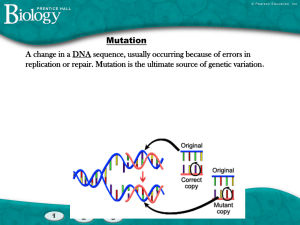
Genetics Study Guide
... The passing of traits from parents to offspring The scientific study of heredity A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes An organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent….all offspring have the same traits as the parent I ...
... The passing of traits from parents to offspring The scientific study of heredity A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes An organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent….all offspring have the same traits as the parent I ...
Source: Holt Biology textbook, Section: Evidence of Evolution, Ch 13
... species. If evolution has taken place, scientists would expect to see less differences in amino acids sequences of species with recent common ancestors. One example of this is by compar-‐ ing hemoglobin ...
... species. If evolution has taken place, scientists would expect to see less differences in amino acids sequences of species with recent common ancestors. One example of this is by compar-‐ ing hemoglobin ...
NAME_________________________________ CLASS:______
... How do sperm and eggs end up with only half the number of chromosomes? Instead of dividing by _________________, the parent cells of sperm and eggs divide by a process called _______________. During meiosis the chromosomes pairs separate and are distributed to two different cells. The resulting cell ...
... How do sperm and eggs end up with only half the number of chromosomes? Instead of dividing by _________________, the parent cells of sperm and eggs divide by a process called _______________. During meiosis the chromosomes pairs separate and are distributed to two different cells. The resulting cell ...
Biology Cell reproduction Pre test 1. Most mammals have diploid
... Since the assortment of alleles during meiosis is independent and random, over 8 million different combinations of chromosomes are possible in humans. (Humans have 46 chromosomes. The possible number of combinations is given by the formula 2 n, where n = 23, the haploid number of chromosomes.) 15. I ...
... Since the assortment of alleles during meiosis is independent and random, over 8 million different combinations of chromosomes are possible in humans. (Humans have 46 chromosomes. The possible number of combinations is given by the formula 2 n, where n = 23, the haploid number of chromosomes.) 15. I ...
Unit 4 – GENETICS - How do organisms pass traits to their offspring
... 1. How do asexual and sexual reproduction compare? 2. What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 3. What are the main events in the cell cycle? 4. What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 5. How do daughter cells split apart after mitosis? 6. How is the cell cycle regulate ...
... 1. How do asexual and sexual reproduction compare? 2. What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 3. What are the main events in the cell cycle? 4. What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 5. How do daughter cells split apart after mitosis? 6. How is the cell cycle regulate ...
November 23, 2009
... • How can I use the genotype to determine what an organism will look like? • How can I determine the possible genotype of an organism from its phenotype? ...
... • How can I use the genotype to determine what an organism will look like? • How can I determine the possible genotype of an organism from its phenotype? ...
1 From Lewontin, The Triple Helix IV. Directions in the Study of
... been three attempts to bring biological phenomena under the aegis of very general properties of systems that are changing in time. They are the Three C's: catastrophe theory, chaos theory, and complexity theory. All are attempts to show that extremely simple relationships in dynamical systems will l ...
... been three attempts to bring biological phenomena under the aegis of very general properties of systems that are changing in time. They are the Three C's: catastrophe theory, chaos theory, and complexity theory. All are attempts to show that extremely simple relationships in dynamical systems will l ...
Sexual reproduction
... Fragmentation: the breaking of the body into several pieces, some or all of which develop into complete adults. Requires regeneration of lost body parts. ...
... Fragmentation: the breaking of the body into several pieces, some or all of which develop into complete adults. Requires regeneration of lost body parts. ...
Creature Lab
... Background Information: Traits are genetic characteristics that are unique and help identify one organism from another. The genetic code, or genes, (called the genotype) responsible for determining the traits of an organism can sometimes be determined just by the way the organism looks (the phenotyp ...
... Background Information: Traits are genetic characteristics that are unique and help identify one organism from another. The genetic code, or genes, (called the genotype) responsible for determining the traits of an organism can sometimes be determined just by the way the organism looks (the phenotyp ...
What Did Mendel Find?
... Punnett squares are named for an English geneticist, Reginald Punnett. He discovered some basic principles of genetics, including sex linkage and sex determination. ...
... Punnett squares are named for an English geneticist, Reginald Punnett. He discovered some basic principles of genetics, including sex linkage and sex determination. ...
Unit 3_Lesson 80_Asexual Sexual
... instance, animals that remain in one particular place and are unable to look for mates would need to reproduce asexually. ...
... instance, animals that remain in one particular place and are unable to look for mates would need to reproduce asexually. ...
Unit 2 - Heredity Reproduction
... communication, which are social practices that are governed by a core set of values and norms. 5.3 Life Science All students will understand that life science principles are powerful conceptual tools for making sense of the complexity, diversity, and interconnectedness of life on Earth. Order in nat ...
... communication, which are social practices that are governed by a core set of values and norms. 5.3 Life Science All students will understand that life science principles are powerful conceptual tools for making sense of the complexity, diversity, and interconnectedness of life on Earth. Order in nat ...
c. pedigree charts
... 11. A graphic representation of an individual’s family tree is called a _______________________________ 12. Genetics is the study of ______________________________________. 13. Heredity is defined as __________________________________________________________________. 14. _____________________ is the ...
