a 380 MHz, 25 mA, Triple 2:1 Multiplexers AD8183/AD8185
... 380 MHz, along with slew rate of 1000 V/µs. With better than –90 dB of channel-to-channel crosstalk and isolation at 10 MHz, they are useful in many high-speed applications. The differential gain and differential phase errors of 0.01% and 0.02° respectively, along with 0.1 dB flatness to 90 MHz make ...
... 380 MHz, along with slew rate of 1000 V/µs. With better than –90 dB of channel-to-channel crosstalk and isolation at 10 MHz, they are useful in many high-speed applications. The differential gain and differential phase errors of 0.01% and 0.02° respectively, along with 0.1 dB flatness to 90 MHz make ...
MAX8515 - Maxim Integrated
... (OVP) functions in high-accuracy isolated DC-to-DC converters with output voltages as low as 0.6V. The devices have supply voltage and feedback inputs separated from the output shunt stage, and can operate directly from the DC-to-DC converter output stage when the output voltage is 1.8V to 18V. Alte ...
... (OVP) functions in high-accuracy isolated DC-to-DC converters with output voltages as low as 0.6V. The devices have supply voltage and feedback inputs separated from the output shunt stage, and can operate directly from the DC-to-DC converter output stage when the output voltage is 1.8V to 18V. Alte ...
EXERCISES RESONAT CIRCUITS 5.21 The resonant circuit of the
... Knowing that the quality factor of the coil (L with internal resistance r) in the circuit of the Figure 1 at 0=1Mrad/s is Qb=50, and that the antiresonant circuit receives the maximum power at this frequency, obtain: a) Values of r, L and C. b) Value of the current through the coil if the frequency ...
... Knowing that the quality factor of the coil (L with internal resistance r) in the circuit of the Figure 1 at 0=1Mrad/s is Qb=50, and that the antiresonant circuit receives the maximum power at this frequency, obtain: a) Values of r, L and C. b) Value of the current through the coil if the frequency ...
High Pass Filters A High Pass Filter or HPF, is the exact opposite to
... equivalent low pass filter due to the higher operating frequencies. A very common application of a passive high pass filter, is in audio amplifiers as a coupling capacitor between two audio amplifier stages and in speaker systems to direct the higher frequency signals to the smaller "tweeter" type s ...
... equivalent low pass filter due to the higher operating frequencies. A very common application of a passive high pass filter, is in audio amplifiers as a coupling capacitor between two audio amplifier stages and in speaker systems to direct the higher frequency signals to the smaller "tweeter" type s ...
AD706
... levels (similar to FET input amplifiers at room temperature), while its IB typically only increases by 5⫻ at 125°C (unlike a JFET amp, for which IB doubles every 10°C for a 1000⫻ increase at 125°C). The AD706 also achieves the microvolt offset voltage and low noise characteristics of a precision bip ...
... levels (similar to FET input amplifiers at room temperature), while its IB typically only increases by 5⫻ at 125°C (unlike a JFET amp, for which IB doubles every 10°C for a 1000⫻ increase at 125°C). The AD706 also achieves the microvolt offset voltage and low noise characteristics of a precision bip ...
Resource efficient implementation of PWM core on FPGAs
... found to take up 33 flip-flops on the CLBs taking up a meager 16% of the total available flip-flops. Implementation results also indicate a maximum working frequency of 17.517 Mhz, if speed ...
... found to take up 33 flip-flops on the CLBs taking up a meager 16% of the total available flip-flops. Implementation results also indicate a maximum working frequency of 17.517 Mhz, if speed ...
PHYS 2426 – Engineering Physics II
... 8. Turn the oscilloscope on and allow it to go through startup sequence. Press the ‘AUTO SET’ button. Press ‘MEASURE.’ 9. Adjust the amplitude with the ‘OUTPUT LEVEL’ knob on the function generator so that the oscilloscope indicates 5 V. (Get as close as you can.) 10. Press the Cursor button. Select ...
... 8. Turn the oscilloscope on and allow it to go through startup sequence. Press the ‘AUTO SET’ button. Press ‘MEASURE.’ 9. Adjust the amplitude with the ‘OUTPUT LEVEL’ knob on the function generator so that the oscilloscope indicates 5 V. (Get as close as you can.) 10. Press the Cursor button. Select ...
FAQs for SmartLEWIS RX+ family: TDA5240, TDA5235, TDA5225
... The 5V-to-3.3V regulator needs a slew rate limitation at power-up. Steep slew rates at VDD5V in 5V supply mode cannot be regulated and therefore higher voltages than allowed could result across voltage regulator. For avoiding this, slew rate limitation can be applied with an RC low-pass (22Ohm + 1µF ...
... The 5V-to-3.3V regulator needs a slew rate limitation at power-up. Steep slew rates at VDD5V in 5V supply mode cannot be regulated and therefore higher voltages than allowed could result across voltage regulator. For avoiding this, slew rate limitation can be applied with an RC low-pass (22Ohm + 1µF ...
Student Biographies
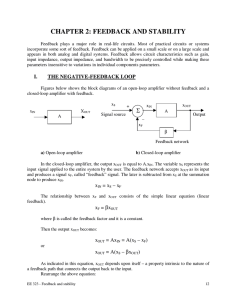
... The op amp is designed to sense the difference between the voltage signals applied to its two inputs (v2-v1), and multiply this by a number A, and cause the resulting voltage A (v2-v1) to appear at the output terminal relative to ground. Note that v1 and v2 are also implied to be relative to ground ...
... The op amp is designed to sense the difference between the voltage signals applied to its two inputs (v2-v1), and multiply this by a number A, and cause the resulting voltage A (v2-v1) to appear at the output terminal relative to ground. Note that v1 and v2 are also implied to be relative to ground ...
HMC549MS8G / 549MS8GE
... The HMC549MS8G & HMC549MS8GE are GaAs PHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifiers that are ideal pre-amplifiers for CATV Set Top Box, Home Gateway, and Digital Television receivers operating between 40 and 960 MHz. This high dynamic range LNA has been optimized to provide 3.5 dB noise figure and +27 dBm output ...
... The HMC549MS8G & HMC549MS8GE are GaAs PHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifiers that are ideal pre-amplifiers for CATV Set Top Box, Home Gateway, and Digital Television receivers operating between 40 and 960 MHz. This high dynamic range LNA has been optimized to provide 3.5 dB noise figure and +27 dBm output ...
NCN49597 - Power Line Communication Modem
... resistor; the Schottky diode pair D5 clamps the voltage within the input range of the zero crossing detector. In the receive path a 2nd order high pass filter blocks the mains frequency. The corner point − defined by C1, C2, R1 and R2 − is designed at 10 kHz. In the transmit path a 3th ...
... resistor; the Schottky diode pair D5 clamps the voltage within the input range of the zero crossing detector. In the receive path a 2nd order high pass filter blocks the mains frequency. The corner point − defined by C1, C2, R1 and R2 − is designed at 10 kHz. In the transmit path a 3th ...