy interfacing to microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal is sampled on the falling edge of CONVST, and conversion is also initiated at this point. BUSY goes high at the start of conversion and goe ...
AD807 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... gain, and thus very large jitter can be tracked with small phase errors between input data and recovered clock. At frequencies closer to the loop bandwidth, the gain of the integrator is much smaller, and thus less input jitter can be tolerated. The AD807 output will have a bit error rate less than ...
... gain, and thus very large jitter can be tracked with small phase errors between input data and recovered clock. At frequencies closer to the loop bandwidth, the gain of the integrator is much smaller, and thus less input jitter can be tolerated. The AD807 output will have a bit error rate less than ...
lampiran - UniMAP Portal
... Diode limiters are wave-shaping circuits: can be used to prevent signal voltages from going above or below certain levels. The limiting level may be either equal to the diode’s barrier potential or made variable with a dc source voltage. These circuits are sometimes called clippers because of its cl ...
... Diode limiters are wave-shaping circuits: can be used to prevent signal voltages from going above or below certain levels. The limiting level may be either equal to the diode’s barrier potential or made variable with a dc source voltage. These circuits are sometimes called clippers because of its cl ...
Ecograph A Advanced Paperless Recorder
... • ReadWin® 2000 PC software package part of delivery • Serial interface, Ethernet or modem communication • Totalisation (integration) of analogue input signals as standard • Min., max., average value recording • Display of the last 7 analyses front end on the unit • Loop power supply as an option • ...
... • ReadWin® 2000 PC software package part of delivery • Serial interface, Ethernet or modem communication • Totalisation (integration) of analogue input signals as standard • Min., max., average value recording • Display of the last 7 analyses front end on the unit • Loop power supply as an option • ...
MAX378/MAX379 High-Voltage, Fault-Protected Analog Multiplexers _______________General Description
... stored charge from internal nodes, and does not compromise the fault-protection scheme. Figure 10 shows the condition of the ON channel with V+ and V- present. With input voltages less than ±10V, all three FETs are on and the input signal appears at the output. If the input voltage exceeds V+ minus ...
... stored charge from internal nodes, and does not compromise the fault-protection scheme. Figure 10 shows the condition of the ON channel with V+ and V- present. With input voltages less than ±10V, all three FETs are on and the input signal appears at the output. If the input voltage exceeds V+ minus ...
There are various ways to measure or detect the amplitude (as
... The circuit relies upon the behavior of the diode — allowing current through when the input is +Ve with respect to the capacitor voltage, hence ‘topping up’ the capacitor voltage to the peak level, but blocking any current from flowing back out through the diode when the input voltage is below the c ...
... The circuit relies upon the behavior of the diode — allowing current through when the input is +Ve with respect to the capacitor voltage, hence ‘topping up’ the capacitor voltage to the peak level, but blocking any current from flowing back out through the diode when the input voltage is below the c ...
Physical Layer definitions
... transmitting analog signals without regard to their content (i.e., the signals may represent analog data or digital data). transmissions are attenuated over distance. Analog signal – the analog transmission system uses amplifiers to boost the energy in the signal. Networks: Physical Layer ...
... transmitting analog signals without regard to their content (i.e., the signals may represent analog data or digital data). transmissions are attenuated over distance. Analog signal – the analog transmission system uses amplifiers to boost the energy in the signal. Networks: Physical Layer ...
Chapter 5
... • Note that the gain here is positive, thus the amplifier is noninverting • Also note that this amplifier retains the infinite input impedance of the op-amp • One aspect of this amplifier’s gain is that it can never go below 1. • One could replace the feedback resistor with a wire and disconnect the ...
... • Note that the gain here is positive, thus the amplifier is noninverting • Also note that this amplifier retains the infinite input impedance of the op-amp • One aspect of this amplifier’s gain is that it can never go below 1. • One could replace the feedback resistor with a wire and disconnect the ...
Chapter 5
... • Note that the gain here is positive, thus the amplifier is noninverting • Also note that this amplifier retains the infinite input impedance of the op-amp • One aspect of this amplifier’s gain is that it can never go below 1. • One could replace the feedback resistor with a wire and disconnect the ...
... • Note that the gain here is positive, thus the amplifier is noninverting • Also note that this amplifier retains the infinite input impedance of the op-amp • One aspect of this amplifier’s gain is that it can never go below 1. • One could replace the feedback resistor with a wire and disconnect the ...
