Poster Example
... The study of neuron-specific factors requires pure neuronal cultures. However, the absence of glia can affect the physiology of neurons negatively. This study compared three different treatments of neuronal cultures in order to find a treatment that reversed the deleterious effects of removing glia ...
... The study of neuron-specific factors requires pure neuronal cultures. However, the absence of glia can affect the physiology of neurons negatively. This study compared three different treatments of neuronal cultures in order to find a treatment that reversed the deleterious effects of removing glia ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... demarcated as ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic receptors constitute as transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic ...
... demarcated as ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic receptors constitute as transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic ...
Neurons - Holterman
... 19. Presynaptic is the neuron before the gap, carrying the message. Postsynaptic is the neuron after the gap, receiving and possibly carrying on the message. 20. The dendrite contains vesicles full of chemicals called neurotransmitters. When the action potential (wave of depolarization) reaches the ...
... 19. Presynaptic is the neuron before the gap, carrying the message. Postsynaptic is the neuron after the gap, receiving and possibly carrying on the message. 20. The dendrite contains vesicles full of chemicals called neurotransmitters. When the action potential (wave of depolarization) reaches the ...
No Slide Title
... – in fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – if mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron is covered by glial cells • prevents neurons from touching each other • gives precision to conduction pathways ...
... – in fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – if mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron is covered by glial cells • prevents neurons from touching each other • gives precision to conduction pathways ...
Neural basis of learning and memory
... Long-term potentiation and long-term depression are enduring (long-lasting) changes in synaptic strength that are brought about by specific patterns of activity at the synapse. These activity-dependent changes are thought to play a critical role in learning and subsequent memory formation. Both have ...
... Long-term potentiation and long-term depression are enduring (long-lasting) changes in synaptic strength that are brought about by specific patterns of activity at the synapse. These activity-dependent changes are thought to play a critical role in learning and subsequent memory formation. Both have ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • unlike EPSPs and IPSPs, APs are not graded; they are all-or-none (they occur full blown or not at all) • most neurons receive hundreds of synaptic contacts; what happens at any one synapse has very little effect on the firing of the neuron; whether or not a neuron fires is determined by the adding ...
... • unlike EPSPs and IPSPs, APs are not graded; they are all-or-none (they occur full blown or not at all) • most neurons receive hundreds of synaptic contacts; what happens at any one synapse has very little effect on the firing of the neuron; whether or not a neuron fires is determined by the adding ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... demarcated as ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic receptors constitute as transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic ...
... demarcated as ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic receptors constitute as transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic ...
The interplay between neurons and glia in synapse
... perisynaptic regions by the hemichannel protein connexin 30 (Cx30). Genetic deletion of Cx30 permits astrocyte process invasion into synaptic clefts, which prevents glutamate activation of the postsynapse and alters excitatory synaptic strength. These effects of Cx30 are independent of its channel f ...
... perisynaptic regions by the hemichannel protein connexin 30 (Cx30). Genetic deletion of Cx30 permits astrocyte process invasion into synaptic clefts, which prevents glutamate activation of the postsynapse and alters excitatory synaptic strength. These effects of Cx30 are independent of its channel f ...
Pausing to Regroup: Thalamic Gating of Cortico
... the D1 or D2 MSNs. However, when the cortical stimulation was applied after a longer delay following the thalamic stimulation (250 ms or 1 s), they found that the corticostriatal EPSCs were facilitated in MSNs expressing D2 receptors, but not in those expressing D1 receptors. The facilitation was pr ...
... the D1 or D2 MSNs. However, when the cortical stimulation was applied after a longer delay following the thalamic stimulation (250 ms or 1 s), they found that the corticostriatal EPSCs were facilitated in MSNs expressing D2 receptors, but not in those expressing D1 receptors. The facilitation was pr ...
review glutamate and gaba receptor signalling in - lópez
... in recent years. The major excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, glutamate and GABA, activate both ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels) and metabotropic (G protein-coupled) receptors, and are generally associated with neuronal communication in the mature brain. However, before ...
... in recent years. The major excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, glutamate and GABA, activate both ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels) and metabotropic (G protein-coupled) receptors, and are generally associated with neuronal communication in the mature brain. However, before ...
Retrograde Signaling in the Development and Modification of
... and connectin, were found to prevent formation of selective innervation by the proper motoneuron when they were expressed at high levels on the target muscle fibers (244, 272), suggesting a repulsive action of these molecules on the growth cone of specific motoneurons. These results from the Drosoph ...
... and connectin, were found to prevent formation of selective innervation by the proper motoneuron when they were expressed at high levels on the target muscle fibers (244, 272), suggesting a repulsive action of these molecules on the growth cone of specific motoneurons. These results from the Drosoph ...
CHARLES UNIVERSITY
... system in epileptiform activity (Schuchmann, 2002). NMDA receptor is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. These receptors when tonically activated can trigger an excessive increase in intracellular calcium; nerve cells start to induce abnormal excessive activity and intracellular calciu ...
... system in epileptiform activity (Schuchmann, 2002). NMDA receptor is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. These receptors when tonically activated can trigger an excessive increase in intracellular calcium; nerve cells start to induce abnormal excessive activity and intracellular calciu ...
Neuronal Calcium Signaling Review
... 1996). Calcium release in cardiac cells is mediated by the type 2 RYR, which is the predominant isoform found in the brain. In cardiac cells, these RYR2 channels are closely apposed to the Ca21 channels in the plasma membrane across the 15 nm junctional gap that separates the sarcolemma from the sar ...
... 1996). Calcium release in cardiac cells is mediated by the type 2 RYR, which is the predominant isoform found in the brain. In cardiac cells, these RYR2 channels are closely apposed to the Ca21 channels in the plasma membrane across the 15 nm junctional gap that separates the sarcolemma from the sar ...
