Electrical Definitions
... Electric potential, measured in volts, is the work to move a unit charge from one point to another in an electric field: V=Work/Q = Ed volts. So Work=QV joules. What is energy? Whenever work is done, energy is produced. Pumping water up to a tank on a hill requires work but results in potential or s ...
... Electric potential, measured in volts, is the work to move a unit charge from one point to another in an electric field: V=Work/Q = Ed volts. So Work=QV joules. What is energy? Whenever work is done, energy is produced. Pumping water up to a tank on a hill requires work but results in potential or s ...
Complicated Circuits
... Background: There are two fundamental ways to connect two devices together in a circuit: series, and parallel. Devices in series must have the same current flowing through them (since there is nowhere else for the current to go). The potential difference across a pair of series devices (from the top ...
... Background: There are two fundamental ways to connect two devices together in a circuit: series, and parallel. Devices in series must have the same current flowing through them (since there is nowhere else for the current to go). The potential difference across a pair of series devices (from the top ...
AGENDA ITEM:____
... 2 % resistor, under any external load condition, shall not exceed the relevant line-toearth limit given in Figure 1. Moreover, this current shall not exceed 10 mA d.c. after 10 s. The intent of this requirement was to limit the current available from an RFT-V power source exceeding 140 V d.c to ...
... 2 % resistor, under any external load condition, shall not exceed the relevant line-toearth limit given in Figure 1. Moreover, this current shall not exceed 10 mA d.c. after 10 s. The intent of this requirement was to limit the current available from an RFT-V power source exceeding 140 V d.c to ...
8 Data Conversion Methods I
... A simplified schematic diagram of an 8-bit Flash Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) is shown in Fig 8.3. A number of reference voltages equal to the number of quantization levels are generated using a resistor chain. These are fed into a series of comparators along with the input voltage, so that ...
... A simplified schematic diagram of an 8-bit Flash Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) is shown in Fig 8.3. A number of reference voltages equal to the number of quantization levels are generated using a resistor chain. These are fed into a series of comparators along with the input voltage, so that ...
Ohm`s Law
... Ohm's Law states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current through the resistor. This relationship is expressed by the equation: ...
... Ohm's Law states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current through the resistor. This relationship is expressed by the equation: ...
Basic Electricity for Computer Scientists
... Electrons moving from source to destination – as in a vacuum tube or CRT; Electrons moving railroad-car style, which means that an electron enters at one end, pushes all the other electrons along a short distance, and a different electron comes out at the other end – as in a metal; Holes moving rail ...
... Electrons moving from source to destination – as in a vacuum tube or CRT; Electrons moving railroad-car style, which means that an electron enters at one end, pushes all the other electrons along a short distance, and a different electron comes out at the other end – as in a metal; Holes moving rail ...
High Voltage Solid-State Circuits for Tube Guitar
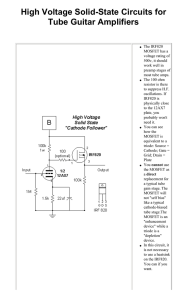
... 500v, it should work well in preamp stages of most tube amps. The 100 ohm resistor is there to suppress H.F. oscillations. If IRF820 is physically close to the 12AX7 plate, you probably won't need it. You can see how the MOSFET is equivalent to a triode: Source = Cathode; Gate = Grid; Drain = Plate ...
... 500v, it should work well in preamp stages of most tube amps. The 100 ohm resistor is there to suppress H.F. oscillations. If IRF820 is physically close to the 12AX7 plate, you probably won't need it. You can see how the MOSFET is equivalent to a triode: Source = Cathode; Gate = Grid; Drain = Plate ...
Homework 6
... We can solve the problem directly from this definition. We have to find the explicit form of the sawtooth function. Consistent with the symbols in the figure, 2V V(t ) = m ⋅ t − (2 N − 1)Vm for NT < t < (N+1)T T (In each time interval [NT, (N+1)T], the voltage is a linear function of time and assume ...
... We can solve the problem directly from this definition. We have to find the explicit form of the sawtooth function. Consistent with the symbols in the figure, 2V V(t ) = m ⋅ t − (2 N − 1)Vm for NT < t < (N+1)T T (In each time interval [NT, (N+1)T], the voltage is a linear function of time and assume ...