Series 94 Peaktronics Positioner
... The DHC positioner is a high performance, high resolution digital positioner. A simple threebutton control is used to configure ALL parameters that the unit needs for a variety of applications, and eliminates the need for special meters and/or tools for calibration. As long as there is supply power, ...
... The DHC positioner is a high performance, high resolution digital positioner. A simple threebutton control is used to configure ALL parameters that the unit needs for a variety of applications, and eliminates the need for special meters and/or tools for calibration. As long as there is supply power, ...
Ultrasonic Distance Measurement
... found in the CN0343 Design Support Package at http://www.analog.com/CN0343-DesignSupport in the CN0343-SourceCode.zip file. ...
... found in the CN0343 Design Support Package at http://www.analog.com/CN0343-DesignSupport in the CN0343-SourceCode.zip file. ...
INA116 - Texas Instruments
... terminal layout. Since traces are not required to run between device pins, this layout is easily accomplished, even with the surface mount package. The guards should completely encircle their respective input connections—see Figure 4. Both sides of the circuit board should be guarded, even if only o ...
... terminal layout. Since traces are not required to run between device pins, this layout is easily accomplished, even with the surface mount package. The guards should completely encircle their respective input connections—see Figure 4. Both sides of the circuit board should be guarded, even if only o ...
a 1.75 MSPS, 4 mW 10-Bit/12-Bit Parallel ADCs AD7470/AD7472
... The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled using standard control inputs, allowing easy interfacing to microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal is sampled on the falling edge of CONVST, and conversion is also initiated at this point. BUSY goes high at the start of conversion and goe ...
... The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled using standard control inputs, allowing easy interfacing to microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal is sampled on the falling edge of CONVST, and conversion is also initiated at this point. BUSY goes high at the start of conversion and goe ...
AD8200 High Common-Mode Voltage, Single
... In many transducer applications, it is necessary to filter the signal to remove spurious high frequency components, including noise, or to extract the mean value of a fluctuating signal with a peak-to-average ratio (PAR) greater than unity. For example, a full-wave rectified sinusoid has a PAR of 1. ...
... In many transducer applications, it is necessary to filter the signal to remove spurious high frequency components, including noise, or to extract the mean value of a fluctuating signal with a peak-to-average ratio (PAR) greater than unity. For example, a full-wave rectified sinusoid has a PAR of 1. ...
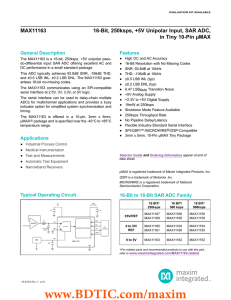
MAX11162 16-Bit, 500ksps, +5V Unipolar Input, SAR ADC, in Tiny 10-Pin µMAX
... The MAX11162 is a 16-bit single-channel, pseudo-differential SAR ADC with maximum throughput rates of 500ksps. This ADC measures a unipolar input voltage interval from 0V to VREF. The external reference interval ranges from 2.5V to VDD. Both inputs, AIN+ and AIN-, are sampled with an integrated pseu ...
... The MAX11162 is a 16-bit single-channel, pseudo-differential SAR ADC with maximum throughput rates of 500ksps. This ADC measures a unipolar input voltage interval from 0V to VREF. The external reference interval ranges from 2.5V to VDD. Both inputs, AIN+ and AIN-, are sampled with an integrated pseu ...
MAX11163 16-Bit, 250ksps, +5V Unipolar Input, SAR ADC, in Tiny 10-Pin µMAX
... The MAX11163 is a 16-bit single-channel, pseudo-differential SAR ADC with maximum throughput rates of 250ksps. This ADC measures a unipolar input voltage interval from 0V to VREF. The external reference interval ranges from 2.5V to VDD. Both inputs, AIN+ and AIN-, are sampled with an integrated pseu ...
... The MAX11163 is a 16-bit single-channel, pseudo-differential SAR ADC with maximum throughput rates of 250ksps. This ADC measures a unipolar input voltage interval from 0V to VREF. The external reference interval ranges from 2.5V to VDD. Both inputs, AIN+ and AIN-, are sampled with an integrated pseu ...
Circuit Note CN-0214
... via a lookup table. These two voltages are added together to give the absolute value at the thermocouple. First, the voltage measured between the two wires of the thermocouple (V1). The RTD voltage is measured, converted to a temperature via a lookup table and this temperature is then converted to i ...
... via a lookup table. These two voltages are added together to give the absolute value at the thermocouple. First, the voltage measured between the two wires of the thermocouple (V1). The RTD voltage is measured, converted to a temperature via a lookup table and this temperature is then converted to i ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).