A 10-GHz Low Phase Noise Differential Colpitts CMOS VCO Using
... There are two shortcomings by using the Colpitts oscillator. On the one hand, in order to avoid feedback circuit destroying the Q-factor of the passive resonance circuit, the values of the resonance circuit components needs to be relatively great. But in this way, it may be limited to some extent in ...
... There are two shortcomings by using the Colpitts oscillator. On the one hand, in order to avoid feedback circuit destroying the Q-factor of the passive resonance circuit, the values of the resonance circuit components needs to be relatively great. But in this way, it may be limited to some extent in ...
AD8005
... the larger phase margin allows for larger capacitive loads with less overshoot. Adding a series resistor at lower closed-loop gains accomplishes the same effect. For large capacitive loads, the frequency response of the amplifier will be dominated by the roll-off of the series resistor and capacitiv ...
... the larger phase margin allows for larger capacitive loads with less overshoot. Adding a series resistor at lower closed-loop gains accomplishes the same effect. For large capacitive loads, the frequency response of the amplifier will be dominated by the roll-off of the series resistor and capacitiv ...
v R + v C + v L
... iC = ωCVC cos (ωt + π/2) The consequence of this is that the capacitor voltage and current do not oscillate in phase. The current leads voltage by π/2 rads, or by T/4. ...
... iC = ωCVC cos (ωt + π/2) The consequence of this is that the capacitor voltage and current do not oscillate in phase. The current leads voltage by π/2 rads, or by T/4. ...
Chopper Modulation Improves OTA Information Transmission
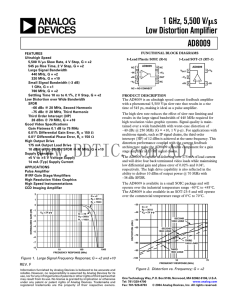
... in the operating range. Increasing the signal power for the chopper amplifier causes the total signal + noise to increase, but not as steeply as for the linear amplifier. This implies that the information rate of the chopper amplifier is higher than for the linear amplifier. Fig 6 shows that the cap ...
... in the operating range. Increasing the signal power for the chopper amplifier causes the total signal + noise to increase, but not as steeply as for the linear amplifier. This implies that the information rate of the chopper amplifier is higher than for the linear amplifier. Fig 6 shows that the cap ...
What is an oscillator
... Oscillators With LC Feedback Circuits The crystal-controlled oscillator is the most stable and accurate of all oscillators. A crystal has a natural frequency of resonance. Quartz material can be cut or shaped to have a certain frequency. We can better understand the use of a crystal in the operatio ...
... Oscillators With LC Feedback Circuits The crystal-controlled oscillator is the most stable and accurate of all oscillators. A crystal has a natural frequency of resonance. Quartz material can be cut or shaped to have a certain frequency. We can better understand the use of a crystal in the operatio ...
Johnson Noise
... to the measurement chain through two switches (SW1 and SW2). A Hewlett-Packard HP54601A digital oscilloscope was used to measure the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage generated by the resistor. Because the Johnson Noise signals are in the microvolt range, a low-noise amplifier (PAR 113) was used to pro ...
... to the measurement chain through two switches (SW1 and SW2). A Hewlett-Packard HP54601A digital oscilloscope was used to measure the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage generated by the resistor. Because the Johnson Noise signals are in the microvolt range, a low-noise amplifier (PAR 113) was used to pro ...
A Highly Linear SAW-less CMOS Receiver Using a
... An on-chip Tx reject band-pass filter using bond-wire inductors is reported for a WCDMA system in [4]. This method has benefits of saving area compare to an on-chip inductor and increasing the selectivity of the filter due to the high-Q of the bond-wire. But this method may have limited feasibility ...
... An on-chip Tx reject band-pass filter using bond-wire inductors is reported for a WCDMA system in [4]. This method has benefits of saving area compare to an on-chip inductor and increasing the selectivity of the filter due to the high-Q of the bond-wire. But this method may have limited feasibility ...
AD8038
... load drive for all outputs. The quiescent power is the voltage between the supply pins (VS) multiplied by the quiescent current (IS). Assuming the load (RL) is referenced to midsupply, then the total drive power is VS /2 ⫻ IOUT, some of which is dissipated in the package and some in the load (VOUT ⫻ ...
... load drive for all outputs. The quiescent power is the voltage between the supply pins (VS) multiplied by the quiescent current (IS). Assuming the load (RL) is referenced to midsupply, then the total drive power is VS /2 ⫻ IOUT, some of which is dissipated in the package and some in the load (VOUT ⫻ ...
Analog-Frequency converter XXXF70-90
... Adjustment is performed using a calibrator or a calibrated sensing device. The zero point (offset) is adjusted via the "Offs" potentiometer and the full scale value is adjusted via the "gain" potentiometer. The zero point is adjusted first and then the full scale. Where large adjustments are necessa ...
