Electrochemistry 2
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry! AP Chemistry is
... nickel (II) carbonate copper (II) hydroxide tin (IV) sulfate ...
... nickel (II) carbonate copper (II) hydroxide tin (IV) sulfate ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 16 - A
... Write a half-equation for the conversion of chlorine into chloride ions. ...
... Write a half-equation for the conversion of chlorine into chloride ions. ...
departmentofmaterials scienceandengineering
... reasons called an M-center) is the analogue of a He atom and comprises two electrons in a (somewhat extended and odd-shaped) box. Because one electron partially screens the positive charge for the second, the first excited electron state is lower in energy than that of the F-center, and the M-band a ...
... reasons called an M-center) is the analogue of a He atom and comprises two electrons in a (somewhat extended and odd-shaped) box. Because one electron partially screens the positive charge for the second, the first excited electron state is lower in energy than that of the F-center, and the M-band a ...
File
... The boiling point of a solution is higher than the boiling point of the solvent. Therefore, a solution can remain a liquid at a higher temperature than its pure solvent. Ex. The boiling point of pure water is 1000C, but when salt is dissolved in it, the boiling point is higher. This is why it takes ...
... The boiling point of a solution is higher than the boiling point of the solvent. Therefore, a solution can remain a liquid at a higher temperature than its pure solvent. Ex. The boiling point of pure water is 1000C, but when salt is dissolved in it, the boiling point is higher. This is why it takes ...
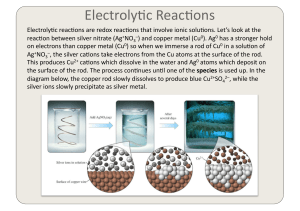
This is an overview of what can happen during the
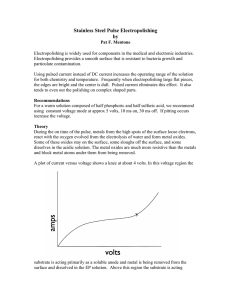
... primarily as an insoluble anode and the water is being electrolyzed to oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. In order for polishing to occur, the current and voltage must be above the knee of the curve, this location is marked with an X in the above graph If the substrate functioned as a 100% soluble anode ...
... primarily as an insoluble anode and the water is being electrolyzed to oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. In order for polishing to occur, the current and voltage must be above the knee of the curve, this location is marked with an X in the above graph If the substrate functioned as a 100% soluble anode ...
ACID AND BASES
... Example If we reacted hydrochloric acid and potassium hydroxide, neutralization would occur HCl + KOH KCl + H2O Our product is potassium chloride, which is a salt, and water ...
... Example If we reacted hydrochloric acid and potassium hydroxide, neutralization would occur HCl + KOH KCl + H2O Our product is potassium chloride, which is a salt, and water ...
WS-11-1
... greater lattice energy that cannot be overcome by the attraction of the water molecules. In NaOH the lattice energy is smaller than the favorable enthalpy of hydration, so it dissolves. 19. water : a, c and e CCl4 – b, d and f 20. Polarity, which creates hydrogen bonding and dipole. a. CH3CH2OH b. C ...
... greater lattice energy that cannot be overcome by the attraction of the water molecules. In NaOH the lattice energy is smaller than the favorable enthalpy of hydration, so it dissolves. 19. water : a, c and e CCl4 – b, d and f 20. Polarity, which creates hydrogen bonding and dipole. a. CH3CH2OH b. C ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... Solute is the substance being dissolved. Solvent is the substance doing the dissolving. When an ionic solid is dissolved in a liquid like water, the negative pole of the water molecule is attracted to the cations of the ionic solid whereas the positive pole of the water molecule is attracted to the ...
... Solute is the substance being dissolved. Solvent is the substance doing the dissolving. When an ionic solid is dissolved in a liquid like water, the negative pole of the water molecule is attracted to the cations of the ionic solid whereas the positive pole of the water molecule is attracted to the ...
Ionic strength effect on the deprotonation of para
... considering the well-known Specific Ion Interaction Theory (SIT).15–19 In the original SIT model, the activity coefficient of ion i with charge zi in a solution of ionic strength I (on the molal scale) at 25 °C can be expressed by the equation: ...
... considering the well-known Specific Ion Interaction Theory (SIT).15–19 In the original SIT model, the activity coefficient of ion i with charge zi in a solution of ionic strength I (on the molal scale) at 25 °C can be expressed by the equation: ...
107 - Bossier Parish Community College
... physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics of pure substances and mixtures. (B,C) 17. categorize mixtures as homogeneous or heter ...
... physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics of pure substances and mixtures. (B,C) 17. categorize mixtures as homogeneous or heter ...
pH scale learning goals
... Learning goals for pH scale Students will be able to use pH Scale to • Write descriptions that demonstrate the use of pH and/or relative hydronium and hydroxide ions as shown in the simulation to: A. Determine if a liquid is acidic or basic B. Place liquids in relative order of acidity or basicity ...
