chemistry 1000 - U of L Class Index
... On March 15, 2007, the US FDA learned that some brands of pet food were making animals very ill – even killing some! This was traced to vegetable proteins imported from China which were found to contain melamine. There was a large-scale recall of pet food and the responsible individuals were indicte ...
... On March 15, 2007, the US FDA learned that some brands of pet food were making animals very ill – even killing some! This was traced to vegetable proteins imported from China which were found to contain melamine. There was a large-scale recall of pet food and the responsible individuals were indicte ...
Lec 15: Nitrogen in biochemistry
... • Different organisms have developed different methods to overcome oxygen‐ sensitivity. • Formation of heterocysts in diazatrophic cyanobacteria • Production of additional cell walls • Glycolipid to form hydrophobic barrier • Degradation of photosystem II • Formation of leghemoglobin in Rhizobium • ...
... • Different organisms have developed different methods to overcome oxygen‐ sensitivity. • Formation of heterocysts in diazatrophic cyanobacteria • Production of additional cell walls • Glycolipid to form hydrophobic barrier • Degradation of photosystem II • Formation of leghemoglobin in Rhizobium • ...
Impact of glucose uptake rate on recombinant protein production in
... product. However, this important breakthrough would never have been realised without the pioneering work made in the early seventies on how to isolate and amplify genes (or DNA) and then insert them into specific genetic locations to create transgenic organisms (Cohen, et al., 1973; Lobban and Kaise ...
... product. However, this important breakthrough would never have been realised without the pioneering work made in the early seventies on how to isolate and amplify genes (or DNA) and then insert them into specific genetic locations to create transgenic organisms (Cohen, et al., 1973; Lobban and Kaise ...
Protein Cross-linkers handbook and selection guide
... common applications of a cross-linker. Proteinprotein cross-linking is used for the preparation of enzyme coupled antibody probes; protein coupling to chromospheres, fluorophores, and other molecules. Enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase coupled to primary and secondary antibodies are ...
... common applications of a cross-linker. Proteinprotein cross-linking is used for the preparation of enzyme coupled antibody probes; protein coupling to chromospheres, fluorophores, and other molecules. Enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase coupled to primary and secondary antibodies are ...
Lecture 4-5 Slides
... Fig. 7-32: translation Initiator tRNA in P site Aminoacyl-tRNA binds to A site Ribosome shift: one codon ...
... Fig. 7-32: translation Initiator tRNA in P site Aminoacyl-tRNA binds to A site Ribosome shift: one codon ...
Document
... • The fold of Aβ(21-30) may provide plausible scenarios for the initial stages of fibril formation of full Aβ(1-40). • Identification of amino acids important for folding stability may lead to strategies to prevent fibril formation. What did we Find? • Aβ(21-30) adopts a loop conformation with cente ...
... • The fold of Aβ(21-30) may provide plausible scenarios for the initial stages of fibril formation of full Aβ(1-40). • Identification of amino acids important for folding stability may lead to strategies to prevent fibril formation. What did we Find? • Aβ(21-30) adopts a loop conformation with cente ...
A Method To Define the Carboxyl Terminal of Proteins
... necessary for accurately describing the results of posttranslational processing and more generally for characterizing protein primary structures. Posttranslational processing at the C-terminus plays a critical role in a variety of biological processes. For example, prenylation, which occurs on cyste ...
... necessary for accurately describing the results of posttranslational processing and more generally for characterizing protein primary structures. Posttranslational processing at the C-terminus plays a critical role in a variety of biological processes. For example, prenylation, which occurs on cyste ...
Translation | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... The ribosome keeps the mRNA and tRNA close to each other and brings the next amino acid to the carboxyl end of the growing polypeptide. Without the ribosome, the hydrogen bonding between the tRNA and mRNA would be too weak to hold it there long enough for a peptide bond to form. The ribosome catalyz ...
... The ribosome keeps the mRNA and tRNA close to each other and brings the next amino acid to the carboxyl end of the growing polypeptide. Without the ribosome, the hydrogen bonding between the tRNA and mRNA would be too weak to hold it there long enough for a peptide bond to form. The ribosome catalyz ...
