The Science of Proteins in Milk (including A1 vs A2 Milk)
... present review of available scientific literature, a cause-effect relationship between BCM7 and etiology or cause of any suggested non-communicable diseases cannot be established.” Report to New Zealand Food Safety Authority (2004): “I do not believe there is sufficient evidence to warrant the gover ...
... present review of available scientific literature, a cause-effect relationship between BCM7 and etiology or cause of any suggested non-communicable diseases cannot be established.” Report to New Zealand Food Safety Authority (2004): “I do not believe there is sufficient evidence to warrant the gover ...
Step 2
... Scientific protocols are driven by their implementation – Scientists use the resources they know • data (quality) • access to data • format, limits, etc. ...
... Scientific protocols are driven by their implementation – Scientists use the resources they know • data (quality) • access to data • format, limits, etc. ...
Document
... There are through-bond interactions and through-space interactions. The latter usually being a consequence of the so-called nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE). Experiments of the nuclear-Overhauser variety may establish distances between atoms. • These distances are subjected to a technique called Dist ...
... There are through-bond interactions and through-space interactions. The latter usually being a consequence of the so-called nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE). Experiments of the nuclear-Overhauser variety may establish distances between atoms. • These distances are subjected to a technique called Dist ...
Workshop VIII Fungal Cell Factories Chair: Cees van den Hondel 183
... Aspergillus niger is considered an excellent system for protein production due to its ability to secrete large amounts of enzymes into the medium. Secretion of certain enzymes of industrial relevance, such as glucoamylase, has been studied in detail and improved very successfully in some cases. Stra ...
... Aspergillus niger is considered an excellent system for protein production due to its ability to secrete large amounts of enzymes into the medium. Secretion of certain enzymes of industrial relevance, such as glucoamylase, has been studied in detail and improved very successfully in some cases. Stra ...
Bio1A Unit 1-2 Biological Molecules Notes File
... • Cysteine (R = -SH) can form a disulfide bond (covalent, rare) • Other side chains will interact through hydrogen (primary) ionic bonding • Ultimate structure is typically most thermodynamically stable (best fit) • Driven by interaction with H2O envirnoment ...
... • Cysteine (R = -SH) can form a disulfide bond (covalent, rare) • Other side chains will interact through hydrogen (primary) ionic bonding • Ultimate structure is typically most thermodynamically stable (best fit) • Driven by interaction with H2O envirnoment ...
DLS-Characterisation of protein melting point
... chains, synthesized within the cell from a pool of 20 different amino acid types. In contrast to manmade and random coil biological polymers, the protein’s polypeptide chains are folded into unique 3-dimensional structures in the natured state. These structures are stabilized by a combination of ele ...
... chains, synthesized within the cell from a pool of 20 different amino acid types. In contrast to manmade and random coil biological polymers, the protein’s polypeptide chains are folded into unique 3-dimensional structures in the natured state. These structures are stabilized by a combination of ele ...
Chapter Five
... Proteins help regulate the quantity of fluids to help maintain fluid balance. Cells and the spaces between cells must contain a constant flux of and amount of fluid. Water can diffuse freely in and out of a cell; proteins can not ...
... Proteins help regulate the quantity of fluids to help maintain fluid balance. Cells and the spaces between cells must contain a constant flux of and amount of fluid. Water can diffuse freely in and out of a cell; proteins can not ...
Discovering Macromolecular Interactions
... Non-denaturing buffers are used when the IP antigen is detergent-soluble and when the antibody can recognize the native form of the protein. These buffers contain non-ionic detergents, such as NP-40 or Triton X-100. Denaturing buffers, such as radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer, are more ...
... Non-denaturing buffers are used when the IP antigen is detergent-soluble and when the antibody can recognize the native form of the protein. These buffers contain non-ionic detergents, such as NP-40 or Triton X-100. Denaturing buffers, such as radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer, are more ...
Protein Synthesis
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
Chapter 2 bio
... a very small volume at the center of an atom called the atomic nucleus. On the other hand, electrons are negatively charged and they can be found revolving around the nucleus. ...
... a very small volume at the center of an atom called the atomic nucleus. On the other hand, electrons are negatively charged and they can be found revolving around the nucleus. ...
simulating protein analysis using gel electrophoresis
... A technique known as gel electrophoresis is widely used to analyze the size of macromolecules. These size differences can be used for evolutionary analysis as well as the analysis of a number of other critical questions regarding both proteins and DNA. Gel electrophoresis works on two relatively sim ...
... A technique known as gel electrophoresis is widely used to analyze the size of macromolecules. These size differences can be used for evolutionary analysis as well as the analysis of a number of other critical questions regarding both proteins and DNA. Gel electrophoresis works on two relatively sim ...
Enzyme Regulation - University of San Diego Home Pages
... What Kinds of Covalent Modification Regulate the Activity of Enzymes? Protein kinases phosphorylate Ser, Thr, and Tyr residues in target proteins Kinases typically recognize specific amino acid sequences in their targets In spite of this specificity, all kinases share a common catalytic mechanism b ...
... What Kinds of Covalent Modification Regulate the Activity of Enzymes? Protein kinases phosphorylate Ser, Thr, and Tyr residues in target proteins Kinases typically recognize specific amino acid sequences in their targets In spite of this specificity, all kinases share a common catalytic mechanism b ...
