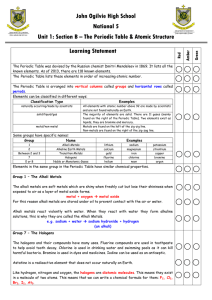
4-3 Families of Elements
... c. Gold, silver, and platinum are transition metals i. Transition metals are much less reactive than sodium or calcium, but they can lose electrons to form positive ions, too. ii. Transition metals can have more than one possible cation. iii. Examples: gold, copper, iron, cobalt, manganese, and mer ...
... c. Gold, silver, and platinum are transition metals i. Transition metals are much less reactive than sodium or calcium, but they can lose electrons to form positive ions, too. ii. Transition metals can have more than one possible cation. iii. Examples: gold, copper, iron, cobalt, manganese, and mer ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE
... chemist who arranged the known 63 elements based on increasing atomic mass so that elements with similar properties fell into the same column on his table; gaps in his table were elements that he predicted the properties of (Sc, Ga, Ge) Periodic—repeating according to a ...
... chemist who arranged the known 63 elements based on increasing atomic mass so that elements with similar properties fell into the same column on his table; gaps in his table were elements that he predicted the properties of (Sc, Ga, Ge) Periodic—repeating according to a ...
The Periodic Table
... By looking at the elements that came before and after Ex- you go to school, and there is no mail in the mailbox. You come home and there is. Although you did not see the mailman you can be ...
... By looking at the elements that came before and after Ex- you go to school, and there is no mail in the mailbox. You come home and there is. Although you did not see the mailman you can be ...
Study Guide - Chapter 12 Quiz
... Dmitri Mendeleev A.. He arranged elements in order of atomic mass. He noticed that they had similar properties that occurred in a repeating pattern, every 7 elements B. He was able to predict the properties of elements not yet found. Periodic - describes something that occurs or repeats at regular i ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev A.. He arranged elements in order of atomic mass. He noticed that they had similar properties that occurred in a repeating pattern, every 7 elements B. He was able to predict the properties of elements not yet found. Periodic - describes something that occurs or repeats at regular i ...
Summary of the Periodic Table of Elements: 1. Elements in the same
... 8. Elements to the right in the periodic table tend to gain electrons. 9. The amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom shows periodic increase from left to right across the periodic table. 10. Metals tend to lose electrons while nonmetals tend to gain electrons. 11. Elements vary p ...
... 8. Elements to the right in the periodic table tend to gain electrons. 9. The amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom shows periodic increase from left to right across the periodic table. 10. Metals tend to lose electrons while nonmetals tend to gain electrons. 11. Elements vary p ...
File
... 18. An interaction that holds two atoms together is a(n) ____________________________. 19. A charged particle that forms when an atom transfers electrons is a(n) ____________________. 20. A bond formed when atoms share electrons is a(n) __________________________. 21. An electron in the outermost en ...
... 18. An interaction that holds two atoms together is a(n) ____________________________. 19. A charged particle that forms when an atom transfers electrons is a(n) ____________________. 20. A bond formed when atoms share electrons is a(n) __________________________. 21. An electron in the outermost en ...
Periodic Table Funsheet (KEY) 1. What family has the most active
... 14. Group 17 elements are called HALOGENS. 15. Group 18 elements are called NOBLE GASES. 16. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from (METALS / nonmetals) to (metals / NONMETALS). 17. The most active element in Group 17 is FLUORINE. 18. What sublevels are filling ...
... 14. Group 17 elements are called HALOGENS. 15. Group 18 elements are called NOBLE GASES. 16. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from (METALS / nonmetals) to (metals / NONMETALS). 17. The most active element in Group 17 is FLUORINE. 18. What sublevels are filling ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... b. is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. c. generally decreases from top to bottom within a group. d. is generally higher for metals than for nonmetals. ...
... b. is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. c. generally decreases from top to bottom within a group. d. is generally higher for metals than for nonmetals. ...
Periodic Table Worksheet 1. Where are the most active metals
... 1. Where are the most active metals located? ____________Group 1____________ 2. Where are the most active non-metals located? _______________Group 17 _______________ 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? Greater ENC, stronger force of attracti ...
... 1. Where are the most active metals located? ____________Group 1____________ 2. Where are the most active non-metals located? _______________Group 17 _______________ 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? Greater ENC, stronger force of attracti ...
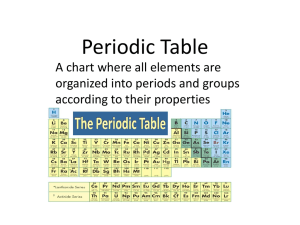
Periodic Table
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
Periodic Table Worksheet
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
Periodic Table Funsheet (KEY) 1. Where are the most active metals
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
5.2 The Modern Periodic Table
... period. (Period # = # of energy levels) • Each column in the periodic table is called a group. (Group # = # of valence electrons) – similar electron configurations – similar chemical properties ...
... period. (Period # = # of energy levels) • Each column in the periodic table is called a group. (Group # = # of valence electrons) – similar electron configurations – similar chemical properties ...
Families of Elements
... Are the most chemically active of all metals (meaning an element readily combines with other substances to form compounds) NEVER found in pure form A way to identify alkali metals is by a flame test. When an alkali metal compound is heated in a flame, the metal produces a colored flame. Alkali ...
... Are the most chemically active of all metals (meaning an element readily combines with other substances to form compounds) NEVER found in pure form A way to identify alkali metals is by a flame test. When an alkali metal compound is heated in a flame, the metal produces a colored flame. Alkali ...
Document
... 17. The subatomic particle that plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element is the a. proton. c. electron. b. neutron. d. photon. 18. Which of the following atoms would you expect to have the largest atomic radius? a. I c. Ca b. K d. Rb 19. From left to ...
... 17. The subatomic particle that plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element is the a. proton. c. electron. b. neutron. d. photon. 18. Which of the following atoms would you expect to have the largest atomic radius? a. I c. Ca b. K d. Rb 19. From left to ...
Periods
... masses increase as you move from the left to the right in a period All atoms of the elements in the same period have the same number of orbitals/levels All atoms of the elements in a specific period have that respective number of ...
... masses increase as you move from the left to the right in a period All atoms of the elements in the same period have the same number of orbitals/levels All atoms of the elements in a specific period have that respective number of ...
Slide 1
... They are the most reactive nonmetal group. They typically react with metals to form salts. The normal states of these elements include two solids, one liquid, and two gases. ...
... They are the most reactive nonmetal group. They typically react with metals to form salts. The normal states of these elements include two solids, one liquid, and two gases. ...
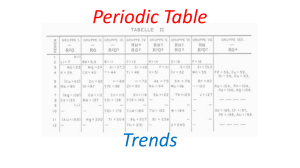
2- Periodic Trends
... • Arranged the 63 elements by atomic mass • Noticed a repetition of properties (periodicity) • Called the pattern of properties “Periodic Law” ...
... • Arranged the 63 elements by atomic mass • Noticed a repetition of properties (periodicity) • Called the pattern of properties “Periodic Law” ...
Chapter 5
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
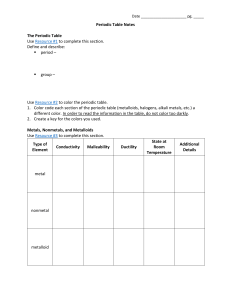
Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1
... Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1 to complete this section. Define and describe: period – ...
... Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1 to complete this section. Define and describe: period – ...