EDIBON
... The Transducers and Instrumentation Trainer “SAIT” shows didactically the function principles of the transducers most used in industry. It is divided into two parts: the lower part, in which all the input and output transducers are found, while in the upper part, the system of signal conditioning an ...
... The Transducers and Instrumentation Trainer “SAIT” shows didactically the function principles of the transducers most used in industry. It is divided into two parts: the lower part, in which all the input and output transducers are found, while in the upper part, the system of signal conditioning an ...
5.5. Darlington configurations
... that no current is flowing in the roS resistor. This is so because the contributions (think superposition!) of the small-signal sources are equal in magnitudes but different in signs. No current through roS means no voltage drop across it, hence, we can ground the emitters of both the transistors wi ...
... that no current is flowing in the roS resistor. This is so because the contributions (think superposition!) of the small-signal sources are equal in magnitudes but different in signs. No current through roS means no voltage drop across it, hence, we can ground the emitters of both the transistors wi ...
DAC715 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specific ...
... The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specific ...
High Frequency Divider/PLL Synthesizer ADF4007 FEATURES
... The reference input signal is applied to the circuit at FREFIN and, in this case, is terminated in 50 Ω. Many systems would have either a TCXO or an OCXO driving the reference input without any 50 Ω termination. To bias the REFIN pin at AVDD/2, ac coupling is used. The value of the coupling capacito ...
... The reference input signal is applied to the circuit at FREFIN and, in this case, is terminated in 50 Ω. Many systems would have either a TCXO or an OCXO driving the reference input without any 50 Ω termination. To bias the REFIN pin at AVDD/2, ac coupling is used. The value of the coupling capacito ...
Balanced Modulator/Demodulator AD630
... which is used to select the active front end. The rapid response time of this comparator coupled with the high slew rate and fast settling of the linear amplifiers minimize switching distortion. In addition, the AD630 has extremely low crosstalk between channels of –100 dB @ 10 kHz. The AD630 is int ...
... which is used to select the active front end. The rapid response time of this comparator coupled with the high slew rate and fast settling of the linear amplifiers minimize switching distortion. In addition, the AD630 has extremely low crosstalk between channels of –100 dB @ 10 kHz. The AD630 is int ...
Article - I
... This paper presents the design of a zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and zero-current switching (ZCS) PWM SEPIC dc/dc converter for high power LED applications. The proposed circuit using a novel lossless commutation cell for high switching frequency operation. The most important property in this circui ...
... This paper presents the design of a zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and zero-current switching (ZCS) PWM SEPIC dc/dc converter for high power LED applications. The proposed circuit using a novel lossless commutation cell for high switching frequency operation. The most important property in this circui ...
isscc 2014 / session 12 / sensors, mems, and displays / 12.8
... standard CMOS. Its interface electronics consists of a continuous-time dutycycle modulator [1], whose output can be easily interfaced to a microcontroller, rather than the discrete-time ΔΣ modulators of most previous work [2-4]. This approach leads to high resolution (3mK in a 2.2ms measurement time ...
... standard CMOS. Its interface electronics consists of a continuous-time dutycycle modulator [1], whose output can be easily interfaced to a microcontroller, rather than the discrete-time ΔΣ modulators of most previous work [2-4]. This approach leads to high resolution (3mK in a 2.2ms measurement time ...
AD8565/AD8566/AD8567 (Rev. G)
... Q6 to Q8 over the range from (VNEG + 1 V) to (VPOS − 1 V). Outside this range, the input bias current is dominated by the sum of base currents of Q10 to Q11 for input signals close to VNEG and of Q6 to Q8 (Q10 to Q11) for signals close to VPOS. From this type of design, the input bias current of the ...
... Q6 to Q8 over the range from (VNEG + 1 V) to (VPOS − 1 V). Outside this range, the input bias current is dominated by the sum of base currents of Q10 to Q11 for input signals close to VNEG and of Q6 to Q8 (Q10 to Q11) for signals close to VPOS. From this type of design, the input bias current of the ...
angle modulation
... of the RX which proportional to the square of modulation index. Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (mi ...
... of the RX which proportional to the square of modulation index. Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (mi ...
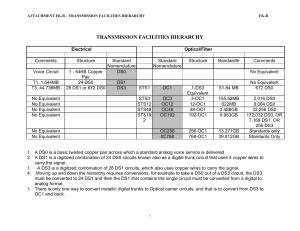
Attachment A – Transmission Facilities Hierarchy
... 2. A DS1 is a digitized combination of 24 DS0 circuits known also as a digital trunk circuit that uses 4 copper wires to carry the signal. 3. A DS3 is a digitized combination of 28 DS1 circuits, which also uses copper wires to carry the signal. 4. Moving up and down the hierarchy requires conversion ...
... 2. A DS1 is a digitized combination of 24 DS0 circuits known also as a digital trunk circuit that uses 4 copper wires to carry the signal. 3. A DS3 is a digitized combination of 28 DS1 circuits, which also uses copper wires to carry the signal. 4. Moving up and down the hierarchy requires conversion ...
Circuit Characteristics
... to the output terminals, unlike 74H and 74S where it is returned to ground which is a more power consuming configuration. This configuration allows the output to pull up to one VBE below VCC for low values of output current. The F00 output includes clamping diodes to limit undershoot and control rin ...
... to the output terminals, unlike 74H and 74S where it is returned to ground which is a more power consuming configuration. This configuration allows the output to pull up to one VBE below VCC for low values of output current. The F00 output includes clamping diodes to limit undershoot and control rin ...
0.05 uV/C max, Single-Supply CMOS
... The input common-mode range extends from (V–) – 0.1 V to (V+) – 1.5 V. For normal operation, the inputs must be limited to this range. The common-mode rejection ratio is only valid within the valid input common-mode range. A lower supply voltage results in lower input common-mode range; therefore, a ...
... The input common-mode range extends from (V–) – 0.1 V to (V+) – 1.5 V. For normal operation, the inputs must be limited to this range. The common-mode rejection ratio is only valid within the valid input common-mode range. A lower supply voltage results in lower input common-mode range; therefore, a ...
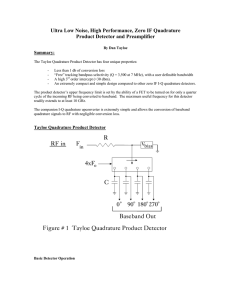
Tayloe Mixer
... Mixers generally produce sum and difference outputs. In zero IF applications, the difference frequency is used, while the sum is thrown away. Therefore, the conversion loss using an ideal mixer is at least 3 db, with a typical conversion loss of 4-6 db in practice. Conversely, this design is not a m ...
... Mixers generally produce sum and difference outputs. In zero IF applications, the difference frequency is used, while the sum is thrown away. Therefore, the conversion loss using an ideal mixer is at least 3 db, with a typical conversion loss of 4-6 db in practice. Conversely, this design is not a m ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).