DC-DC Converters Feedback and Control
... Conditions for stability Poles and zeros Phase margin and quality coefficient Undershoot and crossover frequency Compensating the converter Compensating with a TL431 Watch the optocoupler! Compensating a DCM flyback Compensating a CCM flyback Simulation and bench results Conclu ...
... Conditions for stability Poles and zeros Phase margin and quality coefficient Undershoot and crossover frequency Compensating the converter Compensating with a TL431 Watch the optocoupler! Compensating a DCM flyback Compensating a CCM flyback Simulation and bench results Conclu ...
EMG2016 - Faculty of Engineering
... case if the power is small enough to allow the diode detector to work in its “squarelaw” region. The probe must not protrude too deep into the waveguide so that the power picked up by the probe is small. This is also necessary to ensure that the field distribution in the waveguide is not significant ...
... case if the power is small enough to allow the diode detector to work in its “squarelaw” region. The probe must not protrude too deep into the waveguide so that the power picked up by the probe is small. This is also necessary to ensure that the field distribution in the waveguide is not significant ...
OPER_MAN A1010 (English)
... The BAND knob controls the band switch, and LOAD and TUNE are used to adjust their respective variable air capacitors in the amplifier’s output circuit. The settings of these three controls must be changed at each band change as well as when an antenna is changed. The three LED indicators located ab ...
... The BAND knob controls the band switch, and LOAD and TUNE are used to adjust their respective variable air capacitors in the amplifier’s output circuit. The settings of these three controls must be changed at each band change as well as when an antenna is changed. The three LED indicators located ab ...
Chapter 1
... The most basic and pervasive signal-processing function: signal amplification, and correspondingly, the signal amplifier. How amplifiers are characterized (modeled) as circuit building blocks independent of their internal circuitry. How the frequency response of an amplifier is measured, and h ...
... The most basic and pervasive signal-processing function: signal amplification, and correspondingly, the signal amplifier. How amplifiers are characterized (modeled) as circuit building blocks independent of their internal circuitry. How the frequency response of an amplifier is measured, and h ...
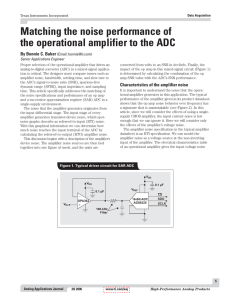
Matching the noise performance of the
... we may jump to the conclusion that we should take this formula down to a very low frequency, such as 0.0001 Hz (0.0001 Hz = 1 cycle per 2.8 hours). However, at frequencies lower than 0.1 Hz, which is one cycle every 10 seconds, it is very possible that other things such as temperature, aging, or com ...
... we may jump to the conclusion that we should take this formula down to a very low frequency, such as 0.0001 Hz (0.0001 Hz = 1 cycle per 2.8 hours). However, at frequencies lower than 0.1 Hz, which is one cycle every 10 seconds, it is very possible that other things such as temperature, aging, or com ...
2 × 2W Filterless Class-D Stereo Audio Amplifier SSM2356
... The fully differential input of the SSM2356 provides excellent rejection of common-mode noise on the input. Input coupling capacitors can be omitted if the dc input common-mode voltage is approximately VDD/2. The preset gain of SSM2356 can be selected between 6 dB and 18 dB with no external componen ...
... The fully differential input of the SSM2356 provides excellent rejection of common-mode noise on the input. Input coupling capacitors can be omitted if the dc input common-mode voltage is approximately VDD/2. The preset gain of SSM2356 can be selected between 6 dB and 18 dB with no external componen ...
ADA4853-1AKSZ-R7中文资料
... package exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric performance of the amplifiers. Exceeding a junction temperature of 150°C for an extended period can result in changes in silicon devices, potentially causing degradation or loss of ...
... package exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric performance of the amplifiers. Exceeding a junction temperature of 150°C for an extended period can result in changes in silicon devices, potentially causing degradation or loss of ...
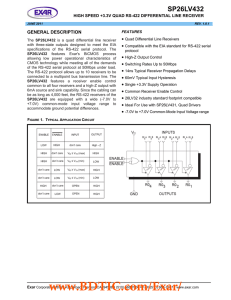
SP26LV432 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The SP26LV432 is a low-power quad differential line receiver designed for digital data transmission meeting the specifications of the EIA standard RS-422 serial protocol. The SP26LV432 features Exar's BiCMOS process allowing low power operational characteristics of CMOS technology while meeting all ...
... The SP26LV432 is a low-power quad differential line receiver designed for digital data transmission meeting the specifications of the EIA standard RS-422 serial protocol. The SP26LV432 features Exar's BiCMOS process allowing low power operational characteristics of CMOS technology while meeting all ...
$doc.title
... functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. NOTE 1: The THS414x may incorporate a PowerPad on the ...
... functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. NOTE 1: The THS414x may incorporate a PowerPad on the ...
