Supplemental Data
... incubating increasing amounts of wildtype or mutant Gal80 protein with a recombinant Gal4p derivative and a ...
... incubating increasing amounts of wildtype or mutant Gal80 protein with a recombinant Gal4p derivative and a ...
91.510_ch9_2
... Ab initio protein structure prediction Ab initio prediction can be performed when a protein has no detectable homologs. Protein folding is modeled based on global free-energy minimum estimates. The “Rosetta Stone” methods was applied to sequence families lacking known structures. For 80 of 131 prot ...
... Ab initio protein structure prediction Ab initio prediction can be performed when a protein has no detectable homologs. Protein folding is modeled based on global free-energy minimum estimates. The “Rosetta Stone” methods was applied to sequence families lacking known structures. For 80 of 131 prot ...
Journal of Chromatography
... sugars, yields important information about the anomeric specificity of the lectin’*21. Glycosides of aromatic aglycones, on the other hand, provide useful information about the nature of the protein site adjacent to the place where carbohydrate binding occurs. However, these later experiments should ...
... sugars, yields important information about the anomeric specificity of the lectin’*21. Glycosides of aromatic aglycones, on the other hand, provide useful information about the nature of the protein site adjacent to the place where carbohydrate binding occurs. However, these later experiments should ...
Document
... • Make predictions of peptides in the presence of substrates using physics-based force-fields such as GROMACS • Analyse for similarity of structures (local and global) as well as common contact patterns between atoms in amino acids – the structural similarities and patterns give us the structural pa ...
... • Make predictions of peptides in the presence of substrates using physics-based force-fields such as GROMACS • Analyse for similarity of structures (local and global) as well as common contact patterns between atoms in amino acids – the structural similarities and patterns give us the structural pa ...
Lh6Ch05
... 1. Reversible binding of ligands is essential – Specificity of ligands and binding sites – Ligand binding is often coupled to conformational changes, sometimes quite dramatic (Induced Fit) – In multisubunit proteins, conformational changes in one subunit can affect the others (Cooperativity) – Inter ...
... 1. Reversible binding of ligands is essential – Specificity of ligands and binding sites – Ligand binding is often coupled to conformational changes, sometimes quite dramatic (Induced Fit) – In multisubunit proteins, conformational changes in one subunit can affect the others (Cooperativity) – Inter ...
Post-translational Modifications and Their
... or not the proteins are post-translationally modified and how. PTM analyses are more difficult than protein identification for the following reasons: Firstly, highly sensitive methods are required for detection due to a low stoichiometry. For example, since only 5-10% of a protein kinase substrate i ...
... or not the proteins are post-translationally modified and how. PTM analyses are more difficult than protein identification for the following reasons: Firstly, highly sensitive methods are required for detection due to a low stoichiometry. For example, since only 5-10% of a protein kinase substrate i ...
Amino Acid Structure
... tetrahedral shape due to the angles of the bonds between the atoms There are twenty different naturally occurring amino acids that differ from one another by virtue of the R group The simplest of the amino acids possesses a hydrogen atom for its R group. This amino acid is called GLYCINE ...
... tetrahedral shape due to the angles of the bonds between the atoms There are twenty different naturally occurring amino acids that differ from one another by virtue of the R group The simplest of the amino acids possesses a hydrogen atom for its R group. This amino acid is called GLYCINE ...
practice making a protein from dna
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
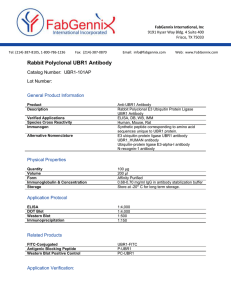
Anti-UBR1 Antibody
... system. The recognition component of this pathway, encoded by this gene, binds to a destabilizing N-terminal residue of a substrate protein and participates in the formation of a substrate-linked multi ubiquitin chain. It recognizes and binds to proteins bearing specific N-terminal residues that are ...
... system. The recognition component of this pathway, encoded by this gene, binds to a destabilizing N-terminal residue of a substrate protein and participates in the formation of a substrate-linked multi ubiquitin chain. It recognizes and binds to proteins bearing specific N-terminal residues that are ...
1.ESTIMATION OF PROTEIN BY LOWRY`S
... heavier particles are called flocs. Flocculants, or flocculating agents are chemicals that promote flocculation by causing colloids and other suspended particles in liquids to aggregate, forming a floc. Flocculants are used in water treatment processes to improve the sedimentation or filterability o ...
... heavier particles are called flocs. Flocculants, or flocculating agents are chemicals that promote flocculation by causing colloids and other suspended particles in liquids to aggregate, forming a floc. Flocculants are used in water treatment processes to improve the sedimentation or filterability o ...
Problem Set 5, 7.06, Spring 2003 1. In order to please your
... • There are no O-linked sugars in this protein • A signal sequence at the N-terminus for insertion into the ER followed by a cleavage site at amino acid residue 23 You have the cDNA that encodes for the protein, so you use it to in-vitro translate the protein in a cell-free system without microsomes ...
