Amplifiers
... In other words, the output signal of a real amplifier is phase shifted with respect to the input. ...
... In other words, the output signal of a real amplifier is phase shifted with respect to the input. ...
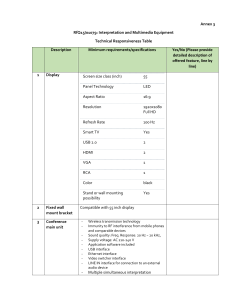
Annex 3 - Technical Responsiveness Table
... Channel selector Battery life (with mic On): min 8 hours Rechargeable battery pack Transmitting up to 64 CHs high quality digital audio Immunity to RF interference from mobile devices Built-in loudspeaker Built-in volume control for headphones 3.5 mm stereo headphone jack ...
... Channel selector Battery life (with mic On): min 8 hours Rechargeable battery pack Transmitting up to 64 CHs high quality digital audio Immunity to RF interference from mobile devices Built-in loudspeaker Built-in volume control for headphones 3.5 mm stereo headphone jack ...
Effects of Op-Amp Finite Gain and Bandwidth
... In our analysis of op-amp circuits this far, we have considered the op-amps to have an infinite gain and an infinite bandwidth. This is not true for physical op-amps. In this section, we examine the effects of a non-infinite gain and non-infinite bandwidth on the inverting and the non-inverting ampl ...
... In our analysis of op-amp circuits this far, we have considered the op-amps to have an infinite gain and an infinite bandwidth. This is not true for physical op-amps. In this section, we examine the effects of a non-infinite gain and non-infinite bandwidth on the inverting and the non-inverting ampl ...
High Pass Filter
... * We know that Xc=1/(2pi)fC. C is fixed and therefore Xc is proportional to 1/f. We also know that the Power=i^2R. From these, as the frequency increases, Xc decreases. As this impedance has decreased, more current can pass through (i increases) and thus Power also increases. Therefore power increas ...
... * We know that Xc=1/(2pi)fC. C is fixed and therefore Xc is proportional to 1/f. We also know that the Power=i^2R. From these, as the frequency increases, Xc decreases. As this impedance has decreased, more current can pass through (i increases) and thus Power also increases. Therefore power increas ...
low-pass filter
... Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency and of an amplitude of 10V to the input of the circuit in the figure. If we let the frequency become lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. This input voltage Vin of 10V will charge the capacitor and in a moment the output volta ...
... Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency and of an amplitude of 10V to the input of the circuit in the figure. If we let the frequency become lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. This input voltage Vin of 10V will charge the capacitor and in a moment the output volta ...
"Filtering Technique Isolating Analog/Digital Power Supplies in PLL
... capacitor (around 0.01 µF) to handle higher frequencies. It is more effective to use an array of three or more bypass capacitors with different capacitance values when filtering a wider noise bandwidth. The frequency response of any capacitor is determined by its parasitics, that is, its equivalent ...
... capacitor (around 0.01 µF) to handle higher frequencies. It is more effective to use an array of three or more bypass capacitors with different capacitance values when filtering a wider noise bandwidth. The frequency response of any capacitor is determined by its parasitics, that is, its equivalent ...
The Fourier Transform
... Digital filtering on a static input time sample can be done taking a FFT of the vector and then applying the desired filter shape to the resultant coefficients. Now apply an inverse FFT and the result is a filtered time set. Clean up your old records this way by converting the sound to digital sampl ...
... Digital filtering on a static input time sample can be done taking a FFT of the vector and then applying the desired filter shape to the resultant coefficients. Now apply an inverse FFT and the result is a filtered time set. Clean up your old records this way by converting the sound to digital sampl ...
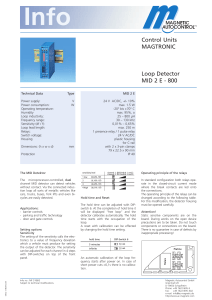
Control Units MAGTRONIC Loop Detector MID 2 E - 800
... without contact. Via the connected induction loop all sorts of metallic vehicles like cars, trucks, buses, fork lifts and even bicycles are easily detected. ...
... without contact. Via the connected induction loop all sorts of metallic vehicles like cars, trucks, buses, fork lifts and even bicycles are easily detected. ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... rheostat through one of its terminals, flows through the wire coil and contact and exits through the other terminal. Rheostats do not have polarity and operate the same when the terminals are reversed. The produced current over the rheostat values is shown in Figure 18. Conclusion: The objective of ...