NMDA and AMPA Receptors: Development and Status Epilepticus
... (Lawrence and Trussell 2000) and activity-dependent forms of synaptic plasticity (Liu and Cull-Candy 2000). In different cell types of the CNS, AMPARs are functionally and molecularly distinct (see Table 2). The specific expression of rapidly gated, Ca2+permeable AMPARs in interneurons and relay neu ...
... (Lawrence and Trussell 2000) and activity-dependent forms of synaptic plasticity (Liu and Cull-Candy 2000). In different cell types of the CNS, AMPARs are functionally and molecularly distinct (see Table 2). The specific expression of rapidly gated, Ca2+permeable AMPARs in interneurons and relay neu ...
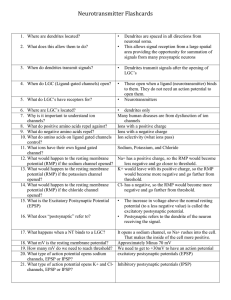
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 95. In a dually innervated organ, how will the organ know if sympathetic or parasympathetic is barking louder? 96. Why are a lot of organs dually innervated? 97. What neurons can cause excitation in one organ yet inhibition in another? 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? ...
... 95. In a dually innervated organ, how will the organ know if sympathetic or parasympathetic is barking louder? 96. Why are a lot of organs dually innervated? 97. What neurons can cause excitation in one organ yet inhibition in another? 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? ...
Cerebellar Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Physiology
... group classified into three types—AMPA (alpha-amino3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid), NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartic acid), and kainate. These are ligand-gated ion channels, meaning that when glutamate binds, charged ions pass through a channel in the receptor center. Both basket and stellate ...
... group classified into three types—AMPA (alpha-amino3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid), NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartic acid), and kainate. These are ligand-gated ion channels, meaning that when glutamate binds, charged ions pass through a channel in the receptor center. Both basket and stellate ...
Yuste-Banbury-2006 - The Swartz Foundation
... We assessed the pathways by which excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters elicit postsynaptic changes in [Ca2+]i in brain slices of developing rat and cat neocortex, using fura 2. Glutamate, NMDA, and quisqualate transiently elevated [Ca2%]i in all neurons. While the quisqualate response relied ...
... We assessed the pathways by which excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters elicit postsynaptic changes in [Ca2+]i in brain slices of developing rat and cat neocortex, using fura 2. Glutamate, NMDA, and quisqualate transiently elevated [Ca2%]i in all neurons. While the quisqualate response relied ...
Interneurons and triadic circuitry of the thalamus
... F2 terminal, and this increases inhibition in the relay cell. This will reduce the responsiveness, or gain, of the relay cell to retinal inputs and, because of the temporal properties of mGlu5 receptors, this reduced contrast gain will last for a second or so even after the retinal afferent firing r ...
... F2 terminal, and this increases inhibition in the relay cell. This will reduce the responsiveness, or gain, of the relay cell to retinal inputs and, because of the temporal properties of mGlu5 receptors, this reduced contrast gain will last for a second or so even after the retinal afferent firing r ...
Hebbian modification of a hippocampal population
... 4. This change was achieved without a rise in overall cell excitability, implying that the synapses providing input to CA1 cells during sharp waves had undergone potentiation. 5. Our findings show that the Hebbian pairing of cellular activation with spontaneous, naturally occurring synaptic events i ...
... 4. This change was achieved without a rise in overall cell excitability, implying that the synapses providing input to CA1 cells during sharp waves had undergone potentiation. 5. Our findings show that the Hebbian pairing of cellular activation with spontaneous, naturally occurring synaptic events i ...
Neurons Excitatory vs Inhibitory Neurons The Neuron and its Ions
... relationships between patterns of activity in a network • Cluster plots are constructed based on the distances between patterns of activity • Euclidean distance = sum (across all units) of the squared difference in activation ...
... relationships between patterns of activity in a network • Cluster plots are constructed based on the distances between patterns of activity • Euclidean distance = sum (across all units) of the squared difference in activation ...
100 The Molecular and Structural Basis of Amblyopia
... depression. Although the contribution of LTD mechanisms to OD plasticity was once considered to be controversial, it is now clear that these same molecular mechanisms are engaged by MD and necessary for the loss of visual responses. Some of this evidence is summarized below. ...
... depression. Although the contribution of LTD mechanisms to OD plasticity was once considered to be controversial, it is now clear that these same molecular mechanisms are engaged by MD and necessary for the loss of visual responses. Some of this evidence is summarized below. ...
1: Nervous System II: Anatomy Review
... The neuron conducting the impulse toward the synapse is called the __________________ neuron. The axon terminal contains ___________ ____________ filled with ______________________. An action potential in the axon terminal of the _____________ neuron causes the chemical transmitter, also known as a ...
... The neuron conducting the impulse toward the synapse is called the __________________ neuron. The axon terminal contains ___________ ____________ filled with ______________________. An action potential in the axon terminal of the _____________ neuron causes the chemical transmitter, also known as a ...
CASE 5
... A good understanding of the autonomic nervous system is imperative in treating many medical conditions, such as asthma. Different cells throughout the body have different ANS receptors with differing agonist and antagonist properties, and medications targeting specific receptors can selectively reli ...
... A good understanding of the autonomic nervous system is imperative in treating many medical conditions, such as asthma. Different cells throughout the body have different ANS receptors with differing agonist and antagonist properties, and medications targeting specific receptors can selectively reli ...
Neurochemistry of Dementias
... leads to release voltage dependent Mg2+ block of NMDA → and excessive, neurotoxic entry of Ca2+ ...
... leads to release voltage dependent Mg2+ block of NMDA → and excessive, neurotoxic entry of Ca2+ ...