Cardiovascular Notes
... Blood Pressure Measure of force exerted by blood against the wall Blood moves through vessels because of blood pressure Measured by listening for Korotkoff sounds produced by turbulent flow in arteries as pressure released from blood pressure cuff ...
... Blood Pressure Measure of force exerted by blood against the wall Blood moves through vessels because of blood pressure Measured by listening for Korotkoff sounds produced by turbulent flow in arteries as pressure released from blood pressure cuff ...
1-Wall of the heart and cardiac
... branching gives each cardiac muscle more sites for attachment to each other. This creates an overall network of inter-connected cardiac fibres, which will give the muscle increased strength. furthermore, the branching will also ensure rapid spread of depolarisation for initiation of cardiac contract ...
... branching gives each cardiac muscle more sites for attachment to each other. This creates an overall network of inter-connected cardiac fibres, which will give the muscle increased strength. furthermore, the branching will also ensure rapid spread of depolarisation for initiation of cardiac contract ...
Ch 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
... • Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the heart and other body tissues. arteries carry blood away from the heart veins carry blood back to the heart • Arteries carry blood high in oxygen. (except for the pulmonary arteries) ...
... • Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the heart and other body tissues. arteries carry blood away from the heart veins carry blood back to the heart • Arteries carry blood high in oxygen. (except for the pulmonary arteries) ...
Pathology Dr. M.M. Lena September 26, 2003 DISEASE OF THE
... o Longitudinal Bicuspid Aortic Valve o May affect the annules of the Mitral valve o May cause stenosis (without commissural fusion), leads to arrythmias, conduction defects, thrombus formation (embolism) and may ulcerate o Starts as aortic valve stenosis at the margin of attachment (valvular fibrosi ...
... o Longitudinal Bicuspid Aortic Valve o May affect the annules of the Mitral valve o May cause stenosis (without commissural fusion), leads to arrythmias, conduction defects, thrombus formation (embolism) and may ulcerate o Starts as aortic valve stenosis at the margin of attachment (valvular fibrosi ...
Primary left atrial angiosarcoma mimicking severe mitral valve stenosis
... the case of cardiac tumours echocardiography provides relevant information during serial follow up in that it allows for accurate monitoring after surgery or during radiation therapy or chemotherapy.9 In conclusion, the present case underlines that heart failure symptoms attributable to mitral valve ...
... the case of cardiac tumours echocardiography provides relevant information during serial follow up in that it allows for accurate monitoring after surgery or during radiation therapy or chemotherapy.9 In conclusion, the present case underlines that heart failure symptoms attributable to mitral valve ...
1. The diagram below shows a section through the human heart
... 4. Capillaries have a large surface area/thin walls/narrow diameter. 5. High pressure forces fluid/plasma out of capillaries or pressure filtration occurs. 6. Tissue fluid (bathes the cells). 7. Plasma proteins do not pass through capillary walls/stay in blood. 8. (Dissolved) substances diffuse/move ...
... 4. Capillaries have a large surface area/thin walls/narrow diameter. 5. High pressure forces fluid/plasma out of capillaries or pressure filtration occurs. 6. Tissue fluid (bathes the cells). 7. Plasma proteins do not pass through capillary walls/stay in blood. 8. (Dissolved) substances diffuse/move ...
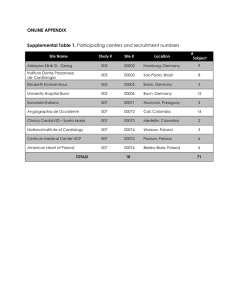
ONLINE APPENDIX Supplemental Table 1. Participating centers
... Suboptimal trans-thoracic echocardiographic (TTE) windows, leading to incomplete quantification of FMR or anatomic assessment Significant subvalvular trabecularization or muscle bridges Subject with mitral stenosis Subject with moderate or severe aortic or tricuspid stenosis and/or moderate or sever ...
... Suboptimal trans-thoracic echocardiographic (TTE) windows, leading to incomplete quantification of FMR or anatomic assessment Significant subvalvular trabecularization or muscle bridges Subject with mitral stenosis Subject with moderate or severe aortic or tricuspid stenosis and/or moderate or sever ...