... 11. A graphic representation of an individual’s family tree is called a _______________________________ 12. Genetics is the study of ______________________________________. 13. Heredity is defined as __________________________________________________________________. 14. _____________________ is the ...
GENETICS REVIEW 7A
... 11. A graphic representation of an individual’s family tree is called a _______________________________ 12. Genetics is the study of ______________________________________. 13. Heredity is defined as __________________________________________________________________. 14. _____________________ is the ...
... 11. A graphic representation of an individual’s family tree is called a _______________________________ 12. Genetics is the study of ______________________________________. 13. Heredity is defined as __________________________________________________________________. 14. _____________________ is the ...
Human Adaptation and Variation The logic of selection
... • is organism growing and developing? • if so, are all relevant psychoneuroendocrine control systems working properly? • is organism producing and rearing offspring? • if so, whole process continues and selection retrospectively endorses DNA at apex of parents’ life cycle ...
... • is organism growing and developing? • if so, are all relevant psychoneuroendocrine control systems working properly? • is organism producing and rearing offspring? • if so, whole process continues and selection retrospectively endorses DNA at apex of parents’ life cycle ...
adam aim5classwork - science339
... one parent and produces offspring with the same genetic make up as the parent is asexual reproduction. The pictures above show how bacteria reproduces on a human’s hand. There are other forms of asexual reproduction in animals. For example, hydra are tiny freshwater animals that reproduce by budding ...
... one parent and produces offspring with the same genetic make up as the parent is asexual reproduction. The pictures above show how bacteria reproduces on a human’s hand. There are other forms of asexual reproduction in animals. For example, hydra are tiny freshwater animals that reproduce by budding ...
PDF version
... organismic biology. The course presents the various taxonomic groups and their characteristics, while using the different groups to demonstrate general principles of organization of the body and its systems. The full course includes a lab module which serves for practical demonstration of principles ...
... organismic biology. The course presents the various taxonomic groups and their characteristics, while using the different groups to demonstrate general principles of organization of the body and its systems. The full course includes a lab module which serves for practical demonstration of principles ...
Populations and Ecosystems
... An individual is one single organism. A population is all the individuals of one kind (one species) in a specified area at one time. A community is all the interacting populations in a specified area. An ecosystem is a system of interacting organisms and nonliving factors in a specified area. Biotic ...
... An individual is one single organism. A population is all the individuals of one kind (one species) in a specified area at one time. A community is all the interacting populations in a specified area. An ecosystem is a system of interacting organisms and nonliving factors in a specified area. Biotic ...
Populations and Ecosystems
... they are present on one chromosome; recessive alleles exhibit their effect only when they are on both chromosomes. An organism’s particular combination of paired alleles is its genotype; the traits produced by those alleles result in the organism’s phenotype. A gene composed of two identical alleles ...
... they are present on one chromosome; recessive alleles exhibit their effect only when they are on both chromosomes. An organism’s particular combination of paired alleles is its genotype; the traits produced by those alleles result in the organism’s phenotype. A gene composed of two identical alleles ...
VII. Natural Selection - Effingham County Schools
... beneficial traits will more likely survive long enough to reproduce and pass on those beneficial traits. Natural Selection- Works much like artificial selection, but the environment “selects” the best traits. – A. Causes Survival of the fittest! – B. Fitness is a result of adaptation. • Fitness= the ...
... beneficial traits will more likely survive long enough to reproduce and pass on those beneficial traits. Natural Selection- Works much like artificial selection, but the environment “selects” the best traits. – A. Causes Survival of the fittest! – B. Fitness is a result of adaptation. • Fitness= the ...
SCIENCE PROFICIENCY STUDY GUIDE – LIFE SCIENCE
... ♦ Explain that DNA copies itself. ♦ Explain that DNA contains hereditary information. ♦ Describe the process of DNA replication in the formation of sex cells. L.12.A.2 Students know DNA molecules provide instructions for assembling protein molecules. E/S ♦ Recognize that the DNA code carries instruc ...
... ♦ Explain that DNA copies itself. ♦ Explain that DNA contains hereditary information. ♦ Describe the process of DNA replication in the formation of sex cells. L.12.A.2 Students know DNA molecules provide instructions for assembling protein molecules. E/S ♦ Recognize that the DNA code carries instruc ...
Document
... tailbones within their skeletons. Many plants that once reproduced sexually (requiring pollination) evolved to reproduce asexually, yet they still produce unnecessary flowers. Sometimes, a mutation causes a vestigial trait to express itself in a more pronounced way. Scientists refer to this as atavi ...
... tailbones within their skeletons. Many plants that once reproduced sexually (requiring pollination) evolved to reproduce asexually, yet they still produce unnecessary flowers. Sometimes, a mutation causes a vestigial trait to express itself in a more pronounced way. Scientists refer to this as atavi ...
12_biology_impQ_CH01_reproduction_in_organisms_01
... (b) Sexual reproduction introduces variations in offsprings and has evolutionary significance. It helps offsprings to adjust according to the changes in environment. It produces better offsprings due to character ...
... (b) Sexual reproduction introduces variations in offsprings and has evolutionary significance. It helps offsprings to adjust according to the changes in environment. It produces better offsprings due to character ...