Rough ER
... Eukaryotic organelle that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles and cisternae within cells. It flattens sacs that serve a variety of functions in the cell. ...
... Eukaryotic organelle that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles and cisternae within cells. It flattens sacs that serve a variety of functions in the cell. ...
The Human Cell Poster Introduction
... that really do the heavy lifting. While there are around 20,000 genes encoded in our DNA, the total number of proteins is estimated to be many times more—possibly as many as a million*. This is because a single gene might produce multiple variants of a particular protein through, for example, altern ...
... that really do the heavy lifting. While there are around 20,000 genes encoded in our DNA, the total number of proteins is estimated to be many times more—possibly as many as a million*. This is because a single gene might produce multiple variants of a particular protein through, for example, altern ...
Cell-based method for analysis of protein
... compared to other cell-based assays (e.g. FRET) complexity and technical requirements are reduced ...
... compared to other cell-based assays (e.g. FRET) complexity and technical requirements are reduced ...
File - SMIC Nutrition Science
... 6. The making of protein from 20 amino acids was compared in the chapter to the use of the English alphabet (26 letters) to make words and speak the English language. Why was this such a fitting analogy? ...
... 6. The making of protein from 20 amino acids was compared in the chapter to the use of the English alphabet (26 letters) to make words and speak the English language. Why was this such a fitting analogy? ...
Interactive Software for the study of membrane biology: lipid
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
Supplementary Information (doc 34K)
... showed good discrimination between the predicted correct and incorrect peptide-spectrum assignments, and only peptides with charge states of +1, +2, and +3 were retained as confident identifications because the Peptide Prophet models were not a good fit to the data for charge states ≥ 4. Protein ide ...
... showed good discrimination between the predicted correct and incorrect peptide-spectrum assignments, and only peptides with charge states of +1, +2, and +3 were retained as confident identifications because the Peptide Prophet models were not a good fit to the data for charge states ≥ 4. Protein ide ...
Towards a More Effective Anticancer Therapy By Mariam Ludim
... these patients are children and we would not want this illness to continue,” that's the way the researcher describes the force that has motivated her to conduct studies in the field of cancer for the past ten years. Although there are many treatments for this disease, science is still exploring othe ...
... these patients are children and we would not want this illness to continue,” that's the way the researcher describes the force that has motivated her to conduct studies in the field of cancer for the past ten years. Although there are many treatments for this disease, science is still exploring othe ...
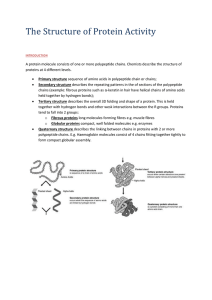
The_Structure_of_Protein_Activity
... held together by hydrogen bonds); Tertiary structure describes the overall 3D folding and shape of a protein. This is held together with hydrogen bonds and other wesk interactions between the R groups. Proteins tend to fall into 2 groups: o Fibrous proteins long molecules forming fibres e.g. muscle ...
... held together by hydrogen bonds); Tertiary structure describes the overall 3D folding and shape of a protein. This is held together with hydrogen bonds and other wesk interactions between the R groups. Proteins tend to fall into 2 groups: o Fibrous proteins long molecules forming fibres e.g. muscle ...
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS IN THE BODY FUNCTIONS OF
... nerve cell function. SOURCES OF PROTEIN "Amino acids" is the name given to the basic structural unit of proteins. Nitrogen molecules are combined with hydrogen molecules to make what is called an amino group. Each amino acid has a carboxyl group which is made up of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. To da ...
... nerve cell function. SOURCES OF PROTEIN "Amino acids" is the name given to the basic structural unit of proteins. Nitrogen molecules are combined with hydrogen molecules to make what is called an amino group. Each amino acid has a carboxyl group which is made up of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. To da ...
A.P.day52 proteins
... ---folded on itself with hydrogen bonds ---determines the active site of the protein ---determined by the R-site ...
... ---folded on itself with hydrogen bonds ---determines the active site of the protein ---determined by the R-site ...
The (Indirect) Costs of Conducting Research: A study of
... Proteins of expected molecular size were produced by transformed E. coli cell cultures and separated by affinity purification. The s-agarose protocols did not result in highly pure samples. Phosphorylation did not appear to be successful in two different concentrations and incubation times, possibly ...
... Proteins of expected molecular size were produced by transformed E. coli cell cultures and separated by affinity purification. The s-agarose protocols did not result in highly pure samples. Phosphorylation did not appear to be successful in two different concentrations and incubation times, possibly ...
File
... • Amino acids are joined together on the ribosome to form long chains called polypeptides, which makes up proteins. • Each type of a.a. differs in the composition of the variable side chain (R). • Different side chains will have distinct chemical properties (charged, nonpolar). • The protein will f ...
... • Amino acids are joined together on the ribosome to form long chains called polypeptides, which makes up proteins. • Each type of a.a. differs in the composition of the variable side chain (R). • Different side chains will have distinct chemical properties (charged, nonpolar). • The protein will f ...
Biomolecules carbonylation in oxidative stress related human
... neurodegeneration, are characterized by elevated levels of oxidatively modified biomolecules (protein, lipids and DNA). Oxidation of biomolecules results in numerous functional dysfunctions associated with disease progression. One of the most abundant and hazardous class of modifications are reactiv ...
