BE LAB
... 19.what is JFET’S and MOSFET’S? Field effect transistors are called as JFET’S. FET”S are of two types 1)J FET’S a)N channel JFET’S b)P channel JFET”S 2)MOSFET’S or IGFET’S Metal oxide semi-conductor field effect transistor or insulated gate field effect transistors are of two types: ...
... 19.what is JFET’S and MOSFET’S? Field effect transistors are called as JFET’S. FET”S are of two types 1)J FET’S a)N channel JFET’S b)P channel JFET”S 2)MOSFET’S or IGFET’S Metal oxide semi-conductor field effect transistor or insulated gate field effect transistors are of two types: ...
Note 1
... positive potential is applied to it. The device permits flow of current in one direction only as a negative potential applied to the anode repels the electrons. This property of diodes was made use of in the first thermionic radios, in which the diode was used to demodulate the transmitted signal. I ...
... positive potential is applied to it. The device permits flow of current in one direction only as a negative potential applied to the anode repels the electrons. This property of diodes was made use of in the first thermionic radios, in which the diode was used to demodulate the transmitted signal. I ...
Linear Position Sensors: LVDT Sensors | TE Connectivity
... Zero adjustments. The design of the LVC-2401 requires that the low voltage DC input power be isolated from the output ground. This means that no part of the DC input power or return may be connected to the output ground. 24V DC power isolation is common on most small PLCs. The LVC-2401 uses a time-p ...
... Zero adjustments. The design of the LVC-2401 requires that the low voltage DC input power be isolated from the output ground. This means that no part of the DC input power or return may be connected to the output ground. 24V DC power isolation is common on most small PLCs. The LVC-2401 uses a time-p ...
Sheet 4
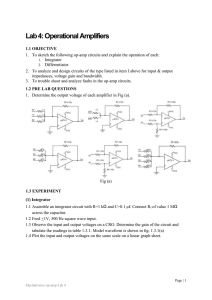
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
word
... the circuit, record them and use these values in calculating the expected gain). Use ±12 V as supply voltage, unless instructed otherwise. (2) Apply a 1kHz sinusoidal signal of about 200mV amplitude (from the function generator) to each input separately with the other grounded and measure the sign ...
... the circuit, record them and use these values in calculating the expected gain). Use ±12 V as supply voltage, unless instructed otherwise. (2) Apply a 1kHz sinusoidal signal of about 200mV amplitude (from the function generator) to each input separately with the other grounded and measure the sign ...
Chapter 17 Alternating Currents
... (b) If the oscillation frequency of B is adjusted to the natural oscillation frequency of A, maximum power transfer will occur and the amplitude of the induced oscillations in system A will maximize – this phenomenon is called resonance. ...
... (b) If the oscillation frequency of B is adjusted to the natural oscillation frequency of A, maximum power transfer will occur and the amplitude of the induced oscillations in system A will maximize – this phenomenon is called resonance. ...
BODE PLOTS
... flat lines with slope [R1 / (R1 + R2 )] and bode plots of lowpass filter as for lag network. Because Re < R1 , ω 2 will be above ω1 (in a lag network ω 2 below ω1 ). ...
... flat lines with slope [R1 / (R1 + R2 )] and bode plots of lowpass filter as for lag network. Because Re < R1 , ω 2 will be above ω1 (in a lag network ω 2 below ω1 ). ...
What is a Lock-in Amplifier? - Center for Precision Metrology
... instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. In modern units the DC output may be presented as a reading on a digital panel meter or as a digital value communicated over a computer interface, rather than a voltage at an output connector, but the principle rema ...
... instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. In modern units the DC output may be presented as a reading on a digital panel meter or as a digital value communicated over a computer interface, rather than a voltage at an output connector, but the principle rema ...
STK4182II AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply
... In an actual application where a music signal is used, it is impractical to estimate the power dissipation based on the continuous signal as shown above, because too large a heat sink must be used. It is reasonable to estimate the power dissipation as 1/10 Po max. (EIAJ). That is, Pd = 39W at 8Ω, Pd ...
... In an actual application where a music signal is used, it is impractical to estimate the power dissipation based on the continuous signal as shown above, because too large a heat sink must be used. It is reasonable to estimate the power dissipation as 1/10 Po max. (EIAJ). That is, Pd = 39W at 8Ω, Pd ...
Solution - University of California, Berkeley
... c) Calculate tsetup of the gate (tsetup is defined as the minimum period of time where inputs have to be stable before the clock transitions into the latched state in order for the correct value to be latched) in terms of intrinsic delay tp0. Assume γ=1. The circuit can be divided into three phases ...
... c) Calculate tsetup of the gate (tsetup is defined as the minimum period of time where inputs have to be stable before the clock transitions into the latched state in order for the correct value to be latched) in terms of intrinsic delay tp0. Assume γ=1. The circuit can be divided into three phases ...