Template For Examination Papers
... 6) a) A simple synchronous counter comprises several flip-flops with some combinational logic as feedback. The flip-flop has a set-up time of 8 nsec and a propagation delay (clock to output Q) of 15 nsec. The combinational logic has a total propagation delay of 17 nsec. Calculate the absolute maximu ...
... 6) a) A simple synchronous counter comprises several flip-flops with some combinational logic as feedback. The flip-flop has a set-up time of 8 nsec and a propagation delay (clock to output Q) of 15 nsec. The combinational logic has a total propagation delay of 17 nsec. Calculate the absolute maximu ...
AD781
... Aperture Jitter—The variations in aperture delay for successive samples. Aperture jitter puts an upper limit on the maximum frequency that can be accurately sampled. Hold Settling Time—The time required for the output to settle to within a specified level of accuracy of its final held value after th ...
... Aperture Jitter—The variations in aperture delay for successive samples. Aperture jitter puts an upper limit on the maximum frequency that can be accurately sampled. Hold Settling Time—The time required for the output to settle to within a specified level of accuracy of its final held value after th ...
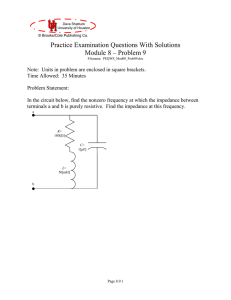
PEQWS_Mod08_Prob09_v06
... Notice that we have isolated the real and imaginary parts of the numerator and denominator in parentheses in this last expression. If this expression for Zab is going to be real, that means that the imaginary part must be zero. However, getting an expression for the Im{Zab} is not easy; we would nee ...
... Notice that we have isolated the real and imaginary parts of the numerator and denominator in parentheses in this last expression. If this expression for Zab is going to be real, that means that the imaginary part must be zero. However, getting an expression for the Im{Zab} is not easy; we would nee ...
Theoretical Background of a Series RLC Circuit
... Note that this solution assumes that the current oscillates at some angular frequency 0 = 2f0 which we now need to determine. Hopefully f0 1/[2(LC)1/2]. But the oscillations are damped or attenuated by an exponential decay term exp-t/, and hence we need also to determine the characteristic dec ...
... Note that this solution assumes that the current oscillates at some angular frequency 0 = 2f0 which we now need to determine. Hopefully f0 1/[2(LC)1/2]. But the oscillations are damped or attenuated by an exponential decay term exp-t/, and hence we need also to determine the characteristic dec ...
Amateur Extra Licensing Class
... A. The transmitted signal jumps from band to band at a predetermined rate B. Two or more information streams are merged into a "baseband", which then modulates the transmitter C. The transmitted signal is divided into packets of information D. Two or more information streams are merged into a digita ...
... A. The transmitted signal jumps from band to band at a predetermined rate B. Two or more information streams are merged into a "baseband", which then modulates the transmitter C. The transmitted signal is divided into packets of information D. Two or more information streams are merged into a digita ...
AD8048
... gain of 2, RF and RG should be set to 200 Ω for the AD8048. When the AD8047 is configured as a unity gain follower, RF should be set to 0 Ω (no feedback resistor should be used) for the plastic DIP and 66.5 Ω for the SOIC. ...
... gain of 2, RF and RG should be set to 200 Ω for the AD8048. When the AD8047 is configured as a unity gain follower, RF should be set to 0 Ω (no feedback resistor should be used) for the plastic DIP and 66.5 Ω for the SOIC. ...
non-inverting amplifier gain derivation
... β is called the feedback transfer function and represents the fraction of the output voltage that is fed back from the output to the input. Combining the equations above gives: vout A vout = A[ vin − βvout ]; vout + Aβvout = Avin ; = Av = vin 1 + Aβ This gives the classic negative feedback amplifier ...
... β is called the feedback transfer function and represents the fraction of the output voltage that is fed back from the output to the input. Combining the equations above gives: vout A vout = A[ vin − βvout ]; vout + Aβvout = Avin ; = Av = vin 1 + Aβ This gives the classic negative feedback amplifier ...
Frequency combs and frequency dissemination for scientific and
... network are also being discussed [10]. In France an ultra-stable reference signal of 100 MHz was transferred over a telecom fibre network and various methods for the noise reduction were investigated [11]. Within the framework of a cooperation with Menlo Systems, at MPQ an optical fibre network was ...
... network are also being discussed [10]. In France an ultra-stable reference signal of 100 MHz was transferred over a telecom fibre network and various methods for the noise reduction were investigated [11]. Within the framework of a cooperation with Menlo Systems, at MPQ an optical fibre network was ...
AD8005
... and are suitable for supply bypassing (see Figure 32). Make sure that one end of the capacitor is within 1/8 inch of each power pin with the other end connected to the ground plane. An additional large (0.47 µF–10 µF) tantalum electrolytic capacitor should also be connected in parallel. This capacit ...
... and are suitable for supply bypassing (see Figure 32). Make sure that one end of the capacitor is within 1/8 inch of each power pin with the other end connected to the ground plane. An additional large (0.47 µF–10 µF) tantalum electrolytic capacitor should also be connected in parallel. This capacit ...
12-Bit R/D Converter with Reference Oscillator AD2S1200
... sinusoidal oscillator that provides sine wave excitation for resolvers. An external 8.192 MHz crystal is required to provide a precision time reference. This clock is internally divided to generate a 4.096 MHz clock to drive all the peripherals. The converter accepts 3.6 V p-p ± 10% input signals, i ...
... sinusoidal oscillator that provides sine wave excitation for resolvers. An external 8.192 MHz crystal is required to provide a precision time reference. This clock is internally divided to generate a 4.096 MHz clock to drive all the peripherals. The converter accepts 3.6 V p-p ± 10% input signals, i ...
Oscillator Phase Noise: Theory vs. Practicality
... tighter in stability and lower in noise. As a result, oscillator designers need to continually push the limit of tight stability, low noise oscillator design. One of the major issues facing oscillator designers is the phase noise phenomenon. Phase noise is an undesirable entity that is present in al ...
... tighter in stability and lower in noise. As a result, oscillator designers need to continually push the limit of tight stability, low noise oscillator design. One of the major issues facing oscillator designers is the phase noise phenomenon. Phase noise is an undesirable entity that is present in al ...
315MHz/433MHz ASK Superheterodyne Receiver with Extended Dynamic Range General Description Features
... frequency range. Its signal range is from -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The chip consists of a low-noise amplifier (LNA), a fully differential ima ...
... frequency range. Its signal range is from -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The chip consists of a low-noise amplifier (LNA), a fully differential ima ...
What do you mean by engineering? Most simply, the art of directing
... law of thermodynamics As a system approaches absolute zero, all processes cease and the entropy of the system approaches a minimum value. It can be concluded as 'If T=0K, then S=0' where T is the temperature of a closed system and S is the entropy of the system. Newton's laws of motion First law: la ...
... law of thermodynamics As a system approaches absolute zero, all processes cease and the entropy of the system approaches a minimum value. It can be concluded as 'If T=0K, then S=0' where T is the temperature of a closed system and S is the entropy of the system. Newton's laws of motion First law: la ...
6 The Time Dimension I
... square wave as well as their summation. The summation bears a reasonably close resemblance to the original square wave but it can be seen that there is some oscillatory variation around the pulse amplitude due to the finite number of components summed. If more components are added, the waveform beco ...
... square wave as well as their summation. The summation bears a reasonably close resemblance to the original square wave but it can be seen that there is some oscillatory variation around the pulse amplitude due to the finite number of components summed. If more components are added, the waveform beco ...