Lecture 3
... that passes the D input to the Q output when the clock signal is high. This latch is said to be in transparent mode. When the clock is low, the input data sampled on the falling edge of the clock is held stable at the output for the entire phase, and the latch is in hold mode. The inputs must be ...
... that passes the D input to the Q output when the clock signal is high. This latch is said to be in transparent mode. When the clock is low, the input data sampled on the falling edge of the clock is held stable at the output for the entire phase, and the latch is in hold mode. The inputs must be ...
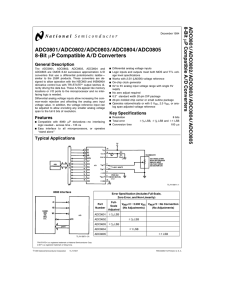
ADC0801/ADC0802/ADC0803/ADC0804/ADC0805 8-Bit mP Compatible A/D Converters 8-Bit m
... as high level analog inputs (5V) can cause this input diode to conduct–especially at elevated temperatures, and cause errors for analog inputs near full-scale. The spec allows 50 mV forward bias of either diode. This means that as long as the analog VIN does not exceed the supply voltage by more tha ...
... as high level analog inputs (5V) can cause this input diode to conduct–especially at elevated temperatures, and cause errors for analog inputs near full-scale. The spec allows 50 mV forward bias of either diode. This means that as long as the analog VIN does not exceed the supply voltage by more tha ...
Low Power Fir Filter Design Using Truncated Multiplier A.Deepika , A.Bhuvaneswari
... without sacrificing the frequency response and output signal accuracy. Non-uniform coefficient quantization with proper filter order to minimize the cost of total area. Multiple constant multiplication/accumulation in a pipelined direct FIR structure is implemented using an improved version of trunc ...
... without sacrificing the frequency response and output signal accuracy. Non-uniform coefficient quantization with proper filter order to minimize the cost of total area. Multiple constant multiplication/accumulation in a pipelined direct FIR structure is implemented using an improved version of trunc ...
A Digitally Modulated Polar CMOS Power Amplifier With
... Envelope-elimination and restoration (EER) is a technique based on performing efficient constant-envelope amplification of the phase-modulated portion of the input signal and then restoring the envelope by amplitude modulation at the output [4]. In effect, an EER system is a polar transmitter in whi ...
... Envelope-elimination and restoration (EER) is a technique based on performing efficient constant-envelope amplification of the phase-modulated portion of the input signal and then restoring the envelope by amplitude modulation at the output [4]. In effect, an EER system is a polar transmitter in whi ...
AD9865
... solutions. Power saving modes include the ability to reduce power consumption of individual functional blocks, or to power down unused blocks in half-duplex applications. A serial port interface (SPI®) allows software programming of the various functional blocks. An on-chip PLL clock multiplier and ...
... solutions. Power saving modes include the ability to reduce power consumption of individual functional blocks, or to power down unused blocks in half-duplex applications. A serial port interface (SPI®) allows software programming of the various functional blocks. An on-chip PLL clock multiplier and ...
TPA2100P1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... positive and negative channels equally and cancels at the differential output. • Excellent RF-immunity and supply noise rejection: – GSM handsets save power by turning on and off the RF transmitter at 217 Hz. The transmitted signal is picked-up on input, output, and power supply traces. The fully di ...
... positive and negative channels equally and cancels at the differential output. • Excellent RF-immunity and supply noise rejection: – GSM handsets save power by turning on and off the RF transmitter at 217 Hz. The transmitted signal is picked-up on input, output, and power supply traces. The fully di ...
Designing With TPS7H3301-SP Double Data Rate (DDR) Termination
... DDR Memory and SSTL Basics In commercial applications, there are two forms of memory that are commonly used in computer systems non-Volatile memory and volatile memory. Whereas non-volatile memory is memory that can retain the stored information even when not powered. Example of non-volatile memory ...
... DDR Memory and SSTL Basics In commercial applications, there are two forms of memory that are commonly used in computer systems non-Volatile memory and volatile memory. Whereas non-volatile memory is memory that can retain the stored information even when not powered. Example of non-volatile memory ...
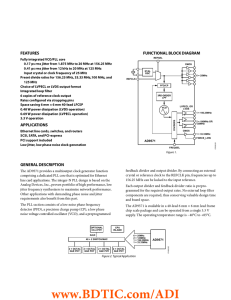
FEATURES FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
... comprising a dedicated PLL core that is optimized for Ethernet line card applications. The integer-N PLL design is based on the Analog Devices, Inc., proven portfolio of high performance, low jitter frequency synthesizers to maximize network performance. Other applications with demanding phase noise ...