Severe Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation Is Not an Innocent Finding to
... enough for the heart to take advantage of a compe- ...
... enough for the heart to take advantage of a compe- ...
Congenital Anomalies of the heart
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
Did you give your friends valentines and little heart
... The two chambers on the bottom are called the ventricles (say: ven-trih-kulz). The heart has a left ventricle and a right ventricle. Their job is to squirt out the blood to the body and lungs. Running down the middle of the heart is a thick wall of muscle called the septum (say: sep-tum). The septum ...
... The two chambers on the bottom are called the ventricles (say: ven-trih-kulz). The heart has a left ventricle and a right ventricle. Their job is to squirt out the blood to the body and lungs. Running down the middle of the heart is a thick wall of muscle called the septum (say: sep-tum). The septum ...
17- interior of heart
... The afferent nerve fibers ascend to the central nervous system through the cardiac branches of the sympathetic trunk and enter the spinal cord through the posterior roots of the upper 4 thoracic nerves . The pain is not felt in the heart but is referred to the skin areas supplied by the correspondin ...
... The afferent nerve fibers ascend to the central nervous system through the cardiac branches of the sympathetic trunk and enter the spinal cord through the posterior roots of the upper 4 thoracic nerves . The pain is not felt in the heart but is referred to the skin areas supplied by the correspondin ...
The Circulatory System
... special valves inside the heart. A valve lets something in and keeps it there by closing. ...
... special valves inside the heart. A valve lets something in and keeps it there by closing. ...
1 The Cardiac Cycle - Hamilton Grammar School Science Website
... Atrial systole transfers the remainder of the blood through the atrioventricular (AV) valves to the ventricles. Ventricular systole closes the AV valves and pumps the blood out through the semi lunar (SL) valves to the aorta and pulmonary artery. In diastole the higher pressure in the arteries close ...
... Atrial systole transfers the remainder of the blood through the atrioventricular (AV) valves to the ventricles. Ventricular systole closes the AV valves and pumps the blood out through the semi lunar (SL) valves to the aorta and pulmonary artery. In diastole the higher pressure in the arteries close ...
Cardiac auscultation - Veterinary Ireland Journal
... diagnosis of moderate sub-aortic valve stenosis. Dogs with a stenosis of the severity seen here will often tolerate the lesion and have a normal lifespan, without showing referable clinical signs or requiring treatment. However, dogs with this condition should not be used for breeding as their offsp ...
... diagnosis of moderate sub-aortic valve stenosis. Dogs with a stenosis of the severity seen here will often tolerate the lesion and have a normal lifespan, without showing referable clinical signs or requiring treatment. However, dogs with this condition should not be used for breeding as their offsp ...
Dissecrtion of sheep Heart - Sinoe Medical Association
... carries oxygen‐rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior vena cava ‐ a large vein (a blood vessel carrying blood to the heart) that carries oxygen‐poor blood to the right atrium from the lower half of the body. Left atrium ‐ the left upper chamber of the heart. It recei ...
... carries oxygen‐rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior vena cava ‐ a large vein (a blood vessel carrying blood to the heart) that carries oxygen‐poor blood to the right atrium from the lower half of the body. Left atrium ‐ the left upper chamber of the heart. It recei ...
Heart
... Also called left semilunar valve Located between the left ventricle & aorta When the left ventricle relaxes, the valve is in a closed position When the left ventricle contracts, blood from the ventricle forces the aortic valve to open Blood flows through the aortic valve into the aorta When the left ...
... Also called left semilunar valve Located between the left ventricle & aorta When the left ventricle relaxes, the valve is in a closed position When the left ventricle contracts, blood from the ventricle forces the aortic valve to open Blood flows through the aortic valve into the aorta When the left ...
The Heart and Circulatory System
... The heart pumps blood when its muscle contracts. As the muscle contracts the chamber gets smaller and squeeze the blood out. The two sides of the heart work together. The atria contract and relax at the same time, as do the ventricles. The next two slides describe what occurs inside the heart during ...
... The heart pumps blood when its muscle contracts. As the muscle contracts the chamber gets smaller and squeeze the blood out. The two sides of the heart work together. The atria contract and relax at the same time, as do the ventricles. The next two slides describe what occurs inside the heart during ...