... elongation during synthesis of proteins on the ribosome. Your answer should include a brief description of the molecules involved, both proteins and nucleic acids, as well as a clear indication of the order of events during the process. A well labeled sketch would be an acceptable answer (10 pts). ...
Cold-Shock Response in Microorganisms
... stable or changing) that microorganisms colonize, it would be anticipated that a variety of mechanisms would be discovered that reflect different evolutionary processes to cope with cold shock. At present, the field is still in its infancy (particularly in comparison to studies on heat shock), altho ...
... stable or changing) that microorganisms colonize, it would be anticipated that a variety of mechanisms would be discovered that reflect different evolutionary processes to cope with cold shock. At present, the field is still in its infancy (particularly in comparison to studies on heat shock), altho ...
2006 Mega Molecules, LLC
... In the human body, amino acids are joined together by a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a reaction, the elements of water are removed and the amino acids are joined forming a peptide bond. The sequential order of amino acids determines the protein’s ultimate shape and function. Body function ...
... In the human body, amino acids are joined together by a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a reaction, the elements of water are removed and the amino acids are joined forming a peptide bond. The sequential order of amino acids determines the protein’s ultimate shape and function. Body function ...
The relative mutability of amino acids
... Scoring Matrices take into account: Conservation – acceptable substitutions while not changing function of protein (charge, size, hydrophobicity) Frequency – reflect how often particular residues occur among entire collection of proteins (rare residues given more weight) Evolution – different scori ...
... Scoring Matrices take into account: Conservation – acceptable substitutions while not changing function of protein (charge, size, hydrophobicity) Frequency – reflect how often particular residues occur among entire collection of proteins (rare residues given more weight) Evolution – different scori ...
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
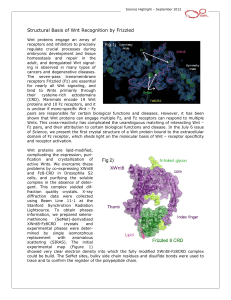
... pairs are responsible for certain biological functions and diseases. However, it has been shown that Wnt proteins can engage multiple Fz, and Fz receptors can respond to multiple Wnts. This cross-reactivity has complicated the unambiguous matching of interacting Wnt – Fz pairs, and their attribution ...
... pairs are responsible for certain biological functions and diseases. However, it has been shown that Wnt proteins can engage multiple Fz, and Fz receptors can respond to multiple Wnts. This cross-reactivity has complicated the unambiguous matching of interacting Wnt – Fz pairs, and their attribution ...
Protein Calorie Malnutrition
... (brain, blood cells, and renal medulla) • release and oxidation of fatty acids • release of glucose from liver glycogen – Liver glycogen capacity: approximately 1000 kcal – Equivalent to 250g carbohydrate/glucose ...
... (brain, blood cells, and renal medulla) • release and oxidation of fatty acids • release of glucose from liver glycogen – Liver glycogen capacity: approximately 1000 kcal – Equivalent to 250g carbohydrate/glucose ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... Proteins are the most varied of the carbon-based molecules in organisms. In movement, eyesight, or digestion, proteins are at work. A protein is a polymer made of monomers called amino acids. Amino acids are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Organisms u ...
... Proteins are the most varied of the carbon-based molecules in organisms. In movement, eyesight, or digestion, proteins are at work. A protein is a polymer made of monomers called amino acids. Amino acids are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Organisms u ...
Structural Description of Viral Particles Based on Affine Extensions
... protein subunits, called capsomeres, that are organised with icosahedral symmetry in the capsid. An example of such an arrangement is shown in Figure 1(a). Part of this viral capsid is shown in magnification in Figure 1(b) in order to demonstrate the organisation in terms of capsomeres: each toroida ...
... protein subunits, called capsomeres, that are organised with icosahedral symmetry in the capsid. An example of such an arrangement is shown in Figure 1(a). Part of this viral capsid is shown in magnification in Figure 1(b) in order to demonstrate the organisation in terms of capsomeres: each toroida ...
