EXPRESSION OF IQ-MOTIF GENES IN HUMAN CELLS AND ASPM
... In summary, the three multi-IQmotif proteins examined in this study were expressed widely in adult human tissues and transformed cell lines. The ASPM gene was expressed in nine transformed cell lines and 16 adult tissues but was absent in skeletal muscle and brain. Bond et al reported that in mice, ...
... In summary, the three multi-IQmotif proteins examined in this study were expressed widely in adult human tissues and transformed cell lines. The ASPM gene was expressed in nine transformed cell lines and 16 adult tissues but was absent in skeletal muscle and brain. Bond et al reported that in mice, ...
Types and effects of protein variations. Vihinen
... insertion/indel site or it has changed, in which case they are called as amphigoric variations. “Protein truncation” is a special case of deletion where deletion occurs either in N- or Cterminus. Indels originate due to both insertion and deletion. The different types of protein variations in a sho ...
... insertion/indel site or it has changed, in which case they are called as amphigoric variations. “Protein truncation” is a special case of deletion where deletion occurs either in N- or Cterminus. Indels originate due to both insertion and deletion. The different types of protein variations in a sho ...
Localization of Protein-Protein lnteractions between Subunits of
... Our efforts to map potential dimerization region(s) in phytochrome have focused on the carboxy-terminal half of the protein that has previously been shown to behave as a dimer (Jones and Quail, 1986). We have defined the carboxy-terminal domain as beginning at approximately amino acid L600 of oat Ph ...
... Our efforts to map potential dimerization region(s) in phytochrome have focused on the carboxy-terminal half of the protein that has previously been shown to behave as a dimer (Jones and Quail, 1986). We have defined the carboxy-terminal domain as beginning at approximately amino acid L600 of oat Ph ...
Localization of Protein-Protein lnteractions between Subunits of
... Our efforts to map potential dimerization region(s) in phytochrome have focused on the carboxy-terminal half of the protein that has previously been shown to behave as a dimer (Jones and Quail, 1986). We have defined the carboxy-terminal domain as beginning at approximately amino acid L600 of oat Ph ...
... Our efforts to map potential dimerization region(s) in phytochrome have focused on the carboxy-terminal half of the protein that has previously been shown to behave as a dimer (Jones and Quail, 1986). We have defined the carboxy-terminal domain as beginning at approximately amino acid L600 of oat Ph ...
Engineering of metabolic pathways by artificial enzyme channels
... function in isolation but form supramolecular complexes (Jørgensen et al., 2005). By providing spatial and temporal organization of molecules within the cell, these complexes allow optimized substrate channeling and thereby prevent loss of intermediates and improve control and efficiency of catalys ...
... function in isolation but form supramolecular complexes (Jørgensen et al., 2005). By providing spatial and temporal organization of molecules within the cell, these complexes allow optimized substrate channeling and thereby prevent loss of intermediates and improve control and efficiency of catalys ...
Review article Zinc finger protein (ZFP) in plants
... motif, which is proposed to be an independently folded DNA-binding domain which can recognize specific DNA sequences (Klug and Rhodes, 1987; Hollenberg and Evans, 1988; Payre and Vincent, 1988). ZFP binds with zinc ion through its Cysteine (Cys) and Histidine (His) using ‘Zinc Finger’. The zinc fing ...
... motif, which is proposed to be an independently folded DNA-binding domain which can recognize specific DNA sequences (Klug and Rhodes, 1987; Hollenberg and Evans, 1988; Payre and Vincent, 1988). ZFP binds with zinc ion through its Cysteine (Cys) and Histidine (His) using ‘Zinc Finger’. The zinc fing ...
computer handout - GEP Community Server
... Examine the data in your output file. Scroll down beyond the initial list of hits so you can see the actual sequence alignments. Sometimes there is more than one hit for the same protein in the same organism – it is just that they have been submitted by different people at different times, or the sa ...
... Examine the data in your output file. Scroll down beyond the initial list of hits so you can see the actual sequence alignments. Sometimes there is more than one hit for the same protein in the same organism – it is just that they have been submitted by different people at different times, or the sa ...