Ohms Law 2015 for 202L
... For ohmic resistances, V versus I is a linear relationship, and they have a constant resistance. Resistance can be calculated using, R = V/I. The slope of the V versus I, line will also give the resistance, R. For non-ohmic resistances, V versus I is a non-linear relationship, and they have a varyin ...
... For ohmic resistances, V versus I is a linear relationship, and they have a constant resistance. Resistance can be calculated using, R = V/I. The slope of the V versus I, line will also give the resistance, R. For non-ohmic resistances, V versus I is a non-linear relationship, and they have a varyin ...
Chap 20 S2017
... AC and DC If the charges move around a circuit in the same direction at all times, the current is said to be direct current (dc), which is the kind produced by batteries. ...
... AC and DC If the charges move around a circuit in the same direction at all times, the current is said to be direct current (dc), which is the kind produced by batteries. ...
DC Fundamentals, 3-2
... The total amount of current in an electrical circuit is determined by the voltage applied to the circuit and the total resistance (R) of the circuit. If the circuit resistance remains the same while voltage is varied, current is altered. If the circuit voltage remains the same while resistance is va ...
... The total amount of current in an electrical circuit is determined by the voltage applied to the circuit and the total resistance (R) of the circuit. If the circuit resistance remains the same while voltage is varied, current is altered. If the circuit voltage remains the same while resistance is va ...
Slide 1 - Helios
... A) Always in one direction B) In one direction for one complete cycle and then the other direction for the next complete cycle C) In one direction for ½ of the cycle and then the other direction for the other ½ of the cycle D) Changing direction 2p times per cycle ...
... A) Always in one direction B) In one direction for one complete cycle and then the other direction for the next complete cycle C) In one direction for ½ of the cycle and then the other direction for the other ½ of the cycle D) Changing direction 2p times per cycle ...
Unit 4 - Section 13.8 2011 Relating V to I
... Voltmeter is connected in a parallel circuit to the load (i.e., circuit resistance (R)). This connection is called “across the load” and it is measuring the drop in voltage across the load (i.e., How much energy is used up to run the resistor). The Ammeter is connected in series with the circuit. It ...
... Voltmeter is connected in a parallel circuit to the load (i.e., circuit resistance (R)). This connection is called “across the load” and it is measuring the drop in voltage across the load (i.e., How much energy is used up to run the resistor). The Ammeter is connected in series with the circuit. It ...
Ohm`s Law
... of the power supply. Change the voltmeter setting to 2V and keep the ammeter setting at 10A. 20. Slowly increase the voltage (and current) until the ammeter reads about 1A. Record the voltage and current readings. Repeat the measurements for 0.90A, 0.80A, 0.70A, 0.60A, 0.50A, 0.45A, 0.40A, 0.35A, 0. ...
... of the power supply. Change the voltmeter setting to 2V and keep the ammeter setting at 10A. 20. Slowly increase the voltage (and current) until the ammeter reads about 1A. Record the voltage and current readings. Repeat the measurements for 0.90A, 0.80A, 0.70A, 0.60A, 0.50A, 0.45A, 0.40A, 0.35A, 0. ...
Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit at terminals A,B - Rose
... The 300 Ω resistor is in parallel with a 0 Ω wire, so the equivalent resistance is 0 Ω. Isc is the current flowing through the two resistors that have a 200 Ω equivalent resistance. Isc is the voltage divided by Req, or 250 mA. So the Thévenin resistance is Voc / Isc, or 120 Ω. Now let’s find Rth us ...
... The 300 Ω resistor is in parallel with a 0 Ω wire, so the equivalent resistance is 0 Ω. Isc is the current flowing through the two resistors that have a 200 Ω equivalent resistance. Isc is the voltage divided by Req, or 250 mA. So the Thévenin resistance is Voc / Isc, or 120 Ω. Now let’s find Rth us ...
review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... - transfer characteristic (vo vs. vin) has negative slope (or zero slope in some regions) - MOSFET version is also called a common-source amplifier - MOSFET inverter with resistor load has nonlinear transfer characteristic in saturation and triode regions (because MOSFETs are “square-law” devices) - ...
... - transfer characteristic (vo vs. vin) has negative slope (or zero slope in some regions) - MOSFET version is also called a common-source amplifier - MOSFET inverter with resistor load has nonlinear transfer characteristic in saturation and triode regions (because MOSFETs are “square-law” devices) - ...