8-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converters With Serial
... NOTES: 3. Analog input voltages greater than that applied to REF+ convert to all ones (11111111), while input voltages less than that applied to REF– convert to all zeros (00000000). For proper operation, the positive reference voltage Vref+, must be at least 1 V greater than the negative reference ...
... NOTES: 3. Analog input voltages greater than that applied to REF+ convert to all ones (11111111), while input voltages less than that applied to REF– convert to all zeros (00000000). For proper operation, the positive reference voltage Vref+, must be at least 1 V greater than the negative reference ...
vxr15-2800s series
... low line. The voltage drop and the actual voltage at the input to the converter will determine the minimum source voltage at which the converter will operate. A high source inductance can interact with the feedback control loop of the converter. VPT’s EMI filters will typically isolate the source an ...
... low line. The voltage drop and the actual voltage at the input to the converter will determine the minimum source voltage at which the converter will operate. A high source inductance can interact with the feedback control loop of the converter. VPT’s EMI filters will typically isolate the source an ...
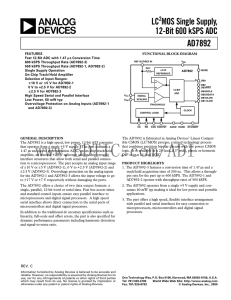
AD7892: LC2MOS Single Supply, 12-Bit 600 kSPS ADC Data Sheet (Rev C, 06/2000)
... microprocessors and digital signal processors. A high speed serial interface allows direct connection to the serial ports of microcontrollers and digital signal processors. In addition to the traditional dc accuracy specifications such as linearity, full-scale and offset errors, the part is also spe ...
... microprocessors and digital signal processors. A high speed serial interface allows direct connection to the serial ports of microcontrollers and digital signal processors. In addition to the traditional dc accuracy specifications such as linearity, full-scale and offset errors, the part is also spe ...
AD7741
... Frequency Output. This pin provides the output of the synchronous VFC. Power Supply Input. These parts can be operated from +4.75 V to +5.25 V and the supply should be adequately decoupled to GND. Ground reference point for all circuitry on the part. Address Inputs used to select the input channel c ...
... Frequency Output. This pin provides the output of the synchronous VFC. Power Supply Input. These parts can be operated from +4.75 V to +5.25 V and the supply should be adequately decoupled to GND. Ground reference point for all circuitry on the part. Address Inputs used to select the input channel c ...
LTC1151 - Dual ±15V Zero-Drift Operational Amplifier
... Gain-Bandwidth Product Supply Current per Amplifier ...
... Gain-Bandwidth Product Supply Current per Amplifier ...
signals and noise
... -shielding consists of surrounding a circuit, or some of the wires in a circuit with a conducting material that is attached to earth ground -this allows electromagnetic radiation to be absorbed by the shield thus avoiding noise generation in the instrument circuit -important when using high-impedanc ...
... -shielding consists of surrounding a circuit, or some of the wires in a circuit with a conducting material that is attached to earth ground -this allows electromagnetic radiation to be absorbed by the shield thus avoiding noise generation in the instrument circuit -important when using high-impedanc ...
Experimental results
... PWM. As CCPs deploys IGBT’s so that the conduction losses are function of average rather than rms current so high peaks are not so detrimental. The paper describes the prototype capacitor charging power supply that has been designed, assembled and tested upto full power. ...
... PWM. As CCPs deploys IGBT’s so that the conduction losses are function of average rather than rms current so high peaks are not so detrimental. The paper describes the prototype capacitor charging power supply that has been designed, assembled and tested upto full power. ...
MAX11156 18-Bit, 500ksps, ±5V SAR ADC with Internal Reference in TDFN General Description
... small size, and internal reference. The MAX11156 measures a ±5V (10VP-P) input range while operating from a single 5V supply. A patented charge-pump architecture allows direct sampling of high- impedance sources. The MAX11156 integrates an optional 6ppm/°C reference with internal buffer, saving the ...
... small size, and internal reference. The MAX11156 measures a ±5V (10VP-P) input range while operating from a single 5V supply. A patented charge-pump architecture allows direct sampling of high- impedance sources. The MAX11156 integrates an optional 6ppm/°C reference with internal buffer, saving the ...
73101 Pocket Digital Multimeter
... Do not mistake the following for a malfunction! • In DC voltage measurement, the Auto Hold function is only available for range over 4V. • The Auto Hold function cannot be applied to unstable signals. ...
... Do not mistake the following for a malfunction! • In DC voltage measurement, the Auto Hold function is only available for range over 4V. • The Auto Hold function cannot be applied to unstable signals. ...
KTA-249 UV Solar and Anemometer Modbus Interface
... resistance of 20,000 Ohms. A calibration register allows the user to set a different value to more accurately match the KTA-249 to a particular anemometer. In most cases this register should be left set to 20000. Temperature Sensor: A dedicated connection is not included for using the DS18S20 temper ...
... resistance of 20,000 Ohms. A calibration register allows the user to set a different value to more accurately match the KTA-249 to a particular anemometer. In most cases this register should be left set to 20000. Temperature Sensor: A dedicated connection is not included for using the DS18S20 temper ...
AD8041
... The output voltage swing extends to within 50 mV of each rail, providing the maximum output dynamic range. Additionally, it features gain flatness of 0.1 dB to 30 MHz while offering differential gain and phase error of 0.03% and 0.03° on a single 5 V supply. This makes the AD8041 ideal for professio ...
... The output voltage swing extends to within 50 mV of each rail, providing the maximum output dynamic range. Additionally, it features gain flatness of 0.1 dB to 30 MHz while offering differential gain and phase error of 0.03% and 0.03° on a single 5 V supply. This makes the AD8041 ideal for professio ...
Ultrasound Physics Volume I
... slide, the basic angles between 0 and 90 degrees (inclusively) are shown, but the cosine values are also given in the table for angles greater than 90 degrees. From this table it should be evident that 45 degrees is basically the “same” angle as 135 degrees, 225 degrees, and 315 degrees (not shown), ...
... slide, the basic angles between 0 and 90 degrees (inclusively) are shown, but the cosine values are also given in the table for angles greater than 90 degrees. From this table it should be evident that 45 degrees is basically the “same” angle as 135 degrees, 225 degrees, and 315 degrees (not shown), ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).