Structural Insights into Catalysis and Inhibition of O
... O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase activity spectrophotometrically at 560 nm by monitoring the formation of cysteine using the acid-ninhydrin method (26). The reactions were carried out in 1500 l of 100 mM MOPS buffer at pH 7.0. O-Acetyl-Lserine and sodium sulfide (dissolved in 1 mM NaOH) were added to f ...
... O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase activity spectrophotometrically at 560 nm by monitoring the formation of cysteine using the acid-ninhydrin method (26). The reactions were carried out in 1500 l of 100 mM MOPS buffer at pH 7.0. O-Acetyl-Lserine and sodium sulfide (dissolved in 1 mM NaOH) were added to f ...
1st Sem (unit I)
... But many others consist of two or more polypeptide chains that may be structurally identical are totally unrelated. The arrangement of these polypeptide subunits is called quaternary structure of protein. Such proteins are called oligomeric proteins. The individual polypeptides are called as monomer ...
... But many others consist of two or more polypeptide chains that may be structurally identical are totally unrelated. The arrangement of these polypeptide subunits is called quaternary structure of protein. Such proteins are called oligomeric proteins. The individual polypeptides are called as monomer ...
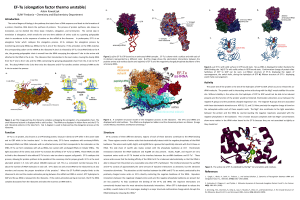
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable)
... The central dogma of biology is the pathway that starts from a DNA sequence and leads to the formation of a protein; therefore, DNA directs the synthesis of proteins. The process of protein synthesis, also known as translation, can be divided into three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination ...
... The central dogma of biology is the pathway that starts from a DNA sequence and leads to the formation of a protein; therefore, DNA directs the synthesis of proteins. The process of protein synthesis, also known as translation, can be divided into three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination ...
CARBOHYDRATES 2016
... found in granules of mast cells, has a structure similar to that of heparan sulfates, but is more highly sulfated. When released into the blood, it inhibits clot (coagulated) formation by interacting with the protein antithrombin. Heparin has an extended helical conformation. ...
... found in granules of mast cells, has a structure similar to that of heparan sulfates, but is more highly sulfated. When released into the blood, it inhibits clot (coagulated) formation by interacting with the protein antithrombin. Heparin has an extended helical conformation. ...
Биохимия жидкостей полости рта
... • In these proteins, the histidine content reaches 25%, much of arginine and lysine. Practically there is no amino acid proline. • They are involved in the protection of the oral cavity, providing anti-fungal, anti-virus and anti-microbial action. Histathines penetrate in microbial cells and cause t ...
... • In these proteins, the histidine content reaches 25%, much of arginine and lysine. Practically there is no amino acid proline. • They are involved in the protection of the oral cavity, providing anti-fungal, anti-virus and anti-microbial action. Histathines penetrate in microbial cells and cause t ...
Infrared spectroscopic studies: from small molecules to large.
... kinases. These enzymes transfer the terminal phosphoryl group from the high-energy donor molecules, such as e.g. ATP to specific substrates, either another nucleotide or a small molecule or to a protein. In Papers II and III several members of this group of enzymes are studied in closer detail. ...
... kinases. These enzymes transfer the terminal phosphoryl group from the high-energy donor molecules, such as e.g. ATP to specific substrates, either another nucleotide or a small molecule or to a protein. In Papers II and III several members of this group of enzymes are studied in closer detail. ...
Supporting Information
... phasing and refinement statistics are shown in Table S1 and S2. It was noted that ⬇80% of screened crystals suffered from significant merohedral twinning; however, little or no twinning was detected in the datasets used for this structural analysis using XTRIAGE from the PHENIX suite (13, 14). The e ...
... phasing and refinement statistics are shown in Table S1 and S2. It was noted that ⬇80% of screened crystals suffered from significant merohedral twinning; however, little or no twinning was detected in the datasets used for this structural analysis using XTRIAGE from the PHENIX suite (13, 14). The e ...
Complementary protein
... whole grains with legumes to get a complete source of protein, such as brown rice and beans. Whole grains like wheat, rye, barley, brown rice and oats lack the amino acid lysine, for example, while legumes like beans, peas and lentils are rich in lysine even though they are low in another amino acid ...
