LM3916 Dot/Bar Display Driver (Rev. A)
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
doc - Rutgers Engineering
... The general circuit for the Thevenin equivalent circuit model is provided in figure 1. The idea behind any equivalent circuit is that a simpler well-understood circuit can be used to replace a more complex circuit between two nodes of the circuit. In applying this circuit technique, we are only requ ...
... The general circuit for the Thevenin equivalent circuit model is provided in figure 1. The idea behind any equivalent circuit is that a simpler well-understood circuit can be used to replace a more complex circuit between two nodes of the circuit. In applying this circuit technique, we are only requ ...
a Precision Instrumentation Amplifier AD624
... merit for instrumentation amplifiers. While initial offset may be adjusted to zero, shifts in offset voltage due to temperature variations will cause errors. Intelligent systems can often correct for this factor with an autozero cycle, but there are many smallsignal high-gain applications that don’t ...
... merit for instrumentation amplifiers. While initial offset may be adjusted to zero, shifts in offset voltage due to temperature variations will cause errors. Intelligent systems can often correct for this factor with an autozero cycle, but there are many smallsignal high-gain applications that don’t ...
MAX3746 Low-Power, 622Mbps to 3.2Gbps Limiting Amplifier General Description
... Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Expo ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Expo ...
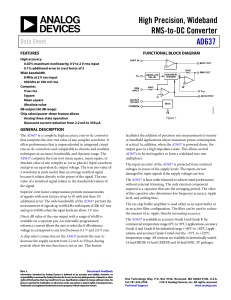
a AN-555 APPLICATION NOTE
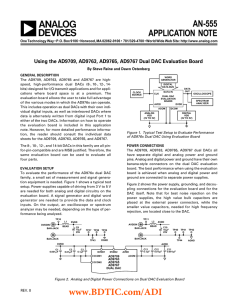
... clock and control lines for the AD976x, and are 50 Ω terminated. The selection of JP9 also allows the user to select a clock generated on the same digital data bus as the input data. Jumpers JP1 to JP7, JP9, and JP16 control the clock inputs for the various clock modes in which the dual DACs can ope ...
... clock and control lines for the AD976x, and are 50 Ω terminated. The selection of JP9 also allows the user to select a clock generated on the same digital data bus as the input data. Jumpers JP1 to JP7, JP9, and JP16 control the clock inputs for the various clock modes in which the dual DACs can ope ...
MAX44205 180MHz, Low-Noise, Low-Distortion, Fully Differential
... clamping solution ensures that the buffer output does not violate the ADC’s maximum input voltage range, even if the MAX44205’s supply rails are higher than the ADC’s full-scale range. Shutdown mode consumes only 6.8µA and extends battery life in battery-powered applications or reduces average power ...
... clamping solution ensures that the buffer output does not violate the ADC’s maximum input voltage range, even if the MAX44205’s supply rails are higher than the ADC’s full-scale range. Shutdown mode consumes only 6.8µA and extends battery life in battery-powered applications or reduces average power ...
Khanna
... minimum on-times to operate at high frequencies. The maximum switching frequency (and size of the inductor and output capacitor) are function of the minimum on-time. The on-time of conventional current mode controllers is limited by current measurement delays and the leading edge spike on the curren ...
... minimum on-times to operate at high frequencies. The maximum switching frequency (and size of the inductor and output capacitor) are function of the minimum on-time. The on-time of conventional current mode controllers is limited by current measurement delays and the leading edge spike on the curren ...
HMC549MS8G / 549MS8GE
... The HMC549MS8G & HMC549MS8GE are GaAs PHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifiers that are ideal pre-amplifiers for CATV Set Top Box, Home Gateway, and Digital Television receivers operating between 40 and 960 MHz. This high dynamic range LNA has been optimized to provide 3.5 dB noise figure and +27 dBm output ...
... The HMC549MS8G & HMC549MS8GE are GaAs PHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifiers that are ideal pre-amplifiers for CATV Set Top Box, Home Gateway, and Digital Television receivers operating between 40 and 960 MHz. This high dynamic range LNA has been optimized to provide 3.5 dB noise figure and +27 dBm output ...