... rheostat through one of its terminals, flows through the wire coil and contact and exits through the other terminal. Rheostats do not have polarity and operate the same when the terminals are reversed. The produced current over the rheostat values is shown in Figure 18. Conclusion: The objective of ...
Automated shimming on Bruker instruments without deuterium
... homogeneous, are one or two so-called coils which encircle the sample in its NMR tube. Each coil is part of an rf circuit which can be tuned to a series of nuclei, which determines what nuclei can be studied with it. For example, the SW probes on the Varian Mercury 300 and VNMRS 500 instruments (SW= ...
... homogeneous, are one or two so-called coils which encircle the sample in its NMR tube. Each coil is part of an rf circuit which can be tuned to a series of nuclei, which determines what nuclei can be studied with it. For example, the SW probes on the Varian Mercury 300 and VNMRS 500 instruments (SW= ...
AD8072
... The PCB should have a ground plane covering all unused portions of the component side of the board to provide a low impedance ground path. The ground plane should be removed from the area near the input pins to reduce stray capacitance. Chip capacitors should be used for supply bypassing. One end of ...
... The PCB should have a ground plane covering all unused portions of the component side of the board to provide a low impedance ground path. The ground plane should be removed from the area near the input pins to reduce stray capacitance. Chip capacitors should be used for supply bypassing. One end of ...
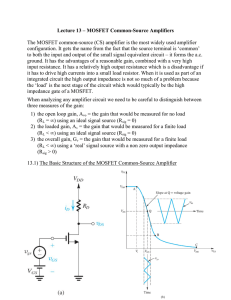
MOSFET Common Source Amplifiers
... configuration. It gets the name from the fact that the source terminal is ‘common’ to both the input and output of the small signal equivalent circuit – it forms the a.c. ground. It has the advantages of a reasonable gain, combined with a very high input resistance. It has a relatively high output r ...
... configuration. It gets the name from the fact that the source terminal is ‘common’ to both the input and output of the small signal equivalent circuit – it forms the a.c. ground. It has the advantages of a reasonable gain, combined with a very high input resistance. It has a relatively high output r ...
ee221_3
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating current
... When a metallic piece is surrounded by a coil carrying high frequency (H.F) alternating current, it becomes hot because eddy currents are produced which in turn produces joule’s heating effect. ...
... When a metallic piece is surrounded by a coil carrying high frequency (H.F) alternating current, it becomes hot because eddy currents are produced which in turn produces joule’s heating effect. ...
Tech Exam Study Aid - effective July 1, 2010
... Which amateur band are you using when transmitting on 146.52 MHz? 2 meter band (2 = approximately 300/146.525) 2m band = 144 to 148MHz Which 70-centimeter frequency is authorized to a Technician class license holder operating in ITU Region 2? 443.350 MHz (70cm = approximately 300/443.350) 70cm band ...
... Which amateur band are you using when transmitting on 146.52 MHz? 2 meter band (2 = approximately 300/146.525) 2m band = 144 to 148MHz Which 70-centimeter frequency is authorized to a Technician class license holder operating in ITU Region 2? 443.350 MHz (70cm = approximately 300/443.350) 70cm band ...
Voltage Controlled Oscillator
... simulations are performed with VDD varying from 0.8V to 1.4V with a 50mV step (Test in simulation) . We clearly observe a very important increase of the output frequency with VDD (Almost a factor of 2 between the lower and upper bounds). This means that any supply fluctuation has a significant impac ...
... simulations are performed with VDD varying from 0.8V to 1.4V with a 50mV step (Test in simulation) . We clearly observe a very important increase of the output frequency with VDD (Almost a factor of 2 between the lower and upper bounds). This means that any supply fluctuation has a significant impac ...
Band-pass filter
... available. It is very cheap especially keeping in mind the fact that it contains several hundred components. The most common Op-Amp is the 741 and it is used in many circuits. The OP AMP is a ‘Linear Amplifier’ with an amazing variety of uses. Its main purpose is to amplify (increase) a weak signal. ...
... available. It is very cheap especially keeping in mind the fact that it contains several hundred components. The most common Op-Amp is the 741 and it is used in many circuits. The OP AMP is a ‘Linear Amplifier’ with an amazing variety of uses. Its main purpose is to amplify (increase) a weak signal. ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.