A photoactivatable green-fluorescent protein from the phylum
... In the years following the publication of ‘A photoactivatable green-fluorescent protein from the phylum Ctenophora’ [1], another research group [2] sequenced hydrozoan (Cnidaria) fluorescent proteins that were very similar to those we cloned from cDNA prepared from ctenophore specimens. We therefore ...
... In the years following the publication of ‘A photoactivatable green-fluorescent protein from the phylum Ctenophora’ [1], another research group [2] sequenced hydrozoan (Cnidaria) fluorescent proteins that were very similar to those we cloned from cDNA prepared from ctenophore specimens. We therefore ...
Transport of Cytoplasmically Synthesized Proteins into Membranous
... – Target sequence N-X-S and N-X-T (X = P) ...
... – Target sequence N-X-S and N-X-T (X = P) ...
Concentration of solutes and solvent in a solution
... o Different functions of lipids: function as long-term energy storage molecules function as structural molecules-in cell membranes (phospholipids and cholesterol) Nucleic acids: o nucleotides, subunits of nucleotides o DNA and RNA o Store genetic information o Central dogma of molecular biology: ...
... o Different functions of lipids: function as long-term energy storage molecules function as structural molecules-in cell membranes (phospholipids and cholesterol) Nucleic acids: o nucleotides, subunits of nucleotides o DNA and RNA o Store genetic information o Central dogma of molecular biology: ...
Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular
... Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular details of protein-DNA interactions is critical for deciphering the mechanisms of gene regulation. This dataset contains 56 proteins bound to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), 427 protein-DNA complexes with resolution better than 3.0 Å were extr ...
... Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular details of protein-DNA interactions is critical for deciphering the mechanisms of gene regulation. This dataset contains 56 proteins bound to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), 427 protein-DNA complexes with resolution better than 3.0 Å were extr ...
Hints on Column Chromatography
... Cysteine (nucleophilic, used in catalysis, controls shape of protein) ...
... Cysteine (nucleophilic, used in catalysis, controls shape of protein) ...
Chapter 5 Separations: I) Based on Charge or pI A) Electrophoresis
... Carboxypeptidases will cleave amino acids sequentially from the C-terminus. There are different types (A, B, C, and Y) that are effective for different amino acids. Aminopeptidases will cleave amino acids sequentially from the N-terminus. Determination of 3-D structure of proteins X-ray diffraction ...
... Carboxypeptidases will cleave amino acids sequentially from the C-terminus. There are different types (A, B, C, and Y) that are effective for different amino acids. Aminopeptidases will cleave amino acids sequentially from the N-terminus. Determination of 3-D structure of proteins X-ray diffraction ...
Structure of a protein - Campus
... The nucleotides of RNA and DNA Each nucleotide is composed of three parts: a phosphate group (orthophosphoric acid), a sugar with 5 carbon atoms (a pentose) and a nitrogenous base. Of these there are 2 types: one group with two rings, the purines, and another with only a single ring called the ...
... The nucleotides of RNA and DNA Each nucleotide is composed of three parts: a phosphate group (orthophosphoric acid), a sugar with 5 carbon atoms (a pentose) and a nitrogenous base. Of these there are 2 types: one group with two rings, the purines, and another with only a single ring called the ...
Protein Folding, Shape, and Function Activity Instructions
... A core idea in life sciences is that there is a fundamental relationship between biological structure and the function it must perform. At the macro-level, Darwin recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food the finch ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship i ...
... A core idea in life sciences is that there is a fundamental relationship between biological structure and the function it must perform. At the macro-level, Darwin recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food the finch ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship i ...
The Molecules of Life
... All proteins are constructed from a common set of 20 kinds of amino acids. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom bonded to four covalent partners in which three of those attachment groups are common to all amino acids. Proteins as Polymers Cells link amino acids together by dehydration r ...
... All proteins are constructed from a common set of 20 kinds of amino acids. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom bonded to four covalent partners in which three of those attachment groups are common to all amino acids. Proteins as Polymers Cells link amino acids together by dehydration r ...
Module code SC-4327 Module Title Bio
... -Carbohydrates: Structures and reactions of monosaccharides. The use of protective groups in the syntheses of carbohydrate derivatives including oligosaccharides. Introduction to some biologically important sugars and their functions. -Amino acids and proteins: Stereoselective syntheses of amin ...
... -Carbohydrates: Structures and reactions of monosaccharides. The use of protective groups in the syntheses of carbohydrate derivatives including oligosaccharides. Introduction to some biologically important sugars and their functions. -Amino acids and proteins: Stereoselective syntheses of amin ...
- St. Aidan School
... Lipids– are rich in energy They consist of fats, oils, waxes and cholesterol. They release two times as much energy than carbohydrates. ...
... Lipids– are rich in energy They consist of fats, oils, waxes and cholesterol. They release two times as much energy than carbohydrates. ...
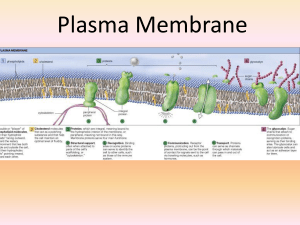
Plasma Membrane
... 4. Cell-to-cell communication – many include carbohydrates attached to protein molecules on outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to ...
... 4. Cell-to-cell communication – many include carbohydrates attached to protein molecules on outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to ...
16-17 membrane notes
... • Held together by weak phobic interactions that make membrane fluid • Components can move laterally ...
... • Held together by weak phobic interactions that make membrane fluid • Components can move laterally ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.