AN97 - Accurate Measurement of LT5514 Third Order Intermodulation Products
... high quality spectrum analyzers, this will be sufficient to exclude the main tones during measurement of the intermodulation products. For some spectrum analyzers, however, the main tones may not be displayed, but their high level may still degrade the performance of the spectrum analyzer. Be carefu ...
... high quality spectrum analyzers, this will be sufficient to exclude the main tones during measurement of the intermodulation products. For some spectrum analyzers, however, the main tones may not be displayed, but their high level may still degrade the performance of the spectrum analyzer. Be carefu ...
MAX16913/MAX16913A Remote Antenna Current-Sense Amplifier and Switches General Description
... current-sense switches feature internal current limiting to prevent system damage due to fault conditions. The MAX16913/MAX16913A input voltage range extends from 5V to 18V, making them ideal for providing phantom power to remote radio-frequency low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) in automotive applications ...
... current-sense switches feature internal current limiting to prevent system damage due to fault conditions. The MAX16913/MAX16913A input voltage range extends from 5V to 18V, making them ideal for providing phantom power to remote radio-frequency low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) in automotive applications ...
HMC244AG16 (v02.0116)
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. N ...
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. N ...
Unit 4 Operational Amplifiers
... The standard Op-Amp symbol is shown in left-hand figure below. It has two input terminals, the inverting (-) input and the non-inverting (+) input. The typical Op-Amp operates with two dc supply voltages, one positive and the other negative, as shown in the right-hand figure below. Usually these dc ...
... The standard Op-Amp symbol is shown in left-hand figure below. It has two input terminals, the inverting (-) input and the non-inverting (+) input. The typical Op-Amp operates with two dc supply voltages, one positive and the other negative, as shown in the right-hand figure below. Usually these dc ...
GAIN +4 STABLE WIDEBAND VOLTAGE LIMITING AMPLIFIER OPA699M FEATURES APPLICATIONS
... gains ≥ +4. Two buffered limiting voltages take control of the output when it attempts to drive beyond these limits. This new output limiting architecture holds the limiter offset error to ±15 mV. The op amp operates linearly to within 30 mV of the limits. The combination of narrow nonlinear range a ...
... gains ≥ +4. Two buffered limiting voltages take control of the output when it attempts to drive beyond these limits. This new output limiting architecture holds the limiter offset error to ±15 mV. The op amp operates linearly to within 30 mV of the limits. The combination of narrow nonlinear range a ...
TLV2543 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... during the next I/O cycle. The current I/O cycle must be exactly 8 bits long to maintain synchronization, even when this means corrupting the output data from the previous conversion. The four LSBs of the conversion result are truncated and discarded. The current conversion is immediately started af ...
... during the next I/O cycle. The current I/O cycle must be exactly 8 bits long to maintain synchronization, even when this means corrupting the output data from the previous conversion. The four LSBs of the conversion result are truncated and discarded. The current conversion is immediately started af ...
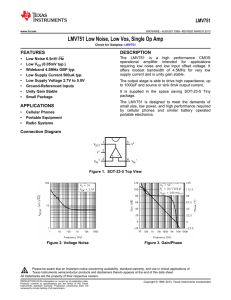
LMV751 Low Noise, Low Vos, Single Op Amp (Rev. E)
... Occasionally operational amplifiers are used as comparators. This is not optimum for the LMV751 for several reasons. First, the LMV751 is compensated for unity gain stability, so the speed will be less than could be obtained on the same process with a circuit specifically designed for comparator ope ...
... Occasionally operational amplifiers are used as comparators. This is not optimum for the LMV751 for several reasons. First, the LMV751 is compensated for unity gain stability, so the speed will be less than could be obtained on the same process with a circuit specifically designed for comparator ope ...
AD8312 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... design to the AD8313; further details about the structure and function may be found in the AD8313 data sheet and the data sheets of other log amplifiers produced by ADI. Figure 21 shows the main features of the AD8312 in block schematic form. ...
... design to the AD8313; further details about the structure and function may be found in the AD8313 data sheet and the data sheets of other log amplifiers produced by ADI. Figure 21 shows the main features of the AD8312 in block schematic form. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).