Activity: Protein Exploration!
... relationships are also true at all levels below the macroscopic level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular level. Here are some important facts about proteins: ...
... relationships are also true at all levels below the macroscopic level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular level. Here are some important facts about proteins: ...
Prof. Dr. Harry F. Noller Prof. Dr. Ada Yonath
... What I would like to do is to relate to their discoveries in perspective to other milestones in biology – since science is a continuum and the various crucial discoveries are like steps of a ladder on which we climb to reach new levels of knowledge. Both our prize winners today have reached their br ...
... What I would like to do is to relate to their discoveries in perspective to other milestones in biology – since science is a continuum and the various crucial discoveries are like steps of a ladder on which we climb to reach new levels of knowledge. Both our prize winners today have reached their br ...
Introduction to Proteins
... Introduction to Proteins Protein gets its name from a Greek word meaning "first" or "primary" because it is the material of primary importance in every process we associate with being alive. Virtually none of the chemical reactions in a living thing would occur at any useful speed if it were not for ...
... Introduction to Proteins Protein gets its name from a Greek word meaning "first" or "primary" because it is the material of primary importance in every process we associate with being alive. Virtually none of the chemical reactions in a living thing would occur at any useful speed if it were not for ...
Classification of Protein
... animal claws, horns, feathers, scales, and hooves. Collagen is the most common protein in the body and comprises approximately 20-30% of all body proteins. It is found in tendons, ligaments, and many tissues that serve structural or mechanical functions. Collagen consists of amino acid sequences t ...
... animal claws, horns, feathers, scales, and hooves. Collagen is the most common protein in the body and comprises approximately 20-30% of all body proteins. It is found in tendons, ligaments, and many tissues that serve structural or mechanical functions. Collagen consists of amino acid sequences t ...
Self-assessment quiz for young scientist interested in autumn school
... completely isolated from its environment (no exchange of heat or substance). What will happen to the organisms if you wait for a long time? Can you argue with a physical law? If yes: with which law? 2. You have a sodium ion and a chloride ion at a distance of 1 nm, (a) in vacuum, (b) in water. Estim ...
... completely isolated from its environment (no exchange of heat or substance). What will happen to the organisms if you wait for a long time? Can you argue with a physical law? If yes: with which law? 2. You have a sodium ion and a chloride ion at a distance of 1 nm, (a) in vacuum, (b) in water. Estim ...
Chapter 7
... • Span the membrane like a tunnel • Change shape to move things in and out • Some use ATP ...
... • Span the membrane like a tunnel • Change shape to move things in and out • Some use ATP ...
Proposta di ricerca: Introduction Ever since the observation that
... Ever since the observation that different concentrations of different salts are required to precipitate a given protein [1] attempts have been made to provide a theoretical foundation for the phenomenon (see the comprehensive reviews of Lo Nostro and Ninham. [2], Collins and Washabaugh [3] and Cacac ...
... Ever since the observation that different concentrations of different salts are required to precipitate a given protein [1] attempts have been made to provide a theoretical foundation for the phenomenon (see the comprehensive reviews of Lo Nostro and Ninham. [2], Collins and Washabaugh [3] and Cacac ...
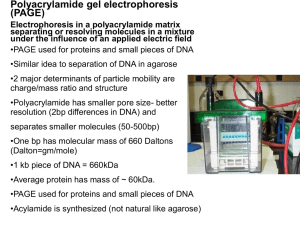
Polyacrylamide gels
... The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
... The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
here - BioGeometry
... smaller vibrations of the thousands of individual atoms in the protein, although they can prove important to understand how the larger protein molecule behaves. “If you try to simulate molecular motion, you may go through thousands of iterations in which the whole system does nothing but vibration m ...
... smaller vibrations of the thousands of individual atoms in the protein, although they can prove important to understand how the larger protein molecule behaves. “If you try to simulate molecular motion, you may go through thousands of iterations in which the whole system does nothing but vibration m ...
Chapter 3 USU - BEHS Science
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
amino acids - Wando High School
... • There are 20 different amino acids 12 amino acids are made in the human body. Humans need to consume the other 8 amino acids from sources such as nuts, beans, or meat. ...
... • There are 20 different amino acids 12 amino acids are made in the human body. Humans need to consume the other 8 amino acids from sources such as nuts, beans, or meat. ...
Biology-Chapter2 (Biology
... Which statement is correct, with regard to the catalase enzyme catalyzing the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen? A. Water is a substrate in this reaction. B. Bonds in the hydrogen peroxide are weakened in catalase's active site, allowing the chemical reaction to occur. C. Hydrogen ...
... Which statement is correct, with regard to the catalase enzyme catalyzing the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen? A. Water is a substrate in this reaction. B. Bonds in the hydrogen peroxide are weakened in catalase's active site, allowing the chemical reaction to occur. C. Hydrogen ...
Protein Synthesis
... Information in DNA is used to make proteins Proteins determine traits (eye color, hair color) Proteins are chains of amino acids 20 different amino acids Combinations of amino acids determine a proteins purpose ...
... Information in DNA is used to make proteins Proteins determine traits (eye color, hair color) Proteins are chains of amino acids 20 different amino acids Combinations of amino acids determine a proteins purpose ...
Document
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
Life of a Protein #1 This outline describes the job of a specialized
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
Protein Structure-Function Relationships - IBIVU
... – Protein – small molecules (drug interaction, structure decoding) • Structural component (e.g. -crystallin) • Regulation • Transcription regulation • Signalling • Immune system • Motor proteins (actin/myosin) ...
... – Protein – small molecules (drug interaction, structure decoding) • Structural component (e.g. -crystallin) • Regulation • Transcription regulation • Signalling • Immune system • Motor proteins (actin/myosin) ...
Figure 5.1 Rapid Diffusion of Membrane Proteins The fluid mosaic
... examined the movement of proteins within the cell membrane by constructing heterokaryons, cells comprised of nuclei from both mice and humans. By using fluorescent stains (red or green) that were specific either to the mouse or human proteins (antigens), Frye and Edidin observed that after 40 minute ...
... examined the movement of proteins within the cell membrane by constructing heterokaryons, cells comprised of nuclei from both mice and humans. By using fluorescent stains (red or green) that were specific either to the mouse or human proteins (antigens), Frye and Edidin observed that after 40 minute ...
File
... Dipeptide Molecule New molecule formed by joining 2 amino acids Polypeptide Molecule Molecule made up of many amino acids joined by ...
... Dipeptide Molecule New molecule formed by joining 2 amino acids Polypeptide Molecule Molecule made up of many amino acids joined by ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.