3. Switched Current Mirror Mixer
... converts the incoming signal into current, which then becomes a voltage across the load. This voltage drives the transconductance input of the mixer, which once again converts the signal into current. Finally, the mixer differential pairs commutate this current, translating it in frequency, to be re ...
... converts the incoming signal into current, which then becomes a voltage across the load. This voltage drives the transconductance input of the mixer, which once again converts the signal into current. Finally, the mixer differential pairs commutate this current, translating it in frequency, to be re ...
Tip-sample control using quartz tuning forks in
... issues concerning optimal piezoelectric current detection will be addressed. The calibration of the measured piezoelectric signal with the actual amplitude of the fork oscillation at the tip level will also be shown in detail. In section 4 the thermodynamic limit to the signal detection will be disc ...
... issues concerning optimal piezoelectric current detection will be addressed. The calibration of the measured piezoelectric signal with the actual amplitude of the fork oscillation at the tip level will also be shown in detail. In section 4 the thermodynamic limit to the signal detection will be disc ...
AD8310 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Logarithmic amplifiers perform a more complex operation than classical linear amplifiers, and their circuitry is significantly different. A good grasp of what log amps do and how they do it can help users avoid many pitfalls in their applications. For a complete discussion of the theory, see the AD8 ...
... Logarithmic amplifiers perform a more complex operation than classical linear amplifiers, and their circuitry is significantly different. A good grasp of what log amps do and how they do it can help users avoid many pitfalls in their applications. For a complete discussion of the theory, see the AD8 ...
TRF37T05 300-MHz to 4-GHz Quadrature Modulator (Rev. A)
... – Output IP3: 30 dBm at 1850 MHz Low Output Noise Floor: –160 dBm/Hz 78-dBc Single-Carrier WCDMA ACPR at –10-dBm Channel Power Unadjusted Carrier Suppression: –40 dBm Unadjusted Sideband Suppression: –45 dBc Single Supply: 3.3-V Operation 1-bit Gain Step Control Fast Power-Up/Power-Down ...
... – Output IP3: 30 dBm at 1850 MHz Low Output Noise Floor: –160 dBm/Hz 78-dBc Single-Carrier WCDMA ACPR at –10-dBm Channel Power Unadjusted Carrier Suppression: –40 dBm Unadjusted Sideband Suppression: –45 dBc Single Supply: 3.3-V Operation 1-bit Gain Step Control Fast Power-Up/Power-Down ...
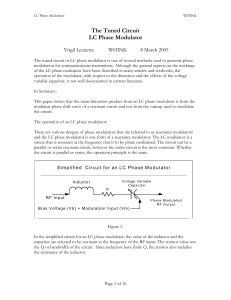
The Tuned Circuit LC Phase Modulator
... that the distortion level would be less susceptible to the tuning of the first multiplier stage. Also from a practical point of view, a distortion level of 1% to 3% is very acceptable in the voice communication systems for which these radios were designed. In summary, I found no improvement that cou ...
... that the distortion level would be less susceptible to the tuning of the first multiplier stage. Also from a practical point of view, a distortion level of 1% to 3% is very acceptable in the voice communication systems for which these radios were designed. In summary, I found no improvement that cou ...
Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
... where 2 is the instantaneous value of the AM wave (or AM), Vc sin 2fc t is the carrier waveform, and (Vm sin 2fmt) (sin 2fc t) is the carrier waveform multiplied by the modulating signal waveform. It is the second part of the expression that is characteristic of AM. A circuit must be able to pr ...
... where 2 is the instantaneous value of the AM wave (or AM), Vc sin 2fc t is the carrier waveform, and (Vm sin 2fmt) (sin 2fc t) is the carrier waveform multiplied by the modulating signal waveform. It is the second part of the expression that is characteristic of AM. A circuit must be able to pr ...
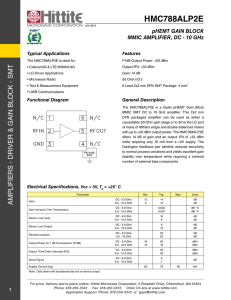
HMC788ALP2E
... The HMC788ALP2E is a GaAs pHEMT Gain Block MMIC SMT DC to 10 GHz amplifier. This 2x2 mm DFN packaged amplifier can be used as either a cascadable 50 Ohm gain stage or to drive the LO port of many of HIttite’s single and double-balanced mixers with up to +20 dBm output power. The HMC788ALP2E offers 1 ...
... The HMC788ALP2E is a GaAs pHEMT Gain Block MMIC SMT DC to 10 GHz amplifier. This 2x2 mm DFN packaged amplifier can be used as either a cascadable 50 Ohm gain stage or to drive the LO port of many of HIttite’s single and double-balanced mixers with up to +20 dBm output power. The HMC788ALP2E offers 1 ...