... Learning goals for pH scale Students will be able to use pH Scale to • Write descriptions that demonstrate the use of pH and/or relative hydronium and hydroxide ions as shown in the simulation to: A. Determine if a liquid is acidic or basic B. Place liquids in relative order of acidity or basicity ...
oxidation and reduction
... f) When a species is oxidised or reduced, what relationship is there between the change in oxidation number of the central atom and the number of electrons lost or gained? Illustrate your answer by referring to the MnO4and Cr2O72- ions, both in acidic solution. ...
... f) When a species is oxidised or reduced, what relationship is there between the change in oxidation number of the central atom and the number of electrons lost or gained? Illustrate your answer by referring to the MnO4and Cr2O72- ions, both in acidic solution. ...
Carrying Charges
... 1. Participant must wear a pair of safety goggles before beginning! 2. Put a small amount of each liquid in separate wells in the well plate. 3. Dip the ends of both wires (electrodes) into each liquid and observe what happens. If the buzzer sounds, then the liquid conducts electricity and has ions ...
... 1. Participant must wear a pair of safety goggles before beginning! 2. Put a small amount of each liquid in separate wells in the well plate. 3. Dip the ends of both wires (electrodes) into each liquid and observe what happens. If the buzzer sounds, then the liquid conducts electricity and has ions ...
plumbum thiogallate optical properties
... With the purpose of making DTA experiments we prepared samples from compositions in the (1 – x)PbS – (x)Ga S system with 2 mole % increment in the range x from 0.2 to 1.0. Each sample weighted not more than 0.7 g. The following process was used to homogenize the composition of the charge in the samp ...
... With the purpose of making DTA experiments we prepared samples from compositions in the (1 – x)PbS – (x)Ga S system with 2 mole % increment in the range x from 0.2 to 1.0. Each sample weighted not more than 0.7 g. The following process was used to homogenize the composition of the charge in the samp ...
Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical Enhancing
... presence of double bond [33] and upfield shift in the signal of saturated methylene protons containing alcoholic group. Monohalogenation of diols [34] is often a stubborn problem in different synthetic endeavoures, as there is considerable formation of disubstituted product. Immiscibility of ionic li ...
... presence of double bond [33] and upfield shift in the signal of saturated methylene protons containing alcoholic group. Monohalogenation of diols [34] is often a stubborn problem in different synthetic endeavoures, as there is considerable formation of disubstituted product. Immiscibility of ionic li ...
291 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES FOR - Ars Separatoria
... regulations. The conventional technologies for removal of various radioisotopes from wastewater include chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption, membrane processes and evaporation. The wastes from storage tanks are pumped to the filtering unit. Battery of various filters is used to separate ...
... regulations. The conventional technologies for removal of various radioisotopes from wastewater include chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption, membrane processes and evaporation. The wastes from storage tanks are pumped to the filtering unit. Battery of various filters is used to separate ...
An Introduction to Chemistry
... be seen with the naked eye but is large enough to be seen with an optical microscope is considered to be microscopic. • MACROSCOPIC: Anything that is large enough to be seen with the naked eye is considered to be macroscopic. ...
... be seen with the naked eye but is large enough to be seen with an optical microscope is considered to be microscopic. • MACROSCOPIC: Anything that is large enough to be seen with the naked eye is considered to be macroscopic. ...
Chapter 4 2013
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
CHAPTER 2
... form a ______________. Since not _____________ bonds need to be _____________, the different substances that make up a mixture can be ___________________ using physical _______________ ________________. A solution is a ___________________ mixture (consisting of at least one ________ and one ______ ...
... form a ______________. Since not _____________ bonds need to be _____________, the different substances that make up a mixture can be ___________________ using physical _______________ ________________. A solution is a ___________________ mixture (consisting of at least one ________ and one ______ ...
UNIT 7 Lecture Notes
... Here are some examples of those equations: • Cu2S + 12 HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + CuSO4 + 10 NO2 + 6 H2O • 2 K2MnF6 + 4 SbF5 4 KSbF6 + 2 MnF3 + F2 • It’s not one of our objectives that your able to place every single chemical reaction into a specific category, just that you are able to clearly identify the ...
... Here are some examples of those equations: • Cu2S + 12 HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + CuSO4 + 10 NO2 + 6 H2O • 2 K2MnF6 + 4 SbF5 4 KSbF6 + 2 MnF3 + F2 • It’s not one of our objectives that your able to place every single chemical reaction into a specific category, just that you are able to clearly identify the ...
Investigating the formulae of Complex Ions
... You will need to think about how much of each solution to prepare. This will depend on how much of each solution is used in each experiment and how many experiments you do (including any repeats). Prepare the following mixtures ...
... You will need to think about how much of each solution to prepare. This will depend on how much of each solution is used in each experiment and how many experiments you do (including any repeats). Prepare the following mixtures ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.