... Adjustment is performed using a calibrator or a calibrated sensing device. The zero point (offset) is adjusted via the "Offs" potentiometer and the full scale value is adjusted via the "gain" potentiometer. The zero point is adjusted first and then the full scale. Where large adjustments are necessa ...
Comparative Analysis of Tuning Range of Regulated
... The conventional method of analysis and design of Colpitts based CMOS Oscillator is not following Barkhausen criterion [1]. By substituting low frequency small signal equivalent circuit of CMOS into single ended Colpitts based CMOS oscillator and injecting input current source into the circuit, we c ...
... The conventional method of analysis and design of Colpitts based CMOS Oscillator is not following Barkhausen criterion [1]. By substituting low frequency small signal equivalent circuit of CMOS into single ended Colpitts based CMOS oscillator and injecting input current source into the circuit, we c ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... is frequently employed in electrical engineering applications. Among several kinds of oscillator, the quadrature oscillator is widely used because it can offer sinusoidal signals with 90° phase difference, for example, in telecommunications for quadrature mixers and singlesideband modulators [1]. Pr ...
... is frequently employed in electrical engineering applications. Among several kinds of oscillator, the quadrature oscillator is widely used because it can offer sinusoidal signals with 90° phase difference, for example, in telecommunications for quadrature mixers and singlesideband modulators [1]. Pr ...
UHF-R Specification Sheet
... All transmitters shall be powered by 2 AA batteries and shall have a power on/off switch. The bodypack will have an LED indicating that power is on. Available transmitters shall include: a body pack for use with electric guitars, basses, and other electric instruments, and a handheld microphone for ...
... All transmitters shall be powered by 2 AA batteries and shall have a power on/off switch. The bodypack will have an LED indicating that power is on. Available transmitters shall include: a body pack for use with electric guitars, basses, and other electric instruments, and a handheld microphone for ...
Document
... [26] A low-pass T-connected symmetrical filter section has an inductance of 200mH in each of its series arms and a capacitance of 0.5 μF in its shunt arm. The cut-off frequency of the filter is (a) 1007 Hz (b) 251.6 Hz (c) 711.8 Hz (d) 177.9 Hz [27] A low-pass π-connected symmetrical filter section ...
... [26] A low-pass T-connected symmetrical filter section has an inductance of 200mH in each of its series arms and a capacitance of 0.5 μF in its shunt arm. The cut-off frequency of the filter is (a) 1007 Hz (b) 251.6 Hz (c) 711.8 Hz (d) 177.9 Hz [27] A low-pass π-connected symmetrical filter section ...
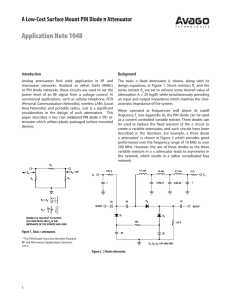
Application Note 1048 A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator Introduction Background
... of the series diode(s), the use of two diodes in place of one will increase the maximum attenuation or double the upper frequency limit for a given value of attenuation. Second, the twin diodes which occupy the position of the series resistor are physically set up 180° out of phase, resulting in the ...
... of the series diode(s), the use of two diodes in place of one will increase the maximum attenuation or double the upper frequency limit for a given value of attenuation. Second, the twin diodes which occupy the position of the series resistor are physically set up 180° out of phase, resulting in the ...
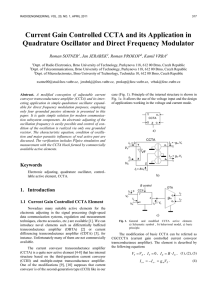
1. Introduction - About the journal
... a limited tuning range. Only capacitors are grounded in [34]. In this work, all passive elements are grounded and the range of current gain (B) for control of oscillation frequency is not limited from principle of design (equation for oscillation frequency). Constrains are given by a limited range o ...
... a limited tuning range. Only capacitors are grounded in [34]. In this work, all passive elements are grounded and the range of current gain (B) for control of oscillation frequency is not limited from principle of design (equation for oscillation frequency). Constrains are given by a limited range o ...
(f-fo0) sin(2rrf0t) + (2n+l)!
... sampled bus voltages has been developed in the last secticn. This algorithm is affected by many factors, such as, the size of data window, sampling frequency, time reference and the level of truncation of the Taylor series expansions of sine and cosine terms. As described in the last secticn, each v ...
... sampled bus voltages has been developed in the last secticn. This algorithm is affected by many factors, such as, the size of data window, sampling frequency, time reference and the level of truncation of the Taylor series expansions of sine and cosine terms. As described in the last secticn, each v ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.