... neurodegeneration, are characterized by elevated levels of oxidatively modified biomolecules (protein, lipids and DNA). Oxidation of biomolecules results in numerous functional dysfunctions associated with disease progression. One of the most abundant and hazardous class of modifications are reactiv ...
Human Proteome advertising miniposter (PDF)
... A proximity ligation assay uses a pair of oligonucleotide labeled antibodies binding to different epitopes on a protein, or to epitopes in close proximity on two proteins in a complex. Used for detection, visualization and quantification of single proteins or protein-protein interactions. ...
... A proximity ligation assay uses a pair of oligonucleotide labeled antibodies binding to different epitopes on a protein, or to epitopes in close proximity on two proteins in a complex. Used for detection, visualization and quantification of single proteins or protein-protein interactions. ...
Dr. Bryan Ballif identifies phosphorylation sites on key proteins regulating cell growth and proliferation.
... Genetics Network Proteomics Facility, which he co‐directs. ...
... Genetics Network Proteomics Facility, which he co‐directs. ...
Proteins
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
PowerPoint
... About (85) % of all plasma proteins are synthesized in the liver. The bulk of the remainder (particularly immunoglobulins) are synthesized by plasma cells and cells of reticuloendothelial system while the site of synthesis of most plasma proteins is known with some certainty; the site of degradation ...
... About (85) % of all plasma proteins are synthesized in the liver. The bulk of the remainder (particularly immunoglobulins) are synthesized by plasma cells and cells of reticuloendothelial system while the site of synthesis of most plasma proteins is known with some certainty; the site of degradation ...
John Torri Basic Nutrition Special Topic: Protein November 13 2014
... carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Most people don’t know how proteins are stored, sources of proteins, or even how they work. I found an article that helps shed light on this topic. According to “Choosing Protein Wisely” Our bodies need proteins to build strong bones, muscles, skin, and cells. Beca ...
... carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Most people don’t know how proteins are stored, sources of proteins, or even how they work. I found an article that helps shed light on this topic. According to “Choosing Protein Wisely” Our bodies need proteins to build strong bones, muscles, skin, and cells. Beca ...
Proteins pages 8 and 9
... type of protein. The body can make eleven amino acids. The remaining nine have to be obtained from protein in the diet. These are known as essential amino acids. ...
... type of protein. The body can make eleven amino acids. The remaining nine have to be obtained from protein in the diet. These are known as essential amino acids. ...
Document
... other proteins and help them fold/assemble properly (can be folding of one protein and assembly of multiple proteins). Heat shock protein story: Two major types: type I includes hsp70---bind and prevent misfolding of the substrate proteins (can also unfold proteins)---cytosol, chloroplast, mitochond ...
... other proteins and help them fold/assemble properly (can be folding of one protein and assembly of multiple proteins). Heat shock protein story: Two major types: type I includes hsp70---bind and prevent misfolding of the substrate proteins (can also unfold proteins)---cytosol, chloroplast, mitochond ...
Importance of Proteins PowerPoint
... Describe ways in which protein is used in food preparation. Identify the essential and nonessential amino acids. Compare and contrast complete and incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles o ...
... Describe ways in which protein is used in food preparation. Identify the essential and nonessential amino acids. Compare and contrast complete and incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles o ...
TWO GENES ENCODING FUNCTIONAL PECTIN
... Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2nd University of Naples, Via Costantinopoli 16, I80138 Napoli, Italy A proteinaceous inhibitor of pectin methylesterase (PMEI) has been reported in kiwi but to date no other proteins acting as PMEI have been found in plants. Two sequences closely related t ...
... Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2nd University of Naples, Via Costantinopoli 16, I80138 Napoli, Italy A proteinaceous inhibitor of pectin methylesterase (PMEI) has been reported in kiwi but to date no other proteins acting as PMEI have been found in plants. Two sequences closely related t ...
Biochemistry Homework
... Polypeptides and proteins are formed by the condensation reactions of amino acids. (a) ...
... Polypeptides and proteins are formed by the condensation reactions of amino acids. (a) ...
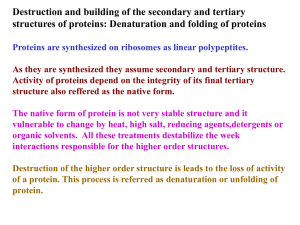
Protein folding
... interactions responsible for the higher order structures. Destruction of the higher order structure is leads to the loss of activity of a protein. This process is referred as denaturation or unfolding of protein. ...
... interactions responsible for the higher order structures. Destruction of the higher order structure is leads to the loss of activity of a protein. This process is referred as denaturation or unfolding of protein. ...
Proteomics

Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term proteomics was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with genomics, the study of the genome. The word proteome is a portmanteau of protein and genome, and was coined by Marc Wilkins in 1994 while working on the concept as a PhD student.The proteome is the entire set of proteins, produced or modified by an organism or system. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain formed on the basis of the research and development of the Human Genome Project; it is also emerging scientific research and exploration of proteomes from the overall level of intracellular protein composition, structure, and its own unique activity patterns. It is an important component of functional genomics.While proteomics generally refers to the large-scale experimental analysis of proteins, it is often specifically used for protein purification and mass spectrometry.