radio communications: am and fm
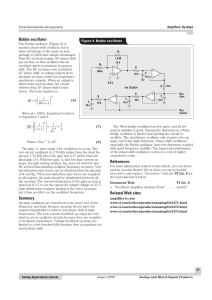
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
Angle Modulation Part 2
... Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (minimizes the effect of noise). Angle modulation allows the use of ...
... Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (minimizes the effect of noise). Angle modulation allows the use of ...
Lab 7 - Electronic Filters (C and G Sections Only)
... Gain (in dB) Ratio of output against input 20*log (Vout/Vin) Always negative value -3dB Point 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
... Gain (in dB) Ratio of output against input 20*log (Vout/Vin) Always negative value -3dB Point 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
work sheet 1 unit-1 two port network theory
... 4. How many two port networks need to be connected for series connection? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 1 5. Name the type of interconnection. ...
... 4. How many two port networks need to be connected for series connection? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 1 5. Name the type of interconnection. ...
UMZ-837-D16-G 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
Local Oscillator / Harmonic Mixer Frequency Measurement System
... based a local oscillator and a harmonic mixer. The components were purchased from stock as discrete components Fig. 1 is a photograph of the assembled system and the circuit can be identified. The signal from the microwave source to be counted is feed into the harmonic mixer along with the output of ...
... based a local oscillator and a harmonic mixer. The components were purchased from stock as discrete components Fig. 1 is a photograph of the assembled system and the circuit can be identified. The signal from the microwave source to be counted is feed into the harmonic mixer along with the output of ...
Op Amps II, Page
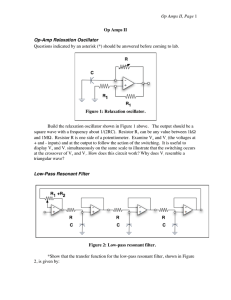
... convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz (It is best to use a resistor ~ 5 kΩ). Examine the resonant behavior by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. Specifically: ...
... convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz (It is best to use a resistor ~ 5 kΩ). Examine the resonant behavior by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. Specifically: ...
PLL synthesizing oscillator (3)
... the comparison frequency and the VCO which generates the digital pulse. There are two kinds of phase comparators. As for the 1st, it outputs the phase difference of the input signal (the reference frequency and the comparison frequency) simply as the pulse duration (The output 1). As for the 2nd, it ...
... the comparison frequency and the VCO which generates the digital pulse. There are two kinds of phase comparators. As for the 1st, it outputs the phase difference of the input signal (the reference frequency and the comparison frequency) simply as the pulse duration (The output 1). As for the 2nd, it ...
UMV-1450-R16-G
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
Lesson 5 - Wednesday Training Net
... Transverter is used to extend the the frequency Capabilities of a HF transceiver. ...
... Transverter is used to extend the the frequency Capabilities of a HF transceiver. ...
Compare and contrast Tuned Radio Frequency
... In TRF receiver, amplification is not constant over the tuning range. In superhet receiver amplification standard is constant since all the time it amplifies a constant frequency at the IF stages. ...
... In TRF receiver, amplification is not constant over the tuning range. In superhet receiver amplification standard is constant since all the time it amplifies a constant frequency at the IF stages. ...
UMV-3550-R16-G 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
COURSE NUMBER: E E 352 Design of a Low
... In this lab we will be analyzing an active low-pass filter circuit. We’ll be examining the theory behind the filter, simulation of the filter, implementation of the filter, and the results. This lab asked for a pole around 1.25 kHz at 20dB per decade and required an active low-pass filter with a gai ...
... In this lab we will be analyzing an active low-pass filter circuit. We’ll be examining the theory behind the filter, simulation of the filter, implementation of the filter, and the results. This lab asked for a pole around 1.25 kHz at 20dB per decade and required an active low-pass filter with a gai ...
UMZ-T2-1042-A16-G 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.