... • There are no O-linked sugars in this protein • A signal sequence at the N-terminus for insertion into the ER followed by a cleavage site at amino acid residue 23 You have the cDNA that encodes for the protein, so you use it to in-vitro translate the protein in a cell-free system without microsomes ...
Protein_structure_II
... Prediction of 3-D Protein Structures • There are about 30,000 structures in PDB, but more than 1.8 million non-redundant protein sequences in UniProt (Swiss-Prot + TrEMBL). • Computational structure prediction may provide valuable information for most of the protein sequences derived from genome se ...
... Prediction of 3-D Protein Structures • There are about 30,000 structures in PDB, but more than 1.8 million non-redundant protein sequences in UniProt (Swiss-Prot + TrEMBL). • Computational structure prediction may provide valuable information for most of the protein sequences derived from genome se ...
Vocabulary Review
... Nucleic Acid that store genetic information and house the code to make all protein. ...
... Nucleic Acid that store genetic information and house the code to make all protein. ...
Cytochrome P450 Proteins
... LC-MS/MS Protein Expression Analysis − Highly sensitive, specific, and fast Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) method has been developed: – 12 different peptides representing 4 unique P450 proteins (CYP 1A2, 2B6, 3A4 and 3A5) were simultaneously monitored and quantified – 2B6, a lower abundant CYP, ...
... LC-MS/MS Protein Expression Analysis − Highly sensitive, specific, and fast Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) method has been developed: – 12 different peptides representing 4 unique P450 proteins (CYP 1A2, 2B6, 3A4 and 3A5) were simultaneously monitored and quantified – 2B6, a lower abundant CYP, ...
Final Presentations Abstract Book - MSOE Center for BioMolecular
... of Wisconsin The cause of Proteus Syndrome, characterized by uncontrolled cell division leading to tumor formations, is currently not understood. Recent work suggests that cells from Proteus Syndrome patients express a higher level of a protein called Plexin D1. Plexin D1 has been found in angiogeni ...
... of Wisconsin The cause of Proteus Syndrome, characterized by uncontrolled cell division leading to tumor formations, is currently not understood. Recent work suggests that cells from Proteus Syndrome patients express a higher level of a protein called Plexin D1. Plexin D1 has been found in angiogeni ...
Display of Artificial Scaffolding Proteins on Yeast Surface
... Keywords: scaffolding protein, yeast, cellulosome, cohesin, dockerin. Introduction Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a very useful microorganism for ethanol production. However, the ability of this yeast for protein secretion was much lower than that of aerobic fungi such as Trichoderma reesei. For develo ...
... Keywords: scaffolding protein, yeast, cellulosome, cohesin, dockerin. Introduction Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a very useful microorganism for ethanol production. However, the ability of this yeast for protein secretion was much lower than that of aerobic fungi such as Trichoderma reesei. For develo ...
Биологическая химия
... 3. The relationship of these reactions to the activity of cells, organs, tissues. 4. The ways of affecting the biochemical processes in a living organism. ...
... 3. The relationship of these reactions to the activity of cells, organs, tissues. 4. The ways of affecting the biochemical processes in a living organism. ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... lipids in general contain lots of energy fats in animal bodies function as a long term energy storage fatty tissue also covers our organs and protects them from injury lipids do not dissolve in water It is possible for us to digest fats because we emulsify them. Bile from our gall bladder is secrete ...
... lipids in general contain lots of energy fats in animal bodies function as a long term energy storage fatty tissue also covers our organs and protects them from injury lipids do not dissolve in water It is possible for us to digest fats because we emulsify them. Bile from our gall bladder is secrete ...
bbr052online 329..336 - Oxford Academic
... study and characterization of a specific family of proteins normally obtain in-depth knowledge (after years of experimental research) of the particular and constrained set of residues, which helps classify a protein into a functional family (i.e. catalytic triads, dinucleotide binding motif, G-motif ...
... study and characterization of a specific family of proteins normally obtain in-depth knowledge (after years of experimental research) of the particular and constrained set of residues, which helps classify a protein into a functional family (i.e. catalytic triads, dinucleotide binding motif, G-motif ...
Amino acids and prot..
... teeth, cartilage, tendons, skin and blood vessels. • Collagen may be present as gel e.g. in extracellular matrix or in vitreous humor of the eye. • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most c ...
... teeth, cartilage, tendons, skin and blood vessels. • Collagen may be present as gel e.g. in extracellular matrix or in vitreous humor of the eye. • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most c ...
Vocabulary Review
... Nucleic Acid that store genetic information and house the code to make all protein. ...
... Nucleic Acid that store genetic information and house the code to make all protein. ...
File - Pi Beta Philes!
... Short answer. Answer each question clearly and concisely based on class discussion. 46. (4 pts) We listed a number of functions of protein on the board, such as hormones like insulin that regulate metabolism. Give me two other functions of proteins in the body. ...
... Short answer. Answer each question clearly and concisely based on class discussion. 46. (4 pts) We listed a number of functions of protein on the board, such as hormones like insulin that regulate metabolism. Give me two other functions of proteins in the body. ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.