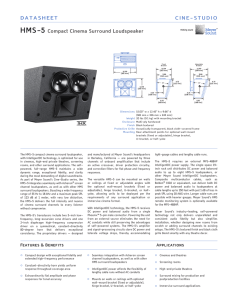
TL880P Engineering Data Sheet 575 KB | December 26, 2007
... beamwidth. (It is assumed that all cones are operating in unison or “in phase.“) This principle is already employed in the dual-woofer TL88OP, and is responsible for the higher sensitivity and narrower vertical beamwidth (with the system long axis vertical) relative to similar single-woofer systems. ...
... beamwidth. (It is assumed that all cones are operating in unison or “in phase.“) This principle is already employed in the dual-woofer TL88OP, and is responsible for the higher sensitivity and narrower vertical beamwidth (with the system long axis vertical) relative to similar single-woofer systems. ...
Signal Theory
... Frequency domain is a commonly used method of signal processing. Frequency response is used to describe a systems characteristics using its response to sinusoidal signal. If a sine wave is fed into a system (input), the output will also be a sine wave, but with different amplitude and usually have ...
... Frequency domain is a commonly used method of signal processing. Frequency response is used to describe a systems characteristics using its response to sinusoidal signal. If a sine wave is fed into a system (input), the output will also be a sine wave, but with different amplitude and usually have ...
Nov 2000 Low Distortion Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers Drive ADCs and Cables
... A low distortion, low voltage filter, suitable for antialiasing applications, is shown in Figure 5. The filter is a cascade of two inverting 2nd order sections, with values selected to give a Butterworth response. In this configuration, signal swing on the inputs of the op amps is small, resulting i ...
... A low distortion, low voltage filter, suitable for antialiasing applications, is shown in Figure 5. The filter is a cascade of two inverting 2nd order sections, with values selected to give a Butterworth response. In this configuration, signal swing on the inputs of the op amps is small, resulting i ...
TQP3M9037 数据资料DataSheet下载
... 2. R3 (0 Ω jumper) is not shown on the schematic and may be replaced with copper trace in the target application layout. 3. All components are of 0402 size unless stated on the schematic. 4. C1, C2, and C3 are non-critical values. The reactive impedance should be as low as possible at the frequency ...
... 2. R3 (0 Ω jumper) is not shown on the schematic and may be replaced with copper trace in the target application layout. 3. All components are of 0402 size unless stated on the schematic. 4. C1, C2, and C3 are non-critical values. The reactive impedance should be as low as possible at the frequency ...
Design of Low Power CMOS Crystal Oscillator with Tuning Capacitors
... for oscillation to start up correspond to the intersections A and B of this locus with that of − Z m ( p ) [6]. For all values of g m where Z c ( g m ) lies between the A and B, the crystal oscillation will occur. Thus, the values of both g m ,min and g m ,max can be derived from the combination of ...
... for oscillation to start up correspond to the intersections A and B of this locus with that of − Z m ( p ) [6]. For all values of g m where Z c ( g m ) lies between the A and B, the crystal oscillation will occur. Thus, the values of both g m ,min and g m ,max can be derived from the combination of ...
High pass filter
... Let‘s construct the gain-frequency characteristic of the RC high-pass filter. Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency to the input of the circuit. If the frequency becomes lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. No DC current can pass through the capacitor because ther ...
... Let‘s construct the gain-frequency characteristic of the RC high-pass filter. Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency to the input of the circuit. If the frequency becomes lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. No DC current can pass through the capacitor because ther ...
Provisional Answer Key GPSC Assistant Professor,Electronics(Govt
... (A) Which has zeros in the right half s-plane (B) Which has zeros only in the left half s-plane (C) Which has poles in the right half s-plane (D) Which has poles in the left half s-plane ...
... (A) Which has zeros in the right half s-plane (B) Which has zeros only in the left half s-plane (C) Which has poles in the right half s-plane (D) Which has poles in the left half s-plane ...
meres stilusfajl
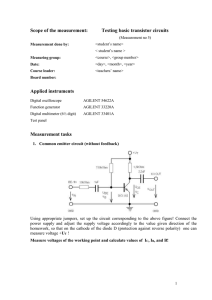
... Using appropriate jumpers, set up the circuit corresponding to the above figure! Connect the power supply and adjust the supply voltage accordingly to the value given direction of the homework, so that on the cathode of the diode D (protection against reverse polarity) one can measure voltage +UT ! ...
... Using appropriate jumpers, set up the circuit corresponding to the above figure! Connect the power supply and adjust the supply voltage accordingly to the value given direction of the homework, so that on the cathode of the diode D (protection against reverse polarity) one can measure voltage +UT ! ...
Design and Simulation of Frequency Divider by Negative Differential
... Vout, i.e. the periods of Vin and Vout are equal as shown in figure 5. When the input frequency is equal to 3GHz, we can observe the relation of Vin and Vout, i.e. the period of Vout is twice as the period of Vin as shown in figure 6. And then we change the input frequency is equal to 2GHz, we can o ...
... Vout, i.e. the periods of Vin and Vout are equal as shown in figure 5. When the input frequency is equal to 3GHz, we can observe the relation of Vin and Vout, i.e. the period of Vout is twice as the period of Vin as shown in figure 6. And then we change the input frequency is equal to 2GHz, we can o ...
writeup
... (constant) part of the signal would saturate the amplifier before obtaining desired amplification of the AC (time varying) part. To get rid of the DC signal we used a high-pass filter because DC signals are effectively extremely low frequency. But we had to be careful not to attenuate the pulse sign ...
... (constant) part of the signal would saturate the amplifier before obtaining desired amplification of the AC (time varying) part. To get rid of the DC signal we used a high-pass filter because DC signals are effectively extremely low frequency. But we had to be careful not to attenuate the pulse sign ...
SGB-2233(Z) 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
Lab 1. LNA characterization, lab manual
... TSEK03 Integrated Radio Frequency Circuits 2017/Ted Johansson ...
... TSEK03 Integrated Radio Frequency Circuits 2017/Ted Johansson ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.