AD8310 Fast, Voltage-Out DC–440 MHz, 95 dB Logarithmic
... Logarithmic amplifiers perform a more complex operation than classical linear amplifiers, and their circuitry is significantly different. A good grasp of what log amps do and how they do it can help users avoid many pitfalls in their applications. For a complete discussion of the theory, see the AD8 ...
... Logarithmic amplifiers perform a more complex operation than classical linear amplifiers, and their circuitry is significantly different. A good grasp of what log amps do and how they do it can help users avoid many pitfalls in their applications. For a complete discussion of the theory, see the AD8 ...
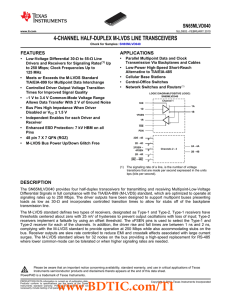
SN65MLVD040 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The M-LVDS standard defines two types of receivers, designated as Type-1 and Type-2. Type-1 receivers have thresholds centered about zero with 25 mV of hysteresis to prevent output oscillations with loss of input; Type-2 receivers implement a failsafe by using an offset threshold. The xFSEN pins is ...
... The M-LVDS standard defines two types of receivers, designated as Type-1 and Type-2. Type-1 receivers have thresholds centered about zero with 25 mV of hysteresis to prevent output oscillations with loss of input; Type-2 receivers implement a failsafe by using an offset threshold. The xFSEN pins is ...
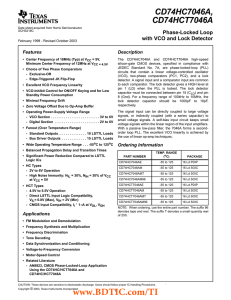
CD74HCT7046A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The waveform preset at the capacitor resembles a sawtooth as shown in Figure 7. The lock detector capacitor value is determined by the VCO center frequency. The typical range of capacitor for a frequency of 10MHz is about 10pF and for a frequency of 100kHz is about 1000pF. The chart in Figure 8 can ...
... The waveform preset at the capacitor resembles a sawtooth as shown in Figure 7. The lock detector capacitor value is determined by the VCO center frequency. The typical range of capacitor for a frequency of 10MHz is about 10pF and for a frequency of 100kHz is about 1000pF. The chart in Figure 8 can ...
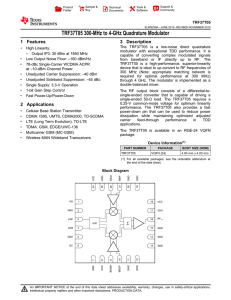
MAX15002 Dual-Output Buck Controller with Tracking/Sequencing General Description
... the power-up/power-down sequence depending on the system requirements. Each of the MAX15002 PWM sections utilizes a voltage-mode control scheme with external compensation, allowing for good noise immunity and maximum flexibility with a wide selection of inductor values and capacitor types. Each PWM ...
... the power-up/power-down sequence depending on the system requirements. Each of the MAX15002 PWM sections utilizes a voltage-mode control scheme with external compensation, allowing for good noise immunity and maximum flexibility with a wide selection of inductor values and capacitor types. Each PWM ...
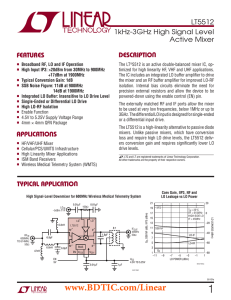
LT5512 - 1kHz-3GHz High Signal Level Down-Converting Mixer.
... LO–, LO+ (Pins 14, 15): Differential Inputs for the Local Oscillator Signal. They can also be driven single-ended by connecting one to an RF ground through a DC blocking capacitor. These pins are internally biased to 2V; thus, DC blocking capacitors are required. An impedance transformation or match ...
... LO–, LO+ (Pins 14, 15): Differential Inputs for the Local Oscillator Signal. They can also be driven single-ended by connecting one to an RF ground through a DC blocking capacitor. These pins are internally biased to 2V; thus, DC blocking capacitors are required. An impedance transformation or match ...
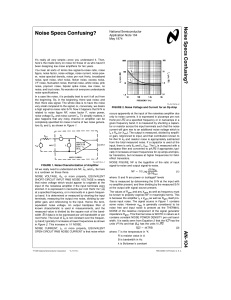
Noise Specs Confusing?
... to design Rgen of a magnetic pick-up to operate with preamps where ROPT is known. It does make sense to increase the design resistance of signal sources to match or exceed ROPT so long as the signal voltage increases with Rgen in at least the ratio esig2 * Rgen. It does not necessarily make sense to ...
... to design Rgen of a magnetic pick-up to operate with preamps where ROPT is known. It does make sense to increase the design resistance of signal sources to match or exceed ROPT so long as the signal voltage increases with Rgen in at least the ratio esig2 * Rgen. It does not necessarily make sense to ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.