... whole grains with legumes to get a complete source of protein, such as brown rice and beans. Whole grains like wheat, rye, barley, brown rice and oats lack the amino acid lysine, for example, while legumes like beans, peas and lentils are rich in lysine even though they are low in another amino acid ...
The HSP90 family of genes in the human genome
... Introduction HSP90 proteins, named according to the 90-kDa average molecular mass of their members, are highly conserved molecular chaperones that account for 1 – 2% of all cellular proteins in most cells under non-stress conditions [1]. HSP90 proteins have key roles in signal transduction, protein ...
... Introduction HSP90 proteins, named according to the 90-kDa average molecular mass of their members, are highly conserved molecular chaperones that account for 1 – 2% of all cellular proteins in most cells under non-stress conditions [1]. HSP90 proteins have key roles in signal transduction, protein ...
No Slide Title
... Carry information from a well studied to a less well studied protein. Such information can be: Phosphorylation sites Glycosylation sites Stabilizing mutations Membrane anchors Ion binding sites Ligand binding residues Cellular localization ...
... Carry information from a well studied to a less well studied protein. Such information can be: Phosphorylation sites Glycosylation sites Stabilizing mutations Membrane anchors Ion binding sites Ligand binding residues Cellular localization ...
The CamSol Method of Rational Design of Protein Mutants with
... method in the case of a recently described singledomain antibody that binds the Aβ peptide [32]. The use of single-domain antibodies is attracting attention because these molecules can exhibit high affinity and specificity to their targets without the complications associated with the complex archit ...
... method in the case of a recently described singledomain antibody that binds the Aβ peptide [32]. The use of single-domain antibodies is attracting attention because these molecules can exhibit high affinity and specificity to their targets without the complications associated with the complex archit ...
Translation - SBI4u Biology Resources
... that corresponds to the second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EFTs), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is clea ...
... that corresponds to the second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EFTs), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is clea ...
Not Every Disulfide Lasts Forever: Disulfide Bond
... To elucidate the activation mechanism of OxyR, mass spectrometry and in vivo thiol-trapping techniques were applied (3, 73). These experiments, which were performed with the quadruple mutant protein OxyR4C Þ A, showed that the activation of OxyR is paralleled by the formation of an intramolecular di ...
... To elucidate the activation mechanism of OxyR, mass spectrometry and in vivo thiol-trapping techniques were applied (3, 73). These experiments, which were performed with the quadruple mutant protein OxyR4C Þ A, showed that the activation of OxyR is paralleled by the formation of an intramolecular di ...
pdf file - The Department of Computer Science
... The first principles of the evolution of the triplet code (Trifonov 2004), suggested by the consensus evolutionary temporal order of amino acids are: (1) Abiotic start, (2) Primacy of thermostability, (3) Complementarity of codons and of early mRNA, (4) Processivity of codon acquirements, each havin ...
... The first principles of the evolution of the triplet code (Trifonov 2004), suggested by the consensus evolutionary temporal order of amino acids are: (1) Abiotic start, (2) Primacy of thermostability, (3) Complementarity of codons and of early mRNA, (4) Processivity of codon acquirements, each havin ...
Biological ontologies for human functional annotation and
... alpha) gene transcription in CD4-CD8- murine Tlymphocyte precursors . Here we map the cisacting elements that mediate interleukin
responsiveness of the mouse IL-2R
alpha gene
... alpha) gene transcription in
•High Boiling Point •High Specific Heat (Heat Capacity) •Very polar
... 1. Intrinsic propensity of amino acids (Ala likes to be in helices) 2. Interactions between R-groups (ionic interactions) 3. Bulkiness of adjacent R groups (Phe, Trp) 4. Occurrence of Pro/Gly (destabilize helices) • Pro is not very flexible and causes helix kinks, Pro cannot H-bond because its N is ...
... 1. Intrinsic propensity of amino acids (Ala likes to be in helices) 2. Interactions between R-groups (ionic interactions) 3. Bulkiness of adjacent R groups (Phe, Trp) 4. Occurrence of Pro/Gly (destabilize helices) • Pro is not very flexible and causes helix kinks, Pro cannot H-bond because its N is ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.