Rheumatic Fever 2010 1st yr2010-10-03 11:1464 KB
... tendons. They commonly appear on the back of the wrist, the outside elbow, and the front of the knees. Erythema marginatum: a long lasting rash that begins on the trunk or arms. This rash never starts on the face and it is made worse with heat. Sydenham's chorea (St. Vitus' dance): a characteristic ...
... tendons. They commonly appear on the back of the wrist, the outside elbow, and the front of the knees. Erythema marginatum: a long lasting rash that begins on the trunk or arms. This rash never starts on the face and it is made worse with heat. Sydenham's chorea (St. Vitus' dance): a characteristic ...
Atherosclerosis - Shantou University
... The walls of the heart chamber behind the stenotic valve will be required to work harder to force blood through the narrow orifice→ hypertrophy. The valve leaflets cannot properly→ blood regurgitates through the valve. The walls of the heart chamber behind the insufficient valve will undergo hypertr ...
... The walls of the heart chamber behind the stenotic valve will be required to work harder to force blood through the narrow orifice→ hypertrophy. The valve leaflets cannot properly→ blood regurgitates through the valve. The walls of the heart chamber behind the insufficient valve will undergo hypertr ...
11/8/12 The Cardiovascular System: Session 32
... A. is initiated by Na diffusion into the cell B. is stimulated by ACh binding to Na and K channels C. triggers the expulsion of Ca out of the cells D. is accomplished by coordinated Na leakage across all tissue cells E. is unnecessary, as the cell fires spontaneously, without preceding changes in me ...
... A. is initiated by Na diffusion into the cell B. is stimulated by ACh binding to Na and K channels C. triggers the expulsion of Ca out of the cells D. is accomplished by coordinated Na leakage across all tissue cells E. is unnecessary, as the cell fires spontaneously, without preceding changes in me ...
The Role of Echocardiography
... The HeartWare™ Ventricular Assist System is indicated for use as a bridge to cardiac transplantation in patients who are at risk of death from refractory end-stage left ventricular heart failure. The HeartWare System is designed for in-hospital and out-of-hospital settings, including transportation ...
... The HeartWare™ Ventricular Assist System is indicated for use as a bridge to cardiac transplantation in patients who are at risk of death from refractory end-stage left ventricular heart failure. The HeartWare System is designed for in-hospital and out-of-hospital settings, including transportation ...
3.Circulatory System - student
... ___________– microscopic vessels which are one cell thick. ____________________________takes place with the body cells via these tiny blood vessels. ...
... ___________– microscopic vessels which are one cell thick. ____________________________takes place with the body cells via these tiny blood vessels. ...
Know the basics
... Be able to identify the parts of the heart. Be able to explain how blood moves through the heart and how it moves through the circulatory system. Be able to explain the components of the blood. Right atrium ...
... Be able to identify the parts of the heart. Be able to explain how blood moves through the heart and how it moves through the circulatory system. Be able to explain the components of the blood. Right atrium ...
SBI3U - Hwdsb
... names are given to the chains – see Figure below). How many oxygen molecules (O2) does each hemoglobin molecule carrier within the blood stream? Assuming a person has 25 trillion (from textbook) RBCs in his/her body and each RBC picks up the maximum amount of oxygen each time through the lungs, how ...
... names are given to the chains – see Figure below). How many oxygen molecules (O2) does each hemoglobin molecule carrier within the blood stream? Assuming a person has 25 trillion (from textbook) RBCs in his/her body and each RBC picks up the maximum amount of oxygen each time through the lungs, how ...
Cardiac Defects: Atrioventricular Canal Defects
... Complete Atrioventricular Canal (CAVC) Complete atrioventricular canal (CAVC) defect is a severe defect in which there is a large hole in the tissue (the septum) that separates the left and right sides of the heart. The hole is in the center of the heart, where the upper chambers (the atria) and the ...
... Complete Atrioventricular Canal (CAVC) Complete atrioventricular canal (CAVC) defect is a severe defect in which there is a large hole in the tissue (the septum) that separates the left and right sides of the heart. The hole is in the center of the heart, where the upper chambers (the atria) and the ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.