... comprising a dedicated PLL core that is optimized for Ethernet line card applications. The integer-N PLL design is based on the Analog Devices, Inc., proven portfolio of high performance, low jitter frequency synthesizers to maximize network performance. Other applications with demanding phase noise ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... Current Differencing Buffered Amplifier (ZC-CG-CDBA). Solution in [40] uses two active elements and five passive elements (capacitors are grounded). Discrete model of one active element employs four diamond transistors [42], [43], [61] and voltage buffer. It is not a problem for future onchip implem ...
... Current Differencing Buffered Amplifier (ZC-CG-CDBA). Solution in [40] uses two active elements and five passive elements (capacitors are grounded). Discrete model of one active element employs four diamond transistors [42], [43], [61] and voltage buffer. It is not a problem for future onchip implem ...
LT6600-10
... set the differential gain to 402Ω/RIN. The inputs to the filter are the voltages VIN+ and VIN– presented to these external components, Figure 1. The difference between VIN+ and VIN– is the differential input voltage. The average of VIN+ and VIN– is the common mode input voltage. Similarly, the voltag ...
... set the differential gain to 402Ω/RIN. The inputs to the filter are the voltages VIN+ and VIN– presented to these external components, Figure 1. The difference between VIN+ and VIN– is the differential input voltage. The average of VIN+ and VIN– is the common mode input voltage. Similarly, the voltag ...
MAX5082/MAX5083 1.5A, 40V, MAXPower Step-Down DC-DC Converters General Description
... The MAX5082/MAX5083 are 250kHz PWM step-down DC-DC converters with an on-chip, 0.3Ω high-side switch. The input voltage range is 4.5V to 40V for the MAX5082 and 7.5V to 40V for the MAX5083. The output is adjustable from 1.23V to 32V and can deliver up to 1.5A of load current. Both devices utilize a ...
... The MAX5082/MAX5083 are 250kHz PWM step-down DC-DC converters with an on-chip, 0.3Ω high-side switch. The input voltage range is 4.5V to 40V for the MAX5082 and 7.5V to 40V for the MAX5083. The output is adjustable from 1.23V to 32V and can deliver up to 1.5A of load current. Both devices utilize a ...
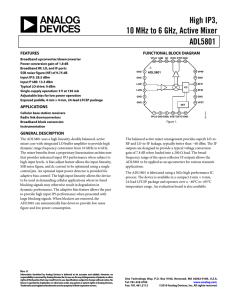
ADL5801 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The ADL5801 uses a high linearity, doubly balanced, active mixer core with integrated LO buffer amplifier to provide high dynamic range frequency conversion from 10 MHz to 6 GHz. The mixer benefits from a proprietary linearization architecture that provides enhanced input IP3 performance when subjec ...
... The ADL5801 uses a high linearity, doubly balanced, active mixer core with integrated LO buffer amplifier to provide high dynamic range frequency conversion from 10 MHz to 6 GHz. The mixer benefits from a proprietary linearization architecture that provides enhanced input IP3 performance when subjec ...
ADCMP606/ADCMP607 Rail-to-Rail, Very Fast, 2.5 V to 5.5 V
... simplified schematic diagram in Figure 14. Each output is backterminated with 50 Ω for best transmission line matching. VCCO ...
... simplified schematic diagram in Figure 14. Each output is backterminated with 50 Ω for best transmission line matching. VCCO ...
AD587 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AD587 is designed for precision reference applications where temperature performance is critical. Extensive temperature testing ensures that the device’s high level of performance is maintained over the operating temperature range. Some confusion exists in the area of defining and specifying ref ...
... The AD587 is designed for precision reference applications where temperature performance is critical. Extensive temperature testing ensures that the device’s high level of performance is maintained over the operating temperature range. Some confusion exists in the area of defining and specifying ref ...
LT1077 - Micropower, Single Supply, Precision Op Amp
... Micropower performance of competing devices is achieved at the expense of seriously degrading precision, noise, speed, and output drive specifications. The LT1077 reduces supply current without sacrificing other parameters. The offset voltage achieved is the lowest of any micropower op amp. Offset c ...
... Micropower performance of competing devices is achieved at the expense of seriously degrading precision, noise, speed, and output drive specifications. The LT1077 reduces supply current without sacrificing other parameters. The offset voltage achieved is the lowest of any micropower op amp. Offset c ...