Biosynthesis and degradation of proteins
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
protein
... There are 20 amino acids. Some of them are nonessential because they can be made by your body, but 9 of them are essential amino acids. That means it is essential for you to ______________________ ...
... There are 20 amino acids. Some of them are nonessential because they can be made by your body, but 9 of them are essential amino acids. That means it is essential for you to ______________________ ...
Proteomics_Overview_BB_3_09_rev1
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
Translation - Lapeer East High School
... DNA and RNA work together to produce proteins Remember: A protein is a specific sequence of amino ...
... DNA and RNA work together to produce proteins Remember: A protein is a specific sequence of amino ...
Structure Reveals How Cells `Sugar
... "We studied one enzyme involved in glycosylation, the one that recognizes the protein sequence and adds the sugar chains to the protein as it is being synthesized by the cell," said William J. Lennarz of Stony Brook University, a coauthor on the paper. "The challenge is that the enzyme, known as oli ...
... "We studied one enzyme involved in glycosylation, the one that recognizes the protein sequence and adds the sugar chains to the protein as it is being synthesized by the cell," said William J. Lennarz of Stony Brook University, a coauthor on the paper. "The challenge is that the enzyme, known as oli ...
What is microbiology? Study of organisms too small to
... and P • Building blocksare nucleotides (composed of a nitrogenous base, sugar and phosphate group. • Types – DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid is the heritable material that codes for proteins. It exists as a double helix ...
... and P • Building blocksare nucleotides (composed of a nitrogenous base, sugar and phosphate group. • Types – DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid is the heritable material that codes for proteins. It exists as a double helix ...
The Chemistry of Living Things
... • A sugar called glucose is the most important monosaccharide on Earth. It is also the simplest sugar. Glucose is used in cellular respiration and created by photosynthesis. When you think of table sugar, like the kind in candy, it is actually a disaccharide. The sugar on your dinner table is made o ...
... • A sugar called glucose is the most important monosaccharide on Earth. It is also the simplest sugar. Glucose is used in cellular respiration and created by photosynthesis. When you think of table sugar, like the kind in candy, it is actually a disaccharide. The sugar on your dinner table is made o ...
Major components of cells
... interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aqueous solutions. ...
... interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aqueous solutions. ...
SIP - Proteins from oil seedsremarks - 20150317
... Non-food protein derivatisation towards adhesives, binders, surfactants and building blocks. Protein properties can be tailored toward specific applications. For instance the surface activity and water resistance of proteins can be adjusted from very low to very high. Preferably, modification reacti ...
... Non-food protein derivatisation towards adhesives, binders, surfactants and building blocks. Protein properties can be tailored toward specific applications. For instance the surface activity and water resistance of proteins can be adjusted from very low to very high. Preferably, modification reacti ...
Modification of Amino Acids
... Directing proteins to specific locations (for example, nucleus, mitochondria, or cell membrane) is accomplished by tagging of proteins (signal sequence for secreted proteins, nuclear localization sequences for nuclear proteins). ...
... Directing proteins to specific locations (for example, nucleus, mitochondria, or cell membrane) is accomplished by tagging of proteins (signal sequence for secreted proteins, nuclear localization sequences for nuclear proteins). ...
Cell Membrane - Seekonk High School
... barrier through which only small, nonpolar substances can pass. ...
... barrier through which only small, nonpolar substances can pass. ...
3.1.1.4 Proteins
... muscle proteins that work together to cause a muscle to contract. There are proteins in cell membranes that help identify a cell or serve as a receptor. Adrenalin and insulin are two examples of hormones that are made of protein. All proteins have a special shape that is the result of the interactio ...
... muscle proteins that work together to cause a muscle to contract. There are proteins in cell membranes that help identify a cell or serve as a receptor. Adrenalin and insulin are two examples of hormones that are made of protein. All proteins have a special shape that is the result of the interactio ...
Summary for Chapter 6 – Protein: Amino Acids
... Chemically speaking, proteins are more complex than carbohydrates or lipids, being made of some 20 different amino acids, 9 of which the body cannot make; they are essential. Each amino acid contains an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side group, all attached to a cent ...
... Chemically speaking, proteins are more complex than carbohydrates or lipids, being made of some 20 different amino acids, 9 of which the body cannot make; they are essential. Each amino acid contains an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side group, all attached to a cent ...
FCS-FS-8. Students will discuss why proteins are important in food
... Structural Protein is needed by every body cell. Helps to replace and repair cells Most of the bodies hormones and enzymes are largely proteins. Some proteins pick up, deliver, and store nutrients in the cells. Antibodies (proteins) help ward off disease. Help to stabilize pH levels Pro ...
... Structural Protein is needed by every body cell. Helps to replace and repair cells Most of the bodies hormones and enzymes are largely proteins. Some proteins pick up, deliver, and store nutrients in the cells. Antibodies (proteins) help ward off disease. Help to stabilize pH levels Pro ...
Protein Metabolism
... (1) Means their carbon skeleton can not be synthesised in the body and are required in the diet (2) They are 9 amino acids Note: arginine and histidine are considered to be essential amino acid during periods of growth ...
... (1) Means their carbon skeleton can not be synthesised in the body and are required in the diet (2) They are 9 amino acids Note: arginine and histidine are considered to be essential amino acid during periods of growth ...
Lecture 2
... all have zwitterionic forms at neutral pH because they have a negatively charged carboxylate and a positively charged ammonia. Zwitterions have two opposite charges that cancel out. Grouping amino acids Amino acids can be classified (sometimes roughly) into groups based on the chemical properties of ...
... all have zwitterionic forms at neutral pH because they have a negatively charged carboxylate and a positively charged ammonia. Zwitterions have two opposite charges that cancel out. Grouping amino acids Amino acids can be classified (sometimes roughly) into groups based on the chemical properties of ...
Protein Synthesis
... • A gene is piece of DNA that codes to make a protein. • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
... • A gene is piece of DNA that codes to make a protein. • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
Figure 20-5. Common intracellular signaling proteins.
... signaling proteins. (a) GTP-binding proteins with GTPase activity function as molecular switches. When bound to GTP they are active; when bound to GDP, they are inactive. They fall into two categories, trimeric G proteins and Ras-like proteins(b) Protein kinases modulate the activity or the binding ...
... signaling proteins. (a) GTP-binding proteins with GTPase activity function as molecular switches. When bound to GTP they are active; when bound to GDP, they are inactive. They fall into two categories, trimeric G proteins and Ras-like proteins(b) Protein kinases modulate the activity or the binding ...
Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
... common amino sugar D-glucosamine, occurs as its N-acetyl derivative-N-acetyl-Dglucosamine. These kind of amino sugar are usually joined by N link to a polypeptide at an aspargine residue. The N links of oligosaccharides to polypeptides occur most often where the polypeptide strand is following a ben ...
... common amino sugar D-glucosamine, occurs as its N-acetyl derivative-N-acetyl-Dglucosamine. These kind of amino sugar are usually joined by N link to a polypeptide at an aspargine residue. The N links of oligosaccharides to polypeptides occur most often where the polypeptide strand is following a ben ...
Word Doc - Biochemistry
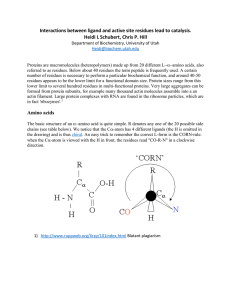
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.