Gene Section JUND (proto-oncogene) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... JUND is a member of the JUN family of basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA-binding proteins. Analysis of the protein expression levels demonstrated an opposite expression pattern between JUN and JUND. When cells entry into the G0 phase of the cell cycle by serum starvation, JUN level decreases and ...
... JUND is a member of the JUN family of basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA-binding proteins. Analysis of the protein expression levels demonstrated an opposite expression pattern between JUN and JUND. When cells entry into the G0 phase of the cell cycle by serum starvation, JUN level decreases and ...
Cloning and sequencing of glutamate mutase component E from
... A mechanism, in which anN-terminal pyruvoyl residue is involved in a Schiffs base formation, can be excluded. For such a mechanism it would be necessary that at least one subunit was synthesized as a precursor molecule and was post-translationally modified via a rearrangement involving an anhydro-se ...
... A mechanism, in which anN-terminal pyruvoyl residue is involved in a Schiffs base formation, can be excluded. For such a mechanism it would be necessary that at least one subunit was synthesized as a precursor molecule and was post-translationally modified via a rearrangement involving an anhydro-se ...
Dicot and monocot plants differ in retinoblastoma
... Similarly, as in animals, RBR proteins can be phosphorylated by cyclin–CDK complexes in plants (Nakagami et al., 1999; Boniotti and Gutiérrez, 2001; Nakagami et al., 2002). Only limited data are available on the mechanisms controlling the amounts of the RBR proteins and the expression pattern of th ...
... Similarly, as in animals, RBR proteins can be phosphorylated by cyclin–CDK complexes in plants (Nakagami et al., 1999; Boniotti and Gutiérrez, 2001; Nakagami et al., 2002). Only limited data are available on the mechanisms controlling the amounts of the RBR proteins and the expression pattern of th ...
evolution of protein function by domain swapping
... phate in a complex reaction. GLNase- and SYNase-like domains are found in CPSase domains of higher species. CPSase, ATCase and CHOase are independent in bacteria but fused into multienzyme proteins in eukaryotes (CAD) in the order CPSase-DHOase-ATCase (Fig. 3). Unlike in the purine enzymes previousl ...
... phate in a complex reaction. GLNase- and SYNase-like domains are found in CPSase domains of higher species. CPSase, ATCase and CHOase are independent in bacteria but fused into multienzyme proteins in eukaryotes (CAD) in the order CPSase-DHOase-ATCase (Fig. 3). Unlike in the purine enzymes previousl ...
Protein Arginine Methylation in Candida albicans: Role
... clinical insights. In addition to two PRMTs, C. albicans and S. cerevisiae share many genes that encode likely Hmt1 substrates due to the presence of arginine-glycine-(RG)-rich domains, including an ortholog of the major S. cerevisiae mRNA-binding protein Npl3. In this study, we present the first id ...
... clinical insights. In addition to two PRMTs, C. albicans and S. cerevisiae share many genes that encode likely Hmt1 substrates due to the presence of arginine-glycine-(RG)-rich domains, including an ortholog of the major S. cerevisiae mRNA-binding protein Npl3. In this study, we present the first id ...
Separation of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rEPO
... Recombinant human EPO protein is one of the most widely produced by many bio and pharmaceutical companies throughout the world for therapeutic agents. Erythropoietin protein (EPO) is a glycoprotein hormone found in plasma. It is a cytokine for erythrocyte (red blood cell) precursors in the bone marr ...
... Recombinant human EPO protein is one of the most widely produced by many bio and pharmaceutical companies throughout the world for therapeutic agents. Erythropoietin protein (EPO) is a glycoprotein hormone found in plasma. It is a cytokine for erythrocyte (red blood cell) precursors in the bone marr ...
Lecture 1 – Classification - LCQB
... Domains belonging to the same fold have the same major secondary structures in the same arrangement with the same topological connections. Ex: Globin-like, Long alpha-hairpin, Type I dockerin domain… The domains within a fold are further classified into superfamilies. Domains belonging to the same s ...
... Domains belonging to the same fold have the same major secondary structures in the same arrangement with the same topological connections. Ex: Globin-like, Long alpha-hairpin, Type I dockerin domain… The domains within a fold are further classified into superfamilies. Domains belonging to the same s ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.