LTC1152 - Rail-to-Rail Input Rail-to-Rail Output Zero-Drift Op Amp
... exhibit aliasing behavior and clock noise at frequencies near the internal 2.3kHz sampling frequency. The LTC1152 includes an internal anti-aliasing circuit to keep these error terms to a minimum. As a rule, alias frequencies will be down by (80dB – ACLG) in most standard amplifier configurations, w ...
... exhibit aliasing behavior and clock noise at frequencies near the internal 2.3kHz sampling frequency. The LTC1152 includes an internal anti-aliasing circuit to keep these error terms to a minimum. As a rule, alias frequencies will be down by (80dB – ACLG) in most standard amplifier configurations, w ...
AN3 - Applications for a Switched-Capacitor Instrumentation Building Block
... sampled data systems which approximate continuous functions with bandwidth limited by the sampling frequency. Their operation is described in the distribution of charge over time. To best understand the circuits which follow, this distinction should be kept in mind. Analog sampled data and carrier-b ...
... sampled data systems which approximate continuous functions with bandwidth limited by the sampling frequency. Their operation is described in the distribution of charge over time. To best understand the circuits which follow, this distinction should be kept in mind. Analog sampled data and carrier-b ...
W. Inam, K.K. Afridi and D.J. Perreault, “Variable Frequency Multiplier Technique for High Efficiency Conversion Over a Wide Operating Range,” 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition , Sept. 2014.
... cannot be optimally designed. Furthermore, circulating currents may increase proportionally as load is decreased resulting in higher losses at light loads. With phase shift control, operation over a wide range is likewise challenging. In many resonant converters, when two legs of the inverter are ph ...
... cannot be optimally designed. Furthermore, circulating currents may increase proportionally as load is decreased resulting in higher losses at light loads. With phase shift control, operation over a wide range is likewise challenging. In many resonant converters, when two legs of the inverter are ph ...
lecture1428911481
... DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS:Instruments rarely respond instantaneously to changes in the measured variables. Instead, they exhibit slowness or sluggishness due to such things as mass, thermal capacitance, fluid capacitance or electric capacitance. In addition to this, pure delay in time is often encou ...
... DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS:Instruments rarely respond instantaneously to changes in the measured variables. Instead, they exhibit slowness or sluggishness due to such things as mass, thermal capacitance, fluid capacitance or electric capacitance. In addition to this, pure delay in time is often encou ...
LTC6360 - Very Low Noise Single-Ended SAR ADC Driver with True Zero Output
... While powered from a single 5V supply, the amplifier output can swing to 0V while maintaining high linearity. This is made possible with the inclusion of a very low noise on-chip charge pump that generates a negative voltage to bias the output stage of the amplifier, increasing the allowable negativ ...
... While powered from a single 5V supply, the amplifier output can swing to 0V while maintaining high linearity. This is made possible with the inclusion of a very low noise on-chip charge pump that generates a negative voltage to bias the output stage of the amplifier, increasing the allowable negativ ...
BM1410A
... converter. A low ESR capacitor is highly recommended. Since large current flows in and out of this capacitor during switching, its ESR also affects efficiency. ...
... converter. A low ESR capacitor is highly recommended. Since large current flows in and out of this capacitor during switching, its ESR also affects efficiency. ...
Operational Amplifiers and Applications Lecture Slides
... Successive Approximation ADC • Binary search is used by the SAL to determine vX. • n-bit conversion needs n clock periods. Speed is limited by the time taken by the DAC output to settle within a fraction of an LSB of VFS , and by the comparator to respond to input signals differing by small amounts ...
... Successive Approximation ADC • Binary search is used by the SAL to determine vX. • n-bit conversion needs n clock periods. Speed is limited by the time taken by the DAC output to settle within a fraction of an LSB of VFS , and by the comparator to respond to input signals differing by small amounts ...
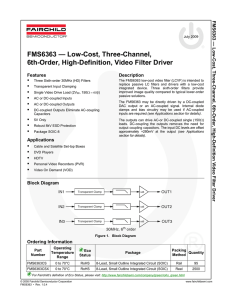
FMS6363 — Low-Cost, Three-Channel, 6th-Order, High-Definition, Video Filter Driver FM S6363 — Low-
... without notice. Please note the revision and/or date on the drawing and contact a Fairchild Semiconductor representative to verify or obtain the most recent revision. Package specifications do not expand the terms of Fairchild’s worldwide terms and conditions, specifically the warranty therein, whic ...
... without notice. Please note the revision and/or date on the drawing and contact a Fairchild Semiconductor representative to verify or obtain the most recent revision. Package specifications do not expand the terms of Fairchild’s worldwide terms and conditions, specifically the warranty therein, whic ...
Inverting amplifier
... • If a high gain of, for example 100, is required this means that the ratio of R2 : R1 is 100. It is good practice to keep the resistors in op amp circuits within reasonable bounds. In view of this the maximum value for R2 should be 1 M Ohm. This means that the input resistor and hence the input res ...
... • If a high gain of, for example 100, is required this means that the ratio of R2 : R1 is 100. It is good practice to keep the resistors in op amp circuits within reasonable bounds. In view of this the maximum value for R2 should be 1 M Ohm. This means that the input resistor and hence the input res ...
Q point
... The point of intersection of IBQ characteristics and load line is “Qpoint” “Q point” is thus point on the load line representing dc bias conditions of the amplifier circuit ...
... The point of intersection of IBQ characteristics and load line is “Qpoint” “Q point” is thus point on the load line representing dc bias conditions of the amplifier circuit ...
Chapter 11 Homework - Digilent Learn site
... 11.1 For the circuit below, the input voltage Vin(t) = 3cos(2t-20) – 2cos(3t+30) + cos(4t). Determine: a. The steady-state response of the voltage v(t). b. The steady-state response of the current iR(t). (Hint: take advantage of your results from part a) 1Ω ...
... 11.1 For the circuit below, the input voltage Vin(t) = 3cos(2t-20) – 2cos(3t+30) + cos(4t). Determine: a. The steady-state response of the voltage v(t). b. The steady-state response of the current iR(t). (Hint: take advantage of your results from part a) 1Ω ...
MAX5302 Low-Power, 12-Bit Voltage-Output DAC with Serial Interface __________________General Description
... bits (C2, C1, C0), followed by the 12+1 data bits D11...D0, S0 (Figure 4). Set the sub-bit (S0) to zero. The 3-bit control code determines the register to be updated and the configuration when exiting shutdown. Figures 5 and 6 show the serial-interface timing requirements. The chip-select (CS) pin m ...
... bits (C2, C1, C0), followed by the 12+1 data bits D11...D0, S0 (Figure 4). Set the sub-bit (S0) to zero. The 3-bit control code determines the register to be updated and the configuration when exiting shutdown. Figures 5 and 6 show the serial-interface timing requirements. The chip-select (CS) pin m ...
Frequency Response of Sensors
... mechanical components are involved, they possess mass and in themselves tend to restrict rapid force changes. Virtually everything you ever want to know about a mechanical system occurs at frequencies below 100 Hz, with probably +90% of the action occuring below 30 Hz. As a final note, instrumentati ...
... mechanical components are involved, they possess mass and in themselves tend to restrict rapid force changes. Virtually everything you ever want to know about a mechanical system occurs at frequencies below 100 Hz, with probably +90% of the action occuring below 30 Hz. As a final note, instrumentati ...
GaGe PCIe/PCI Digitizer Data Sheet
... CH 1 or 2, EXT or manual Internal: ±2% of Full Scale External: ±10% of Full Scale Positive or Negative 5% of Full Scale Signal swing must be at least 5% of full scale in order to cause a trigger event. Smaller signals are rejected as noise. 64 points minimum May be increased with 64 point resolut ...
... CH 1 or 2, EXT or manual Internal: ±2% of Full Scale External: ±10% of Full Scale Positive or Negative 5% of Full Scale Signal swing must be at least 5% of full scale in order to cause a trigger event. Smaller signals are rejected as noise. 64 points minimum May be increased with 64 point resolut ...
MAX1132/MAX1133 16-Bit ADC, 200ksps, 5V Single-Supply with Reference General Description
... Note 1: Tested at AVDD = DVDD = +5V, bipolar input mode. Note 2: Relative accuracy is the deviation of the analog value at any code from its theoretical value after the gain error and offset error have been nulled. Note 3: Offset nulled. Note 4: Conversion time is defined as the number of clock cycl ...
... Note 1: Tested at AVDD = DVDD = +5V, bipolar input mode. Note 2: Relative accuracy is the deviation of the analog value at any code from its theoretical value after the gain error and offset error have been nulled. Note 3: Offset nulled. Note 4: Conversion time is defined as the number of clock cycl ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).